This repository presents an unsupervised method to estimate the repertoire size in the European Greenfinch (Chloris Chloris). The proposed method receives as input a set of audio time series which is segmented and converted into a reduced representation set called a feature vector. The system is finally evaluated using clustering performance metrics to find the ideal number of syllables in the data set.
Based on "Estimating the repertoire size in birds using Unsupervised Clustering Techniques" 2022, Joachim Poutaraud
Download Anaconda and prepare your environment using the command line
conda create --name chloris
conda activate chloris
Use the package manager pip to install the required libraires
conda install -c anaconda pip
pip install -r requirements.txt
The data set contains a total of 339 audio recordings of an average duration of 48.64 seconds each. The data are downloaded from the Xeno-Canto sound library, a collaborative project dedicated to sharing bird sounds from all over the world. We use an area-based query gathering European recordings of the European Greenfinch (Chloris Chloris). We select only high quality recordings according to the Xeno-Canto quality ratings ranging from A (highest quality) to E (lowest quality) and remove recordings that have an other species referenced in the background.
To download the data set, you need to install wget
- For macOS, write the following command in the terminal:
brew install wget - For Windows, download the package, copy the
wget.exefile into yourC:\Windows\System32folder and runwgeton the command line to see if it is correctly installed.
Finally, you can run the following script
python downloading.py
Note: data have already been downloaded and are stored in the
data/recordingsfolder
Segmentation is a preliminary phase for the analysis and classification of bird syllables. This makes it easier to build analysis and classification systems with segmented objects than with raw data and reduces the size of the dataset which will facilitate computer processing and make it easier to carry on recognition and retrieval.
Here, input signals are segmented using the Continuous Wavelet Transform (CWT). The transformation process is computed with the free library for the Python programming language PyWavelets. Aditionally, we calculate the energy envelope of each wavelet vector using Root Mean Square (RMS) energy function. That way, we can isolate segments by finding high-energy peaks in the energy envelope and apply a threshold mask set to -20 dB.
To segment audio recordings, you can run the following script
python segmenting.py
Note: audio recordings have already been segmented and temporal information values are stored in the
dataset.csvfile
Features are extracted from each bird syllable and constitute a feature vector, which is a representation of the syllable. Since bird songs are musical in nature, time and frequency-based features used in audio and music retrieval are extracted for the bird syllable classification. The feature vector is composed of 14 Descriptive Features (DFs), 13 Mel-Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCCs) to which the duration of the syllable (DUR) is concatenated, thus yielding a feature vector of length 28.
Descriptive Features (DFs)
- Energy (EN)
- Zero Crossing Rate (ZCR)
- Duration of the Syllable (DUR)
- Spectral Centroid (SC)
- Spectral Bandwidth (SB)
- Spectral Flux (SF)
- Spectral Roll Off (SR)
- Spectral Flatness (SF)
Mel-Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCCs)
To extract time and frequency-based features, you can run the following script
python extracting.py
Note: features have already been extracted for each syllable and are stored in the
dataset.csvfile
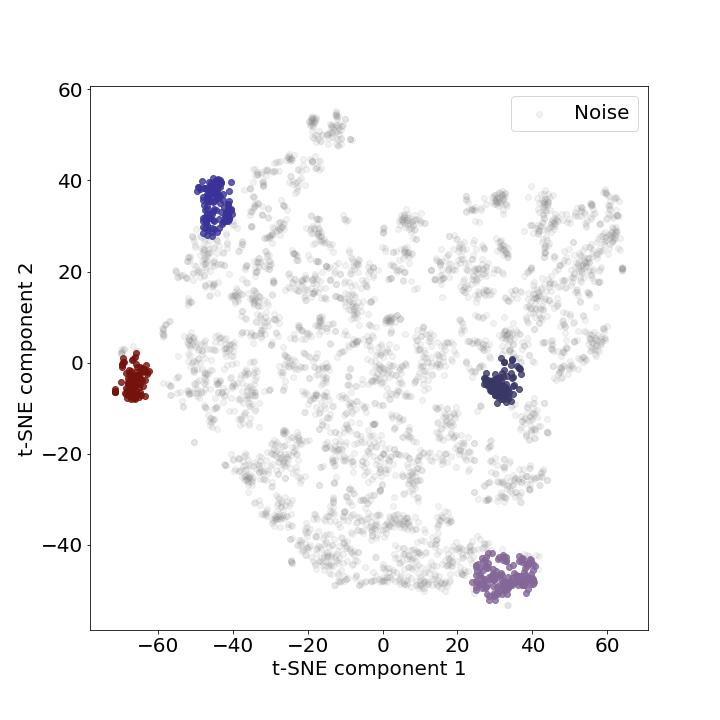
After the features are extracted from augmented data, they are normalized using the Min–Max method. They are then selected based on individual ranking using common feature selection techniques such as the Variance Threshold and the Laplacian Score, and fed into an unsupervised clustering algorithm to automatically cluster bird syllables in the audio recordings.
To evaluate the proposed system, you can run the following script
python evaluating.py
Note: feature vectors have already been selected according to the results found in the notebook 4.selecting.ipynb
Pull requests are welcome. For major changes, please open an issue first to discuss what you would like to change. Please make sure to update tests as appropriate.