An NPM module and CLI to run Lighthouse audits programmatically. This project aims to add bells and whistles to automated Lighthouse testing for DevOps workflows. Easily implement in your Continuous Integration or Continuous Delivery pipeline.
This project provides two ways of running audits - locally in your own environment or remotely via Foo's Automated Lighthouse Check API. For basic usage, running locally will suffice, but if you'd like to maintain a historical record of Lighthouse audits and utilize other features, you can run audits remotely by following the steps and examples.
- Simple usage - only one parameter required.
- Run multiple Lighthouse audits with one command.
- Optionally run Lighthouse remotely and save audits with the Foo's Automated Lighthouse Check API.
- Optionally save an HTML report locally.
- Optionally save an HTML report in an AWS S3 bucket.
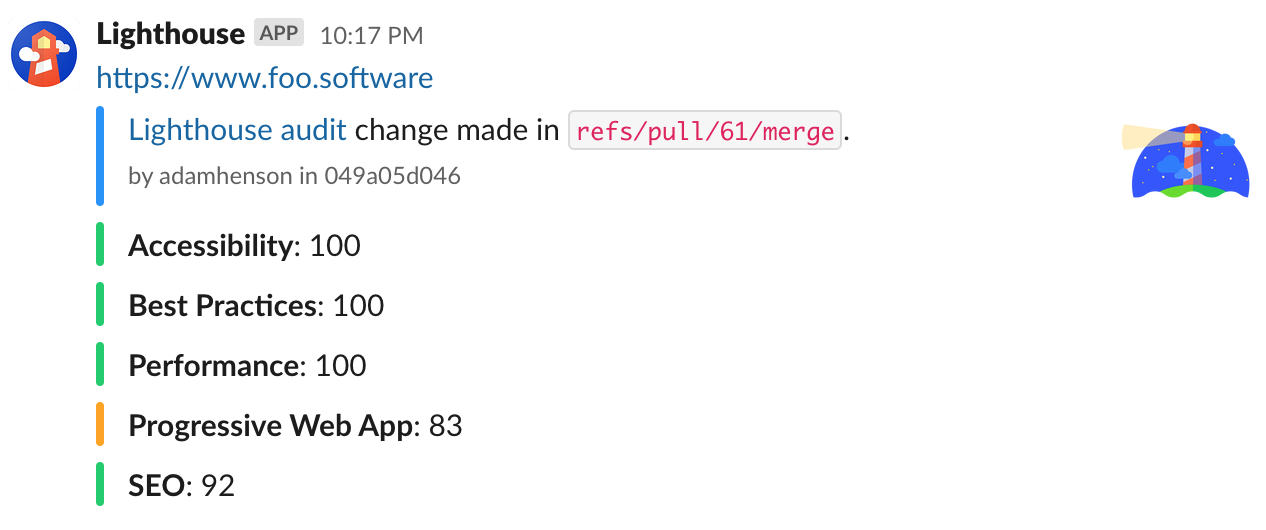
- Easy setup with Slack Webhooks. Just add your Webhook URL and
lighthouse-checkwill send results and optionally include versioning data like branch, author, PR, etc (typically from GitHub). - PR comments of audit scores.
- NPM module for programmatic usage.
- CLI - see CLI Usage.
- Docker - see Docker Usage.
- Support for implementations like CircleCI.
npm install @foo-software/lighthouse-check@foo-software/lighthouse-check provides several functionalities beyond standard Lighthouse audits. It's recommended to start with a basic implementation and expand on it as needed.
Calling lighthouseCheck will run Lighthouse audits against https://www.foo.software/lighthouse and https://www.foo.software/contact.
import { lighthouseCheck } from '@foo-software/lighthouse-check';
(async () => {
const response = await lighthouseCheck({
urls: [
'https://www.foo.software/lighthouse',
'https://www.foo.software/contact',
],
});
console.log('response', response);
})();Or via CLI.
$ lighthouse-check --urls "https://www.foo.software/lighthouse,https://www.foo.software/contact"The CLI will log the results.
Foo's Automated Lighthouse Check can monitor your website's quality by running audits automatically! It can provide a historical record of audits over time to track progression and degradation of website quality. Create a free account to get started. With this, not only will you have automatic audits, but also any that you trigger additionally. Below are steps to trigger audits on URLs that you've created in your account.
