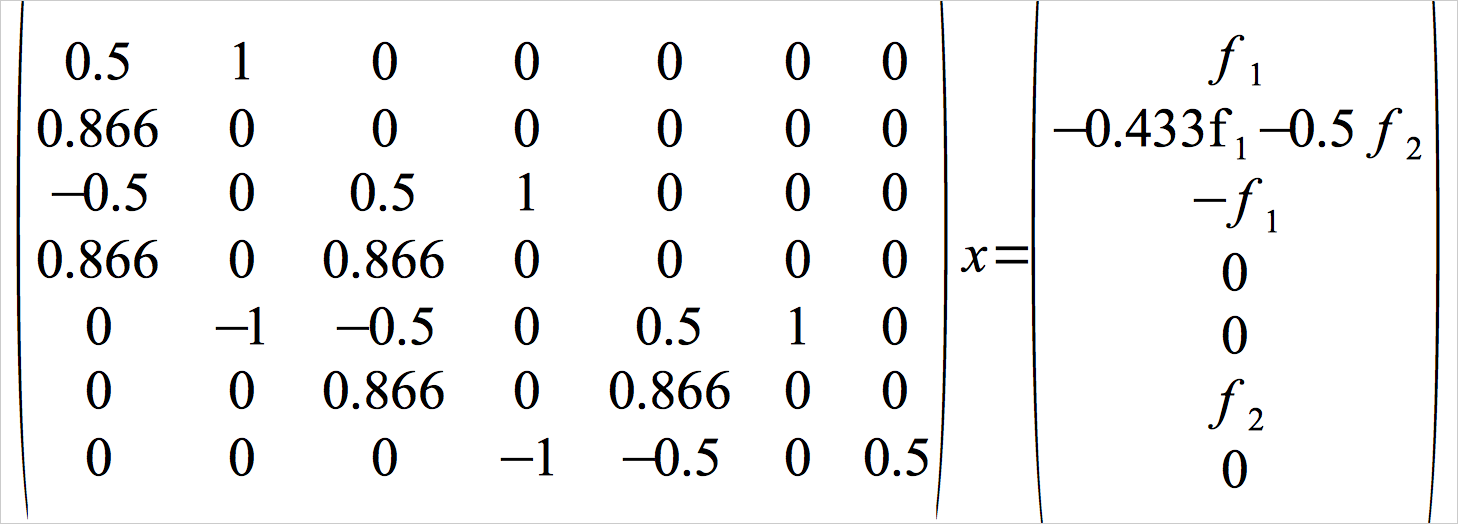Computational Science and Engineering
MATLAB is a powerhouse language ubiquitous in engineering applications in academia and industry. This workshop series will introduce you to basic and advanced MATLAB modules and concepts, including a focus on data processing and data analytics workflows.
The EWS Linux machines have everything we need for the workshop. If you plan to use your personal laptop, you'll need to install a version of MATLAB from MathWorks.
All workshops will be held in the EWS computer laboratory, 1001 Mechanical Engineering Laboratory.
There is no sign-up for this series—walk-ins are welcome and encouraged!
Feb. 22, 1:00 p.m.–3:00 p.m.
We will conduct a hands-on walkthrough of what MATLAB has to offer as a foundation for later tutorials throughout the semester. We will cover the following topics:
-
Introduction - MATLAB, programming
-
Variables(scalar, vector, matrices) and Operators
-
Functions
-
Basic numerical examples & matrix solutions
-
Control flow & matrix definitions
Example: Area of a circle & volume of a sphere (functions)
function [A] = areaOfCircle(r)
A = pi * r^2;
Example: Fahrenheit/Celsius (functions)
function Tf = TempC2F(Tc)
Tf = Tc .* (180/100) + 32;
end
Example: Falling ballistic object (vectorization, functions)
a=-9.8; %m/s^2
v=2520; %m/s
x0=0;
t=1;
y=a*t^2+v*t+x0;
t=linspace(0,5,101)
Example: Truss forces (Elementwise & matrix operators)
x = inv(T)*f
x = T \ f;
Example: Control Flow, Define Matrix
% Preallocate a matrix
nrows = 4;
ncols = 4;
myData = ones(nrows, ncols);
% Loop through the matrix
for r = 1:nrows
for c = 1:ncols
if r == c
myData(r,c) = 2;
elseif abs(r - c) == 1
myData(r,c) = -1;
else
myData(r,c) = 0;
end
end
end
Mar. 1, 1:00 p.m.–3:00 p.m.
- Control Flow in Matlab
- Heat conduction example
- Explicit function vs. Function control
- Radioactive decay chain (systems of linear ODEs) example
- Systems of nonlinear ODEs example
Mar. 8, 1:00 p.m.–3:00 p.m.
- Data access and data cleaning
Mar. 15, 1:00 p.m.–3:00 p.m.
- Principle Component Analysis
- Monte Carlo Simulation
Spring Break
Mar. 29, 1:00 p.m.–3:00 p.m.
- Support Vector Machine
April 5, 1:00 p.m.–3:00 p.m.
- Classification: K-nearest neighbor method, Tree Model
April 12, 1:00 p.m.–3:00 p.m.
- K means clustering, Hierarchical clustering
April 19, 1:00 p.m.–3:00 p.m.
- Classification: Linear and Quadratic Discriminant Analysis, Naive Bayes
April 26, 1:00 p.m.–3:00 p.m.
- Logistic Regression, Regression with Regularization
May 3, 1:00 p.m.–3:00 p.m.
- Hidden Markov Model
- Data import from sql server