Gracy handles failures, logging, retries, throttling, parsing, and reporting for all your HTTP interactions. Gracy uses httpx under the hood.
"Let Gracy do the boring stuff while you focus on your application"
Summary
- 🧑💻 Get started
- Settings
- Reports
- Replay requests
- Resource Namespacing
- Pagination
- Advanced Usage
- 📚 Extra Resources
- Change log
- License
- Credits
pip install gracy
OR
poetry add gracy
Examples will be shown using the PokeAPI.
# 0. Import
import asyncio
import typing as t
from gracy import BaseEndpoint, Gracy, GracyConfig, LogEvent, LogLevel
# 1. Define your endpoints
class PokeApiEndpoint(BaseEndpoint):
GET_POKEMON = "/pokemon/{NAME}" # 👈 Put placeholders as needed
# 2. Define your Graceful API
class GracefulPokeAPI(Gracy[str]):
class Config:
BASE_URL = "https://pokeapi.co/api/v2/" # 👈 Optional BASE_URL
# 👇 Define settings to apply for every request
SETTINGS = GracyConfig(
log_request=LogEvent(LogLevel.DEBUG),
log_response=LogEvent(LogLevel.INFO, "{URL} took {ELAPSED}"),
parser={
"default": lambda r: r.json()
}
)
async def get_pokemon(self, name: str) -> t.Awaitable[dict]:
return await self.get(PokeApiEndpoint.GET_POKEMON, {"NAME": name})
pokeapi = GracefulPokeAPI()
async def main():
try:
pokemon = await pokeapi.get_pokemon("pikachu")
print(pokemon)
finally:
pokeapi.report_status("rich")
asyncio.run(main())- PokeAPI with retries, parsers, logs
- PokeAPI with throttling
- PokeAPI with SQLite replay
- PokeAPI with Mongo replay
By default Gracy considers any successful status code (200-299) as successful.
Strict
You can modify this behavior by defining a strict status code or increase the range of allowed status codes:
from http import HTTPStatus
GracyConfig(
strict_status_code=HTTPStatus.CREATED
)or a list of values:
from http import HTTPStatus
GracyConfig(
strict_status_code={HTTPStatus.OK, HTTPStatus.CREATED}
)Using strict_status_code means that any other code not specified will raise an error regardless of being successful or not.
Allowed
You can also keep the behavior, but extend the range of allowed codes.
from http import HTTPStatus
GracyConfig(
allowed_status_code=HTTPStatus.NOT_FOUND
)or a list of values
from http import HTTPStatus
GracyConfig(
allowed_status_code={HTTPStatus.NOT_FOUND, HTTPStatus.FORBIDDEN}
)Using allowed_status_code means that all successful codes plus your defined codes will be considered successful.
This is quite useful for parsing as you'll see soon.
strict_status_code takes precedence over allowed_status_code, probably you don't want to combine those. Prefer one or the other.
You can implement your own custom validator to do further checks on the response and decide whether to consider the request failed (and as consequence trigger retries if they're set).
from gracy import GracefulValidator
class MyException(Exception):
pass
class MyCustomValidator(GracefulValidator):
def check(self, response: httpx.Response) -> None:
jsonified = response.json()
if jsonified.get('error', None):
raise MyException("Error is not expected")
return None
...
class Config:
SETTINGS = GracyConfig(
...,
retry=GracefulRetry(retry_on=MyException, ...), # Set up retry to work whenever our validator fails
validators=MyCustomValidator(), # Set up validator
)Parsing allows you to handle the request based on the status code returned.
The basic example is parsing json:
GracyConfig(
parser={
"default": lambda r: r.json()
}
)In this example all successful requests will automatically return the json() result.
