-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 22
Commit
This commit does not belong to any branch on this repository, and may belong to a fork outside of the repository.
- Loading branch information
Showing
24 changed files
with
1,037 additions
and
0 deletions.
There are no files selected for viewing
28 changes: 28 additions & 0 deletions
28
src/main/kotlin/g3301_3400/s3330_find_the_original_typed_string_i/Solution.kt
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,28 @@ | ||
| package g3301_3400.s3330_find_the_original_typed_string_i | ||
|
|
||
| // #Easy #String #2024_10_29_Time_142_ms_(88.24%)_Space_34.7_MB_(70.59%) | ||
|
|
||
| class Solution { | ||
| fun possibleStringCount(word: String): Int { | ||
| val n = word.length | ||
| var count = 1 | ||
| var pre = word[0] | ||
| var temp = 0 | ||
| for (i in 1 until n) { | ||
| val ch = word[i] | ||
| if (ch == pre) { | ||
| temp++ | ||
| } else { | ||
| if (temp >= 1) { | ||
| count += temp | ||
| } | ||
| temp = 0 | ||
| pre = ch | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| if (temp >= 1) { | ||
| count += temp | ||
| } | ||
| return count | ||
| } | ||
| } |
42 changes: 42 additions & 0 deletions
42
src/main/kotlin/g3301_3400/s3330_find_the_original_typed_string_i/readme.md
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,42 @@ | ||
| 3330\. Find the Original Typed String I | ||
|
|
||
| Easy | ||
|
|
||
| Alice is attempting to type a specific string on her computer. However, she tends to be clumsy and **may** press a key for too long, resulting in a character being typed **multiple** times. | ||
|
|
||
| Although Alice tried to focus on her typing, she is aware that she may still have done this **at most** _once_. | ||
|
|
||
| You are given a string `word`, which represents the **final** output displayed on Alice's screen. | ||
|
|
||
| Return the total number of _possible_ original strings that Alice _might_ have intended to type. | ||
|
|
||
| **Example 1:** | ||
|
|
||
| **Input:** word = "abbcccc" | ||
|
|
||
| **Output:** 5 | ||
|
|
||
| **Explanation:** | ||
|
|
||
| The possible strings are: `"abbcccc"`, `"abbccc"`, `"abbcc"`, `"abbc"`, and `"abcccc"`. | ||
|
|
||
| **Example 2:** | ||
|
|
||
| **Input:** word = "abcd" | ||
|
|
||
| **Output:** 1 | ||
|
|
||
| **Explanation:** | ||
|
|
||
| The only possible string is `"abcd"`. | ||
|
|
||
| **Example 3:** | ||
|
|
||
| **Input:** word = "aaaa" | ||
|
|
||
| **Output:** 4 | ||
|
|
||
| **Constraints:** | ||
|
|
||
| * `1 <= word.length <= 100` | ||
| * `word` consists only of lowercase English letters. |
50 changes: 50 additions & 0 deletions
50
src/main/kotlin/g3301_3400/s3331_find_subtree_sizes_after_changes/Solution.kt
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,50 @@ | ||
| package g3301_3400.s3331_find_subtree_sizes_after_changes | ||
|
|
||
| // #Medium #Array #String #Hash_Table #Tree #Depth_First_Search | ||
| // #2024_10_29_Time_139_ms_(95.24%)_Space_82.2_MB_(19.05%) | ||
|
|
||
| class Solution { | ||
| private lateinit var finalAns: IntArray | ||
|
|
||
| fun findSubtreeSizes(parent: IntArray, s: String): IntArray { | ||
| val n = parent.size | ||
| val arr = s.toCharArray() | ||
| val newParent = IntArray(n) | ||
| finalAns = IntArray(n) | ||
| val tree = HashMap<Int, ArrayList<Int>>() | ||