- Navigate to your account details, click into "Account Management" and make note of the "API Token".
- Use the account token as the
apiTokenoption.
Basic example with the CLI
$ lighthouse-check --apiToken "abcdefg"- Navigate to your account details, click into "Account Management" and make note of the "API Token".
- Navigate to your dashboard and once you've created URLs to monitor, click on the "More" link of the URL you'd like to use. From the URL details screen, click the "Edit" link at the top of the page. You should see an "API Token" on this page. It represents the token for this specific page (not to be confused with an account API token).
- Use the account token as the
apiTokenoption and page token (or group of page tokens) asurlsoption.
Basic example with the CLI
$ lighthouse-check --apiToken "abcdefg" \
--urls "hijklmnop,qrstuv"You can combine usage with other options for a more advanced setup. Example below.
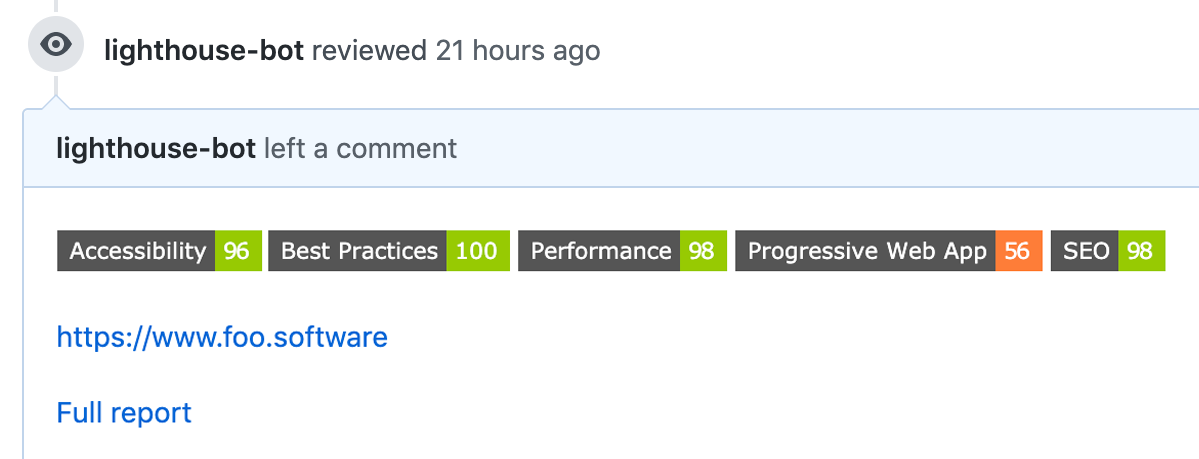
Runs audits remotely and posts results as comments in a PR
$ lighthouse-check --apiToken "abcdefg" \
--urls "hijklmnop,qrstuv" \
--prCommentAccessToken "abcpersonaltoken" \
--prCommentUrl "https://api.github.com/repos/foo-software/lighthouse-check/pulls/3/reviews"You may notice above we had two lines of output; Report and Local Report. These values are populated when options are provided to save the report locally and to S3. These options are not required and can be used together or alone.
Saving a report locally example below.
import { lighthouseCheck } from '@foo-software/lighthouse-check';
(async () => {
const response = await lighthouseCheck({
// relative to the file. NOTE: when using the CLI `--outputDirectory` is relative
// to where the command is being run from.
outputDirectory: '../artifacts',
urls: [
'https://www.foo.software/lighthouse',
'https://www.foo.software/contact',
],
});
console.log('response', response);
})();Or via CLI.
$ lighthouse-check --urls "https://www.foo.software/lighthouse,https://www.foo.software/contact" \
--ouputDirectory "./artifacts"import { lighthouseCheck } from '@foo-software/lighthouse-check';
(async () => {
const response = await lighthouseCheck({
awsAccessKeyId: 'abc123',
awsBucket: 'my-bucket',
awsRegion: 'us-east-1',
awsSecretAccessKey: 'def456',
urls: [
'https://www.foo.software/lighthouse',
'https://www.foo.software/contact',
],
});
console.log('response', response);
})();Or via CLI.