You can also narrow it down to handle specific status codes.
class Config:
SETTINGS = GracyConfig(
...,
allowed_status_code=HTTPStatusCode.NOT_FOUND,
parser={
"default": lambda r: r.json()
HTTPStatusCode.NOT_FOUND: None
}
)
async def get_pokemon(self, name: str) -> dict| None:
# 👇 Returns either dict or None
return await self.get(PokeApiEndpoint.GET_POKEMON, {"NAME": name})Or even customize exceptions to improve your code readability:
class PokemonNotFound(GracyUserDefinedException):
... # More on exceptions below
class Config:
GracyConfig(
...,
allowed_status_code=HTTPStatusCode.NOT_FOUND,
parser={
"default": lambda r: r.json()
HTTPStatusCode.NOT_FOUND: PokemonNotFound
}
)
async def get_pokemon(self, name: str) -> Awaitable[dict]:
# 👇 Returns either dict or raises PokemonNotFound
return await self.get(PokeApiEndpoint.GET_POKEMON, {"NAME": name})Because parsers allow you to dynamically parse a payload based on the status code your IDE will not identify the return type by itself.
To avoid boring typing.cast for every method, Gracy provides typed http methods, so you can define a specific return type:
async def list(self, offset: int = 0, limit: int = 20):
params = dict(offset=offset, limit=limit)
return await self.get[ResourceList]( # Specifies this method return a `ResourceList`
PokeApiEndpoint.BERRY_LIST, params=params
)
async def get_one(self, name_or_id: str | int):
return await self.get[models.Berry | None](
PokeApiEndpoint.BERRY_GET, params=dict(KEY=str(name_or_id))
)Who doesn't hate flaky APIs? 🙋
Yet there're many of them.
Using tenacity, backoff, retry, aiohttp_retry, and any other retry libs is NOT easy enough. 🙅
You still would need to code the implementation for each request which is annoying.
Here's how Gracy allows you to implement your retry logic:
class Config:
GracyConfig(
retry=GracefulRetry(
delay=1,
max_attempts=3,
delay_modifier=1.5,
retry_on=None,
log_before=None,
log_after=LogEvent(LogLevel.WARNING),
log_exhausted=LogEvent(LogLevel.CRITICAL),
behavior="break",
)
)| Parameter | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
delay |
How many seconds to wait between retries | 2 would wait 2 seconds, 1.5 would wait 1.5 seconds, and so on |
max_attempts |
How many times should Gracy retry the request? | 10 means 1 regular request with additional 10 retries in case they keep failing. 1 should be the minimum |
delay_modifier |
Allows you to specify increasing delay times by multiplying this value to delay |
Setting 1 means no delay change. Setting 2 means delay will be doubled every retry |
retry_on |
Should we retry for which status codes/exceptions? None means for any non successful status code or exception |
HTTPStatus.BAD_REQUEST, or {HTTPStatus.BAD_REQUEST, HTTPStatus.FORBIDDEN}, or Exception or {Exception, HTTPStatus.NOT_FOUND} |
log_before |
Specify log level. None means don't log |
More on logging later |
log_after |
Specify log level. None means don't log |
More on logging later |
log_exhausted |
Specify log level. None means don't log |
More on logging later |
behavior |
Allows you to define how to deal if the retry fails. pass will accept any retry failure |
pass or break (default) |
overrides |
Allows to override delay based on last response status code |
{HTTPStatus.BAD_REQUEST: OverrideRetryOn(delay=0), HTTPStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR: OverrideRetryOn(delay=10)} |
Rate limiting issues? No more.
Gracy helps you proactively deal with it before any API throws 429 in your face.