|
|
||
| for (i in 1 until n) { | ||
| var parentNode = parent[i] | ||
| newParent[i] = parentNode | ||
| while (parentNode != -1) { | ||
| if (arr[parentNode] == arr[i]) { | ||
| newParent[i] = parentNode | ||
| break | ||
| } | ||
| parentNode = parent[parentNode] | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| for (i in 1 until n) { | ||
| if (!tree.containsKey(newParent[i])) { | ||
| tree.put(newParent[i], ArrayList<Int>()) | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| tree[newParent[i]]!!.add(i) | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| findNodes(0, tree) | ||
| return finalAns | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| private fun findNodes(parent: Int, tree: HashMap<Int, ArrayList<Int>>): Int { | ||
| var count = 1 | ||
| if (tree.containsKey(parent)) { | ||
| for (i in tree[parent]!!) { | ||
| count += findNodes(i, tree) | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| finalAns[parent] = count | ||
| return count | ||
| } | ||
| } |
53 changes: 53 additions & 0 deletions
53
src/main/kotlin/g3301_3400/s3331_find_subtree_sizes_after_changes/readme.md
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,53 @@ | ||
| 3331\. Find Subtree Sizes After Changes | ||
|
|
||
| Medium | ||
|
|
||
| You are given a tree rooted at node 0 that consists of `n` nodes numbered from `0` to `n - 1`. The tree is represented by an array `parent` of size `n`, where `parent[i]` is the parent of node `i`. Since node 0 is the root, `parent[0] == -1`. | ||
|
|
||
| You are also given a string `s` of length `n`, where `s[i]` is the character assigned to node `i`. | ||
|
|
||
| We make the following changes on the tree **one** time **simultaneously** for all nodes `x` from `1` to `n - 1`: | ||
|
|
||
| * Find the **closest** node `y` to node `x` such that `y` is an ancestor of `x`, and `s[x] == s[y]`. | ||
| * If node `y` does not exist, do nothing. | ||
| * Otherwise, **remove** the edge between `x` and its current parent and make node `y` the new parent of `x` by adding an edge between them. | ||
|
|
||
| Return an array `answer` of size `n` where `answer[i]` is the **size** of the subtree rooted at node `i` in the **final** tree. | ||
|
|
||
| A **subtree** of `treeName` is a tree consisting of a node in `treeName` and all of its descendants. | ||
|
|
||
| **Example 1:** | ||
|
|
||
| **Input:** parent = [-1,0,0,1,1,1], s = "abaabc" | ||
|
|
||
| **Output:** [6,3,1,1,1,1] | ||
|
|
||
| **Explanation:** | ||
|
|
||
| 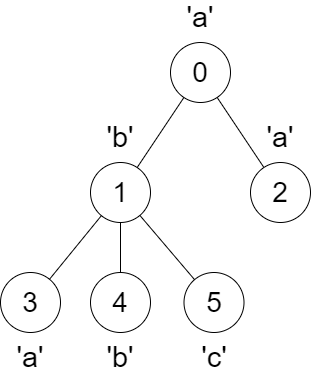 | ||
|
|
||
| The parent of node 3 will change from node 1 to node 0. | ||
|
|
||
| **Example 2:** | ||
|
|
||
| **Input:** parent = [-1,0,4,0,1], s = "abbba" | ||
|
|
||
| **Output:** [5,2,1,1,1] | ||
|
|
||
| **Explanation:** | ||
|
|
||
| 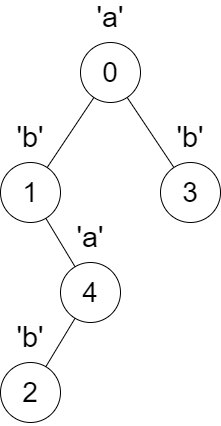 | ||
|
|
||
| The following changes will happen at the same time: | ||
|
|
||
| * The parent of node 4 will change from node 1 to node 0. | ||
| * The parent of node 2 will change from node 4 to node 1. | ||
|
|
||
| **Constraints:** | ||
|
|
||
| * `n == parent.length == s.length` | ||
| * <code>1 <= n <= 10<sup>5</sup></code> | ||
| * `0 <= parent[i] <= n - 1` for all `i >= 1`. | ||
| * `parent[0] == -1` | ||
| * `parent` represents a valid tree. | ||
| * `s` consists only of lowercase English letters. |