$ lighthouse-check --urls "https://www.foo.software/lighthouse,https://www.foo.software/contact" \
--awsAccessKeyId abc123 \
--awsBucket my-bucket \
--awsRegion us-east-1 \
--awsSecretAccessKey def456 \Below is a basic Slack implementation. To see how you can accomplish notifications with code versioning data - see the CircleCI example (ie GitHub authors, PRs, branches, etc).
import { lighthouseCheck } from '@foo-software/lighthouse-check';
(async () => {
const response = await lighthouseCheck({
slackWebhookUrl: 'https://www.my-slack-webhook-url.com',
urls: [
'https://www.foo.software/lighthouse',
'https://www.foo.software/contact',
],
});
console.log('response', response);
})();Or via CLI.
$ lighthouse-check --urls "https://www.foo.software/lighthouse,https://www.foo.software/contact" \
--slackWebhookUrl "https://www.my-slack-webhook-url.com"The below screenshot shows an advanced implementation as detailed in the CircleCI example.
Populate prCommentAccessToken and prCommentUrl options to enable comments on pull requests.
You can use validateStatus to enforce minimum scores. This could be handy in a DevOps workflow for example.
import {
lighthouseCheck,
validateStatus,
} from '@foo-software/lighthouse-check';
(async () => {
try {
const response = await lighthouseCheck({
awsAccessKeyId: 'abc123',
awsBucket: 'my-bucket',
awsRegion: 'us-east-1',
awsSecretAccessKey: 'def456',
urls: [
'https://www.foo.software/lighthouse',
'https://www.foo.software/contact',
],
});
const status = await validateStatus({
minAccessibilityScore: 90,
minBestPracticesScore: 90,
minPerformanceScore: 70,
minProgressiveWebAppScore: 70,
minSeoScore: 80,
results: response,
});
console.log('all good?', status); // 'all good? true'
} catch (error) {
console.log('error', error.message);
// log would look like:
// Minimum score requirements failed:
// https://www.foo.software/lighthouse: Performance: minimum score: 70, actual score: 64
// https://www.foo.software/contact: Performance: minimum score: 70, actual score: 44
}
})();Or via CLI. Important: outputDirectory value must be defined and the same in both commands.
$ lighthouse-check --urls "https://www.foo.software/lighthouse,https://www.foo.software/contact" \
--outputDirectory /tmp/artifacts \
$ lighthouse-check-status --outputDirectory /tmp/artifacts \
--minAccessibilityScore 90 \
--minBestPracticesScore 90 \
--minPerformanceScore 70 \
--minProgressiveWebAppScore 70 \
--minSeoScore 80In the below example we run Lighthouse audits on two URLs, save reports as artifacts, deploy reports to S3 and send a Slack notification with GitHub info. We defined environment variables like LIGHTHOUSE_CHECK_AWS_BUCKET in the CircleCI project settings.
This implementation utilizes a CircleCI Orb - lighthouse-check-orb.
version: 2.1
orbs:
lighthouse-check: foo-software/lighthouse-check@0.0.6 # ideally later :)
jobs:
test:
executor: lighthouse-check/default
steps:
- lighthouse-check/audit:
urls: https://www.foo.software/lighthouse,https://www.foo.software/contact
# this serves as an example, however if the below environment variables
# are set - the below params aren't even necessary. for example - if
# LIGHTHOUSE_CHECK_AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID is already set - you don't need
# the line below.
awsAccessKeyId: $LIGHTHOUSE_CHECK_AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID
awsBucket: $LIGHTHOUSE_CHECK_AWS_BUCKET
awsRegion: $LIGHTHOUSE_CHECK_AWS_REGION
awsSecretAccessKey: $LIGHTHOUSE_CHECK_AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY
slackWebhookUrl: $LIGHTHOUSE_CHECK_SLACK_WEBHOOK_URL
workflows:
test:
jobs:
- testReports are saved as "artifacts".
Upon clicking the HTML file artifacts, we can see the full report!
In the example above we also uploaded reports to S3. Why would we do this? If we want to persist historical data - we don't want to rely on temporary cloud storage.
Similar to the CircleCI implementation, we can also create a workflow implementation with GitHub Actions using lighthouse-check-action. Example below.