Creating rules
You can define rules per endpoint using regex:
SIMPLE_RULE = ThrottleRule(
url_pattern=r".*",
max_requests=2
)
print(SIMPLE_RULE)
# Output: "2 requests per second for URLs matching re.compile('.*')"
COMPLEX_RULE = ThrottleRule(
url_pattern=r".*\/pokemon\/.*",
max_requests=10,
per_time=timedelta(minutes=1, seconds=30),
)
print(COMPLEX_RULE)
# Output: 10 requests per 90 seconds for URLs matching re.compile('.*\\/pokemon\\/.*')Setting throttling
You can set up logging and assign rules as:
class Config:
GracyConfig(
throttling=GracefulThrottle(
rules=ThrottleRule(r".*", 2), # 2 reqs/s for any endpoint
log_limit_reached=LogEvent(LogLevel.ERROR),
log_wait_over=LogEvent(LogLevel.WARNING),
),
)Maybe the API you're hitting have some slow endpoints and you want to ensure that no more than a custom number of requests are being made concurrently.
You can define a ConcurrentRequestLimit config.
The simplest usage is:
from gracy import ConcurrentRequestLimit
class Config:
GracyConfig(
concurrent_requests=ConcurrentRequestLimit(
limit=1, # How many concurrent requests
log_limit_reached=LogEvent(LogLevel.WARNING),
log_limit_freed=LogEvent(LogLevel.INFO),
),
)But you can also define it easily per method as:
class MyApiClient(Gracy[Endpoint]):
@graceful(concurrent_requests=5)
async def get_concurrently_five(self, name: str):
...You can define and customize logs for events by using LogEvent and LogLevel:
verbose_log = LogEvent(LogLevel.CRITICAL)
custom_warn_log = LogEvent(LogLevel.WARNING, custom_message="{METHOD} {URL} is quite slow and flaky")
custom_error_log = LogEvent(LogLevel.INFO, custom_message="{URL} returned a bad status code {STATUS}, but that's fine")Note that placeholders are formatted and replaced later on by Gracy based on the event type, like:
Placeholders per event
| Placeholder | Description | Example | Supported Events |
|---|---|---|---|
{URL} |
Full url being targetted | https://pokeapi.co/api/v2/pokemon/pikachu |
All |
{UURL} |
Full Unformatted url being targetted | https://pokeapi.co/api/v2/pokemon/{NAME} |
All |
{ENDPOINT} |
Endpoint being targetted | /pokemon/pikachu |
All |
{UENDPOINT} |
Unformatted endpoint being targetted | /pokemon/{NAME} |
All |
{METHOD} |
HTTP Request being used | GET, POST |
All |
{STATUS} |
Status code returned by the response | 200, 404, 501 |
After Request |
{ELAPSED} |
Amount of seconds taken for the request to complete | Numeric | After Request |
{REPLAY} |
A placeholder that is displayed only when request is replayed | REPLAYED when replay, otherwise it's a blank str (``) |
After Request |
{IS_REPLAY} |
Boolean value to show whether it's replayed or not | String with TRUE when replayed or FALSE |
After Request |
{RETRY_DELAY} |
How long Gracy will wait before repeating the request | Numeric | Any Retry event |
{RETRY_CAUSE} |
What caused the retry logic to trigger | [Bad Status Code: 404], [Request Error: ConnectionTimeout] |
Any Retry event |
{CUR_ATTEMPT} |
Current attempt count for the current request | Numeric | Any Retry event |
{MAX_ATTEMPT} |
Max attempt defined for the current request | Numeric | Any Retry event |
{THROTTLE_LIMIT} |
How many reqs/s is defined for the current request | Numeric | Any Throttle event |
{THROTTLE_TIME} |
How long Gracy will wait before calling the request | Numeric | Any Throttle event |
{THROTTLE_TIME_RANGE} |
Time range defined by the throttling rule | second, 90 seconds |
Any Throttle event |
and you can set up the log events as follows:
Requests
- Before request
- After response
- Response has non successful errors
GracyConfig(
log_request=LogEvent(),
log_response=LogEvent(),
log_errors=LogEvent(),
)Retry
- Before retry
- After retry
- When retry exhausted
GracefulRetry(
...,
log_before=LogEvent(),
log_after=LogEvent(),
log_exhausted=LogEvent(),
)Throttling
- When reqs/s limit is reached
- When limit decreases again
GracefulThrottle(
...,
log_limit_reached=LogEvent()
log_wait_over=LogEvent()
)Dynamic Customization
You can customize it even further by passing a lambda:
LogEvent(
LogLevel.ERROR,
lambda r: "Request failed with {STATUS}" f" and it was {'redirected' if r.is_redirect else 'NOT redirected'}"
if r
else "",
)Consider that:
- Not all log events have the response available, so you need to guard yourself against it
- Placeholders still works (e.g.