27 changes: 27 additions & 0 deletions
27
src/main/kotlin/g3301_3400/s3332_maximum_points_tourist_can_earn/Solution.kt
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,27 @@ | ||
| package g3301_3400.s3332_maximum_points_tourist_can_earn | ||
|
|
||
| // #Medium #Array #Dynamic_Programming #Matrix | ||
| // #2024_10_29_Time_216_ms_(100.00%)_Space_64_MB_(78.95%) | ||
|
|
||
| import kotlin.math.max | ||
|
|
||
| class Solution { | ||
| fun maxScore(n: Int, k: Int, stayScores: Array<IntArray>, travelScores: Array<IntArray>): Int { | ||
| // dp[day][city] | ||
| val dp = Array<IntArray?>(k + 1) { IntArray(n) } | ||
| var result = 0 | ||
| for (day in k - 1 downTo 0) { | ||
| for (city in 0 until n) { | ||
| val stayScore = stayScores[day][city] + dp[day + 1]!![city] | ||
| var travelScore = 0 | ||
| for (nextCity in 0 until n) { | ||
| val nextScore = travelScores[city][nextCity] + dp[day + 1]!![nextCity] | ||
| travelScore = max(nextScore, travelScore) | ||
| } | ||
| dp[day]!![city] = max(stayScore, travelScore) | ||
| result = max(dp[day]!![city], result) | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| return result | ||
| } | ||
| } |
44 changes: 44 additions & 0 deletions
44
src/main/kotlin/g3301_3400/s3332_maximum_points_tourist_can_earn/readme.md
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,44 @@ | ||
| 3332\. Maximum Points Tourist Can Earn | ||
|
|
||
| Medium | ||
|
|
||
| You are given two integers, `n` and `k`, along with two 2D integer arrays, `stayScore` and `travelScore`. | ||
|
|
||
| A tourist is visiting a country with `n` cities, where each city is **directly** connected to every other city. The tourist's journey consists of **exactly** `k` **0-indexed** days, and they can choose **any** city as their starting point. | ||
|
|
||
| Each day, the tourist has two choices: | ||
|
|
||
| * **Stay in the current city**: If the tourist stays in their current city `curr` during day `i`, they will earn `stayScore[i][curr]` points. | ||
| * **Move to another city**: If the tourist moves from their current city `curr` to city `dest`, they will earn `travelScore[curr][dest]` points. | ||
|
|
||
| Return the **maximum** possible points the tourist can earn. | ||
|
|
||
| **Example 1:** | ||
|
|
||
| **Input:** n = 2, k = 1, stayScore = [[2,3]], travelScore = [[0,2],[1,0]] | ||
|
|
||
| **Output:** 3 | ||
|
|
||
| **Explanation:** | ||
|
|
||
| The tourist earns the maximum number of points by starting in city 1 and staying in that city. | ||
|
|
||
| **Example 2:** | ||
|
|
||
| **Input:** n = 3, k = 2, stayScore = [[3,4,2],[2,1,2]], travelScore = [[0,2,1],[2,0,4],[3,2,0]] | ||
|
|
||
| **Output:** 8 | ||
|
|
||
| **Explanation:** | ||
|
|
||
| The tourist earns the maximum number of points by starting in city 1, staying in that city on day 0, and traveling to city 2 on day 1. | ||
|
|
||
| **Constraints:** | ||
|
|
||
| * `1 <= n <= 200` | ||
| * `1 <= k <= 200` | ||
| * `n == travelScore.length == travelScore[i].length == stayScore[i].length` | ||
| * `k == stayScore.length` | ||
| * `1 <= stayScore[i][j] <= 100` | ||
| * `0 <= travelScore[i][j] <= 100` | ||
| * `travelScore[i][i] == 0` |
58 changes: 58 additions & 0 deletions
58
src/main/kotlin/g3301_3400/s3333_find_the_original_typed_string_ii/Solution.kt