.github/workflows/test.yml
name: Test Lighthouse Check
on: [push]
jobs:
lighthouse-check:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@master
- run: mkdir /tmp/artifacts
- name: Run Lighthouse
uses: foo-software/lighthouse-check-action@master
with:
accessToken: ${{ secrets.LIGHTHOUSE_CHECK_GITHUB_ACCESS_TOKEN }}
author: ${{ github.actor }}
awsAccessKeyId: ${{ secrets.LIGHTHOUSE_CHECK_AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID }}
awsBucket: ${{ secrets.LIGHTHOUSE_CHECK_AWS_BUCKET }}
awsRegion: ${{ secrets.LIGHTHOUSE_CHECK_AWS_REGION }}
awsSecretAccessKey: ${{ secrets.LIGHTHOUSE_CHECK_AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY }}
branch: ${{ github.ref }}
outputDirectory: /tmp/artifacts
urls: 'https://www.foo.software/lighthouse,https://www.foo.software/contact'
sha: ${{ github.sha }}
slackWebhookUrl: ${{ secrets.LIGHTHOUSE_CHECK_WEBHOOK_URL }}
- name: Upload artifacts
uses: actions/upload-artifact@master
with:
name: Lighthouse reports
path: /tmp/artifactsYou can override default config and options by specifying overridesJsonFile option. Contents of this overrides JSON file can have two possible fields; options and config. These two fields are eventually used by Lighthouse to populate opts and config arguments respectively as illustrated in Using programmatically. The two objects populating this JSON file are merged shallowly with the default config and options.
Example content of
overridesJsonFile
{
"config": {
"settings": {
"onlyCategories": ["performance"]
}
},
"options": {
"chromeFlags": ["--disable-dev-shm-usage"]
}
}Running lighthouse-check in the example below will run Lighthouse audits against https://www.foo.software/lighthouse and https://www.foo.software/contact and output a report in the '/tmp/artifacts' directory.
Format is --option <argument>. Example below.
$ lighthouse-check --urls "https://www.foo.software/lighthouse,https://www.foo.software/contact" \
--outputDirectory /tmp/artifacts
lighthouse-check-statusexample
$ lighthouse-check-status --outputDirectory /tmp/artifacts \
--minAccessibilityScore 90 \
--minBestPracticesScore 90 \
--minPerformanceScore 70 \
--minProgressiveWebAppScore 70 \
--minSeoScore 80All options mirror the NPM module. The only difference is that array options like urls are passed in as a comma-separated string as an argument using the CLI.
$ docker pull foosoftware/lighthouse-check:latest
$ docker run foosoftware/lighthouse-check:latest \
lighthouse-check --verbose \
--urls "https://www.foo.software/lighthouse,https://www.foo.software/contact"lighthouse-check functions accept a single configuration object.
You can choose from two ways of running audits - locally in your own environment or remotely via Foo's Automated Lighthouse Check API. You can think of local runs as the default implementation. For directions about how to run remotely see the Foo's Automated Lighthouse Check API Usage section. We denote which options are available to a run type with the Run Type values of either local, remote, or both.
Below are options for the exported lighthouseCheck function or lighthouse-check command with CLI.