{STATUS}) - You need to watch out for some attrs that might break the formatting logic (e.g.
r.headers)
You can define custom exceptions for more fine grained control over your exception messages/types.
The simplest you can do is:
from gracy import Gracy, GracyConfig
from gracy.exceptions import GracyUserDefinedException
class MyCustomException(GracyUserDefinedException):
pass
class MyApi(Gracy[str]):
class Config:
SETTINGS = GracyConfig(
...,
parser={
HTTPStatus.BAD_REQUEST: MyCustomException
}
)This will raise your custom exception under the conditions defined in your parser.
You can improve it even further by customizing your message:
class PokemonNotFound(GracyUserDefinedException):
BASE_MESSAGE = "Unable to find a pokemon with the name [{NAME}] at {URL} due to {STATUS} status"
def _format_message(self, request_context: GracyRequestContext, response: httpx.Response) -> str:
format_args = self._build_default_args()
name = request_context.endpoint_args.get("NAME", "Unknown")
return self.BASE_MESSAGE.format(NAME=name, **format_args)Recommended for production environments.
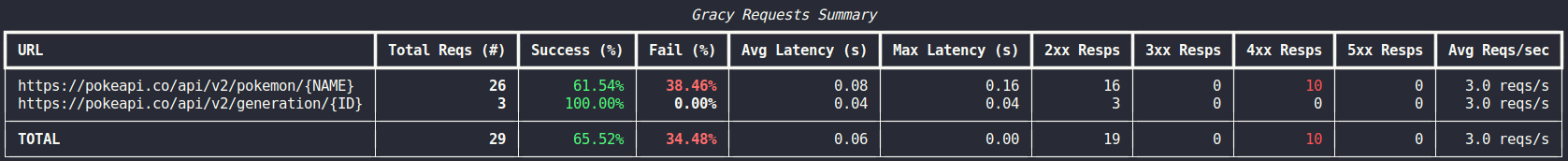
Gracy reports a short summary using logger.info.
pokeapi = GracefulPokeAPI()
# do stuff with your API
pokeapi.report_status("logger")
# OUTPUT
❯ Gracy tracked that 'https://pokeapi.co/api/v2/pokemon/{NAME}' was hit 1 time(s) with a success rate of 100.00%, avg latency of 0.45s, and a rate of 1.0 reqs/s.
❯ Gracy tracked a total of 2 requests with a success rate of 100.00%, avg latency of 0.24s, and a rate of 1.0 reqs/s.Uses print to generate a short list with all attributes:
pokeapi = GracefulPokeAPI()
# do stuff with your API
pokeapi.report_status("list")
# OUTPUT
____
/ ___|_ __ __ _ ___ _ _
| | _| '__/ _` |/ __| | | |
| |_| | | | (_| | (__| |_| |
\____|_| \__,_|\___|\__, |
|___/ Requests Summary Report
1. https://pokeapi.co/api/v2/pokemon/{NAME}
Total Reqs (#): 1
Success (%): 100.00%
Fail (%): 0.00%
Avg Latency (s): 0.39
Max Latency (s): 0.39
2xx Resps: 1
3xx Resps: 0
4xx Resps: 0
5xx Resps: 0
Avg Reqs/sec: 1.0 reqs/s
2. https://pokeapi.co/api/v2/generation/{ID}/
Total Reqs (#): 1
Success (%): 100.00%
Fail (%): 0.00%
Avg Latency (s): 0.04
Max Latency (s): 0.04
2xx Resps: 1
3xx Resps: 0
4xx Resps: 0
5xx Resps: 0
Avg Reqs/sec: 1.0 reqs/s
TOTAL
Total Reqs (#): 2
Success (%): 100.00%
Fail (%): 0.00%
Avg Latency (s): 0.21
Max Latency (s): 0.00
2xx Resps: 2
3xx Resps: 0
4xx Resps: 0
5xx Resps: 0
Avg Reqs/sec: 1.0 reqs/sIt requires you to install Rich.