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,58 @@ | ||
| package g3301_3400.s3333_find_the_original_typed_string_ii | ||
|
|
||
| // #Hard #String #Dynamic_Programming #Prefix_Sum | ||
| // #2024_10_29_Time_490_ms_(100.00%)_Space_52.2_MB_(33.33%) | ||
|
|
||
| class Solution { | ||
| fun possibleStringCount(word: String, k: Int): Int { | ||
| val list: MutableList<Int> = ArrayList<Int>() | ||
| val n = word.length | ||
| var i = 0 | ||
| while (i < n) { | ||
| var j = i + 1 | ||
| while (j < n && word[j] == word[j - 1]) { | ||
| j++ | ||
| } | ||
| list.add(j - i) | ||
| i = j | ||
| } | ||
| val m = list.size | ||
| val power = LongArray(m) | ||
| power[m - 1] = list[m - 1].toLong() | ||
| i = m - 2 | ||
| while (i >= 0) { | ||
| power[i] = (power[i + 1] * list[i]) % MOD | ||
| i-- | ||
| } | ||
| if (m >= k) { | ||
| return power[0].toInt() | ||
| } | ||
| val dp = Array<LongArray?>(m) { LongArray(k - m + 1) } | ||
| i = 0 | ||
| while (i < k - m + 1) { | ||
| if (list[m - 1] + i + m > k) { | ||
| dp[m - 1]!![i] = list[m - 1] - (k - m - i).toLong() | ||
| } | ||
| i++ | ||
| } | ||
| i = m - 2 | ||
| while (i >= 0) { | ||
| var sum: Long = dp[i + 1]!![k - m] * list[i] % MOD | ||
| for (j in k - m downTo 0) { | ||
| sum += dp[i + 1]!![j] | ||
| if (j + list[i] > k - m) { | ||
| sum = (sum - dp[i + 1]!![k - m] + MOD) % MOD | ||
| } else { | ||
| sum = (sum - dp[i + 1]!![j + list[i]] + MOD) % MOD | ||
| } | ||
| dp[i]!![j] = sum | ||
| } | ||
| i-- | ||
| } | ||
| return dp[0]!![0].toInt() | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| companion object { | ||
| private const val MOD = 1e9.toLong() + 7 | ||
| } | ||
| } |
43 changes: 43 additions & 0 deletions
43
src/main/kotlin/g3301_3400/s3333_find_the_original_typed_string_ii/readme.md
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,43 @@ | ||
| 3333\. Find the Original Typed String II | ||
|
|
||
| Hard | ||
|
|
||
| Alice is attempting to type a specific string on her computer. However, she tends to be clumsy and **may** press a key for too long, resulting in a character being typed **multiple** times. | ||
|
|
||
| You are given a string `word`, which represents the **final** output displayed on Alice's screen. You are also given a **positive** integer `k`. | ||
|
|
||
| Return the total number of _possible_ original strings that Alice _might_ have intended to type, if she was trying to type a string of size **at least** `k`. | ||
|
|
||
| Since the answer may be very large, return it **modulo** <code>10<sup>9</sup> + 7</code>. | ||
|
|
||
| **Example 1:** | ||
|
|
||
| **Input:** word = "aabbccdd", k = 7 | ||
|
|
||
| **Output:** 5 | ||
|
|
||
| **Explanation:** | ||
|
|
||
| The possible strings are: `"aabbccdd"`, `"aabbccd"`, `"aabbcdd"`, `"aabccdd"`, and `"abbccdd"`. | ||
|
|
||
| **Example 2:** | ||
|
|
||
| **Input:** word = "aabbccdd", k = 8 | ||
|
|
||
| **Output:** 1 | ||
|
|
||
| **Explanation:** | ||
|
|
||
| The only possible string is `"aabbccdd"`. | ||
|
|
||
| **Example 3:** | ||
|
|
||
| **Input:** word = "aaabbb", k = 3 | ||
|
|
||
| **Output:** 8 | ||
|
|
||
| **Constraints:** | ||
|
|
||
| * <code>1 <= word.length <= 5 * 10<sup>5</sup></code> | ||
| * `word` consists only of lowercase English letters. | ||
| * `1 <= k <= 2000` |
Oops, something went wrong.