| Name | Description | Type | Run Type | Default | Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
apiToken |
The foo.software account API token found in the dashboard. | string |
remote |
undefined |
no |
author |
For Slack notifications: A user handle, typically from GitHub. | string |
both |
undefined |
no |
awsAccessKeyId |
The AWS accessKeyId for an S3 bucket. |
string |
local |
undefined |
no |
awsBucket |
The AWS Bucket for an S3 bucket. |
string |
local |
undefined |
no |
awsRegion |
The AWS region for an S3 bucket. |
string |
local |
undefined |
no |
awsSecretAccessKey |
The AWS secretAccessKey for an S3 bucket. |
string |
local |
undefined |
no |
branch |
For Slack notifications: A version control branch, typically from GitHub. | string |
both |
undefined |
no |
configFile |
A configuration file path in JSON format which holds all options defined here. This file should be relative to the file being interpretted. | string |
both |
undefined |
no |
extraHeaders |
HTTP Header key/value pairs to send in requests. If using the CLI this will need to be stringified, for example: "{\"Cookie\":\"monster=blue\", \"x-men\":\"wolverine\"}" |
object |
local |
undefined |
no |
emulatedFormFactor |
Lighthouse setting only used for local audits. See src/lighthouseConfig.js comments for details. | oneOf(['mobile', 'desktop', 'all']) |
local |
undefined |
no |
locale |
A locale for Lighthouse reports. Example: ja |
string |
local |
undefined |
no |
maxRetries |
The maximum number of times to retry.Note: This is not supported when running against Foo's API as retry logic is already in place. | number |
local |
0 |
no |
maxWaitForLoad |
The maximum amount of time to wait for a page to load in ms. | number |
local |
undefined |
no |
overridesJsonFile |
A JSON file with config and option fields to overrides defaults. Read more here. | string |
local |
undefined |
no |
outputDirectory |
An absolute directory path to output report. You can do this an an alternative or combined with an S3 upload. | string |
local |
undefined |
no |
pr |
For Slack notifications: A version control pull request URL, typically from GitHub. | string |
local |
undefined |
no |
prCommentAccessToken |
Access token of a user to post PR comments. | string |
both |
undefined |
no |
prCommentEnabled |
If true and prCommentAccessToken is set along with prCommentUrl, scores will be posted as comments. |
boolean |
both |
true |
no |
prCommentSaveOld |
If true and PR comment options are set, new comments will be posted on every change vs only updating once comment with most recent scores. |
boolean |
both |
false |
no |
prCommentUrl |
An endpoint to post comments to. Typically this will be from GitHub's API. Example: https://api.github.com/repos/:owner/:repo/pulls/:pull_number/reviews |
string |
both |
undefined |
no |
slackWebhookUrl |
A Slack Incoming Webhook URL to send notifications to. | string |
both |
undefined |
no |
sha |
For Slack notifications: A version control sha, typically from GitHub. |
string |
both |
undefined |
no |
tag |
An optional tag or name (example: build #2 or v0.0.2). |
string |
remote |
undefined |
no |
throttlingMethod |
Lighthouse setting only used for local audits. See src/lighthouseConfig.js comments for details. | oneOf(['simulate', 'devtools', 'provided']) |
local |
undefined |
no |
throttling |
Lighthouse setting only used for local audits. See src/lighthouseConfig.js comments for details. | oneOf(['mobileSlow4G', 'mobileRegluar3G', 'desktopDense4G']) |
local |
undefined |
no |
timeout |
Minutes to timeout. If wait is true (it is by default), we wait for results. If this timeout is reached before results are received an error is thrown. |
number |
local |
10 |
no |
urls |
An array of URLs (or page API tokens if running remotely). In the CLI this value should be a comma-separated list. | array |
both |
undefined |
yes |
verbose |
If true, print out steps and results to the console. |
boolean |
both |
true |
no |
wait |
If true, waits for all audit results to be returned, otherwise URLs are only enqueued. |
boolean |
remote |
true |
no |
results parameter is required or alternatively outputDirectory. To utilize outputDirectory - the same value would also need to be specified when calling lighthouseCheck.
| Name | Description | Type | Default | Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
minAccessibilityScore |
The minimum accessibility Lighthouse score required. | number |
undefined |
no |
minBestPracticesScore |
The minimum best practices Lighthouse score required. | number |
undefined |
no |
minPerformanceScore |
The minimum performance Lighthouse score required. | number |
undefined |
no |
minProgressiveWebAppScore |
The minimum progressive web app Lighthouse score required. | number |
undefined |
no |
minSeoScore |
The minimum SEO Lighthouse score required. | number |
undefined |
no |
outputDirectory |
An absolute directory path to output report. When the results object isn't specified, this value will need to be. | string |
undefined |
no |
results |
A results object representing results of Lighthouse audits. | number |
undefined |
no |
lighthouseCheck function returns a promise which either resolves as an object or rejects as an error object. In both cases the payload will be of the same shape documented below.
| Name | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|
code |
A code to signify failure or succes. | oneOf(["SUCCESS", "ERROR_GENERIC", ...]) see errorCodes.js for all error codes. |
data |
An array of results returned by the API. | array |
message |
A message to elaborate on the code. This field isn't always populated. | string |
This package was brought to you by Foo - a website performance monitoring tool. Create a free account with standard performance testing. Automatic website performance testing, uptime checks, charts showing performance metrics by day, month, and year. Foo also provides real time notifications when performance and uptime notifications when changes are detected. Users can integrate email, Slack and PagerDuty notifications.