pokeapi = GracefulPokeAPI()
# do stuff with your API
pokeapi.report_status("rich")Here's an example of how it looks:
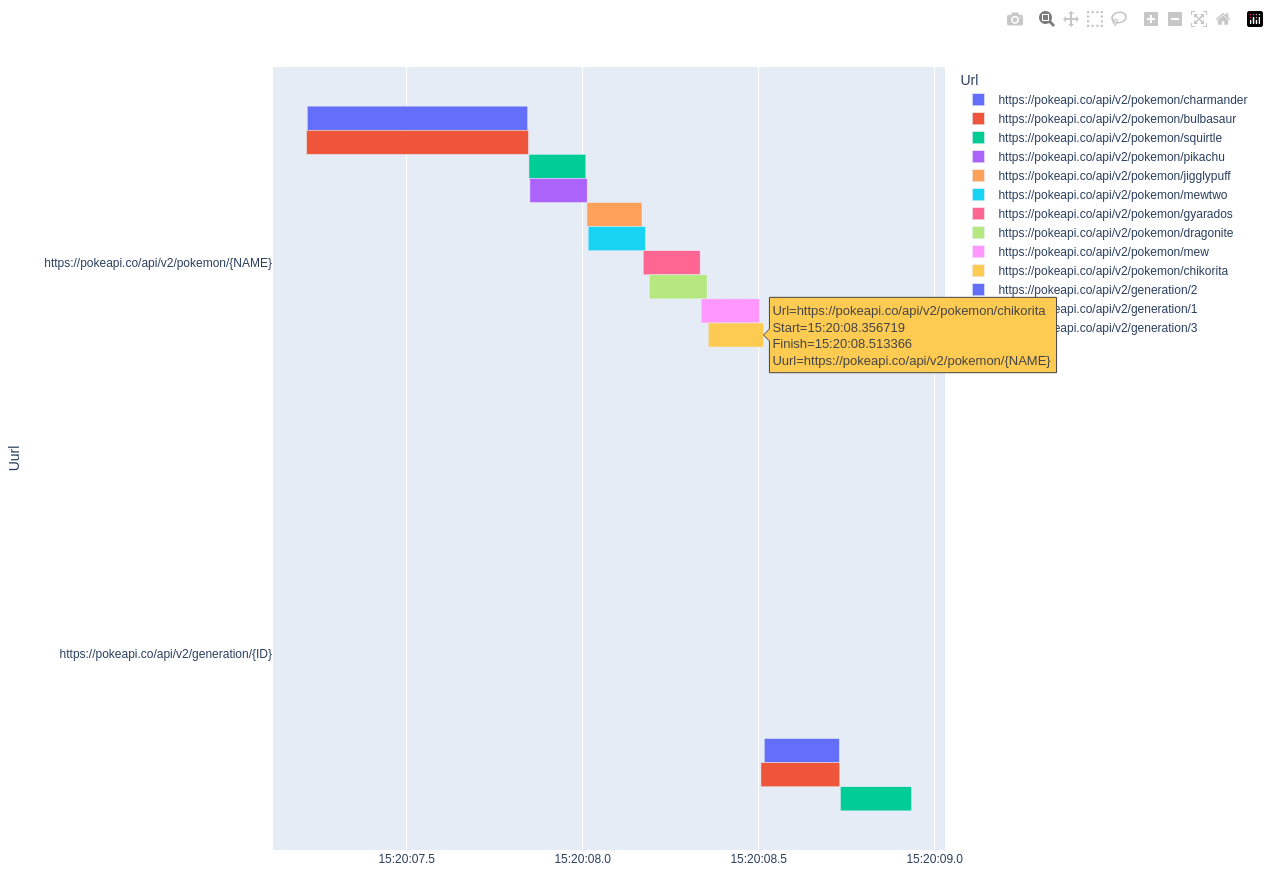
It requires you to install plotly 📊 and pandas 🐼.
pokeapi = GracefulPokeAPI()
# do stuff with your API
plotly_fig = pokeapi.report_status("plotly")
plotly_fig.show()Here's an example of how it looks:
Gracy allows you to replay requests and responses from previous interactions.
This is powerful because it allows you to test APIs without latency or consuming your rate limit. Now writing unit tests that relies on third-party APIs is doable.
It works in two steps:
| Step | Description | Hits the API? |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Recording | Stores all requests/responses to be later replayed | Yes |
| 2. Replay | Returns all previously generated responses based on your request as a "replay" | No |
The effort to record requests/responses is ZERO. You just need to pass a recording config to your Graceful API:
from gracy import GracyReplay
from gracy.replays.storages.sqlite import SQLiteReplayStorage
record_mode = GracyReplay("record", SQLiteReplayStorage("pokeapi.sqlite3"))
pokeapi = GracefulPokeAPI(record_mode)Every request will be recorded to the defined data source.
Once you have recorded all your requests you can enable the replay mode:
from gracy import GracyReplay
from gracy.replays.storages.sqlite import SQLiteReplayStorage
replay_mode = GracyReplay("replay", SQLiteReplayStorage("pokeapi.sqlite3"))
pokeapi = GracefulPokeAPI(replay_mode)Every request will be routed to the defined data source resulting in faster responses.
You can have multiple namespaces to organize your API endpoints as you wish.
To do so, you just have to inherit from GracyNamespace and instantiate it within the GracyAPI:
from gracy import Gracy, GracyNamespace, GracyConfig
class PokemonNamespace(GracyNamespace[PokeApiEndpoint]):
async def get_one(self, name: str):
return await self.get(PokeApiEndpoint.GET_POKEMON, {"NAME": name})
class BerryNamespace(GracyNamespace[PokeApiEndpoint]):
async def get_one(self, name: str):
return await self.get(PokeApiEndpoint.GET_BERRY, {"NAME": name})
class GracefulPokeAPI(Gracy[PokeApiEndpoint]):
class Config:
BASE_URL = "https://pokeapi.co/api/v2/"
SETTINGS = GracyConfig(
retry=RETRY,
allowed_status_code={HTTPStatus.NOT_FOUND},
parser={HTTPStatus.NOT_FOUND: None},
)
# These will be automatically assigned on init
berry: BerryNamespace
pokemon: PokemonNamespaceAnd the usage will work as:
await pokeapi.pokemon.get_one("pikachu")
await pokeapi.berry.get_one("cheri")Note all configs are propagated to namespaces, but namespaces can still have their own which would cause merges when instantiatedg.
There're endpoints that may require pagination. For that you can use GracyPaginator.
For a simple case where you pass offset and limit, you can use GracyOffsetPaginator:
from gracy import GracyOffsetPaginator
class BerryNamespace(GracyNamespace[PokeApiEndpoint]):
@parsed_response(ResourceList)
async def list(self, offset: int = 0, limit: int = 20):
params = dict(offset=offset, limit=limit)
return await self.get(PokeApiEndpoint.BERRY_LIST, params=params)
def paginate(self, limit: int = 20) -> GracyOffsetPaginator[ResourceList]:
return GracyOffsetPaginator[ResourceList](
gracy_func=self.list,
has_next=lambda r: bool(r["next"]) if r else True,
page_size=limit,
)and then use it as:
async def main():
api = PokeApi()
paginator = api.berry.paginate(2)
# Just grabs the next page
first = await paginator.next_page()
print(first)
# Resets current page to 0
paginator.set_page(0)
# Loop throught it all
async for page in paginator:
print(page)APIs may return different responses/conditions/payloads based on the endpoint.
You can override any GracyConfig on a per method basis by using the @graceful decorator.
NOTE: Use @graceful_generator if your function uses yield.
from gracy import Gracy, GracyConfig, GracefulRetry, graceful, graceful_generator
retry = GracefulRetry(...)
class GracefulPokeAPI(Gracy[PokeApiEndpoint]):
class Config:
BASE_URL = "https://pokeapi.co/api/v2/"
SETTINGS = GracyConfig(
retry=retry,
log_errors=LogEvent(
LogLevel.ERROR, "How can I become a pokemon master if {URL} keeps failing with {STATUS}"
),
)
@graceful(
retry=None, # 👈 Disables retry set in Config
log_errors=None, # 👈 Disables log_errors set in Config
allowed_status_code=HTTPStatus.NOT_FOUND,
parser={
"default": lambda r: r.json()["order"],
HTTPStatus.NOT_FOUND: None,
},
)
async def maybe_get_pokemon_order(self, name: str):
val: str | None = await self.get(PokeApiEndpoint.GET_POKEMON, {"NAME": name})
return val
@graceful( # 👈 Retry and log_errors are still set for this one
strict_status_code=HTTPStatus.OK,
parser={"default": lambda r: r.json()["order"]},
)
async def get_pokemon_order(self, name: str):
val: str = await self.get(PokeApiEndpoint.GET_POKEMON, {"NAME": name})
return val
@graceful_generator( # 👈 Retry and log_errors are still set for this one
parser={"default": lambda r: r.json()["order"]},
)
async def get_2_pokemons(self):
names = ["charmander", "pikachu"]
for name in names:
r = await self.get(PokeApiEndpoint.GET_POKEMON, {"NAME": name})
yield rYou might want to modify the HTTPx client settings, do so by:
class YourAPIClient(Gracy[str]):
class Config:
...
def __init__(self, token: token) -> None:
self._token = token
super().__init__()
# 👇 Implement your logic here
def _create_client(self) -> httpx.AsyncClient:
client = super()._create_client()
client.headers = {"Authorization": f"token {self._token}"} # type: ignore
return clientAs default Gracy won't enforce a request timeout.
You can define your own by setting it on Config as:
class GracefulAPI(GracyApi[str]):
class Config:
BASE_URL = "https://example.com"
REQUEST_TIMEOUT = 10.2 # 👈 HereGracy was built with extensibility in mind.
You can create your own storage to store/load anywhere (e.g. SQL Database), here's an example:
import httpx
from gracy import GracyReplayStorage
class MyCustomStorage(GracyReplayStorage):
def prepare(self) -> None: # (Optional) Executed upon API instance creation.
...
async def record(self, response: httpx.Response) -> None:
... # REQUIRED. Your logic to store the response object. Note the httpx.Response has request data.
async def _load(self, request: httpx.Request) -> httpx.Response:
... # REQUIRED. Your logic to load a response object based on the request.
# Usage
record_mode = GracyReplay("record", MyCustomStorage())
replay_mode = GracyReplay("replay", MyCustomStorage())
pokeapi = GracefulPokeAPI(record_mode)You can set up hooks simply by defining async def before and async def after methods.
class GracefulPokeAPI(Gracy[PokeApiEndpoint]):
class Config:
BASE_URL = "https://pokeapi.co/api/v2/"
SETTINGS = GracyConfig(
retry=RETRY,
allowed_status_code={HTTPStatus.NOT_FOUND},
parser={HTTPStatus.NOT_FOUND: None},
)
def __init__(self, *args: t.Any, **kwargs: t.Any) -> None:
self.before_count = 0
self.after_status_counter = defaultdict[HTTPStatus, int](int)
self.after_aborts = 0
self.after_retries_counter = 0
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
async def before(self, context: GracyRequestContext):
self.before_count += 1
async def after(
self,
context: GracyRequestContext, # Current request context
response_or_exc: httpx.Response | Exception, # Either the request or an error
retry_state: GracefulRetryState | None, # Set when this is generated from a retry
):
if retry_state:
self.after_retries_counter += 1
if isinstance(response_or_exc, httpx.Response):
self.after_status_counter[HTTPStatus(response_or_exc.status_code)] += 1
else:
self.after_aborts += 1
async def get_pokemon(self, name: str):
return await self.get(PokeApiEndpoint.GET_POKEMON, {"NAME": name})In the example above invoking get_pokemon() will trigger before()/after() hooks in sequence.
This hook checks for 429 (TOO MANY REQUESTS), and then reads the
retry-after header.
If the value is set, then Gracy pauses ALL client requests until the time is over. This behavior can be modified to happen on a per-endpoint basis if lock_per_endpoint is True.
Example Usage:
from gracy.common_hooks import HttpHeaderRetryAfterBackOffHook
class GracefulAPI(GracyAPI[Endpoint]):
def __init__(self):
self._retry_after_hook = HttpHeaderRetryAfterBackOffHook(
self._reporter,
lock_per_endpoint=True,
log_event=LogEvent(
LogLevel.WARNING,
custom_message=(
"{ENDPOINT} produced {STATUS} and requested to wait {RETRY_AFTER}s "
"- waiting {RETRY_AFTER_ACTUAL_WAIT}s"
),
),
# Wait +10s to avoid this from happening again too soon
seconds_processor=lambda secs_requested: secs_requested + 10,
)
super().__init__()
async def before(self, context: GracyRequestContext):
await self._retry_after_hook.before(context)
async def after(
self,
context: GracyRequestContext,
response_or_exc: httpx.Response | Exception,
retry_state: GracefulRetryState | None,
):
retry_after_result = await self._retry_after_hook.after(context, response_or_exc)This hook checks for 429 (TOO MANY REQUESTS) and locks requests for an arbitrary amount of time defined by you.
If the value is set, then Gracy pauses ALL client requests until the time is over.
This behavior can be modified to happen on a per-endpoint basis if lock_per_endpoint is True.
from gracy.common_hooks import RateLimitBackOffHook
class GracefulAPI(GracyAPI[Endpoint]):
def __init__(self):
self._ratelimit_backoff_hook = RateLimitBackOffHook(
30,
self._reporter,
lock_per_endpoint=True,
log_event=LogEvent(
LogLevel.INFO,
custom_message="{UENDPOINT} got rate limited, waiting for {WAIT_TIME}s",
),
)
super().__init__()
async def before(self, context: GracyRequestContext):
await self._ratelimit_backoff_hook.before(context)
async def after(
self,
context: GracyRequestContext,
response_or_exc: httpx.Response | Exception,
retry_state: GracefulRetryState | None,
):
backoff_result = await self._ratelimit_backoff_hook.after(context, response_or_exc)from gracy.common_hooks import HttpHeaderRetryAfterBackOffHook, RateLimitBackOffHookSome good practices I learned over the past years guided Gracy's philosophy, you might benefit by reading:
- How to log
- How to handle exceptions
- How to use Async correctly
- Book: Python like a PRO
- Book: Effective Python
See CHANGELOG.
MIT
Thanks to the last three startups I worked which forced me to do the same things and resolve the same problems over and over again. I got sick of it and built this lib.
Most importantly: Thanks to God, who allowed me (a random 🇧🇷 guy) to work for many different 🇺🇸 startups. This is ironic since due to God's grace, I was able to build Gracy. 🙌
Also, thanks to the httpx and rich projects for the beautiful and simple APIs that powers Gracy.