forked from javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin
-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 1
Commit
This commit does not belong to any branch on this repository, and may belong to a fork outside of the repository.
- Loading branch information
Showing
12 changed files
with
576 additions
and
0 deletions.
There are no files selected for viewing
34 changes: 34 additions & 0 deletions
34
src/main/kotlin/g3401_3500/s3417_zigzag_grid_traversal_with_skip/Solution.kt
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,34 @@ | ||
| package g3401_3500.s3417_zigzag_grid_traversal_with_skip | ||
|
|
||
| // #Easy #Array #Matrix #Simulation #2025_01_14_Time_2_(100.00%)_Space_43.72_(76.92%) | ||
|
|
||
| class Solution { | ||
| fun zigzagTraversal(grid: Array<IntArray>): List<Int> { | ||
| val ans: MutableList<Int> = ArrayList<Int>() | ||
| val m = grid.size | ||
| val n = grid[0].size | ||
| var i = 0 | ||
| var flag = true | ||
| var skip = false | ||
| while (i < m) { | ||
| if (flag) { | ||
| for (j in 0..<n) { | ||
| if (!skip) { | ||
| ans.add(grid[i][j]) | ||
| } | ||
| skip = !skip | ||
| } | ||
| } else { | ||
| for (j in n - 1 downTo 0) { | ||
| if (!skip) { | ||
| ans.add(grid[i][j]) | ||
| } | ||
| skip = !skip | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| flag = !flag | ||
| i++ | ||
| } | ||
| return ans | ||
| } | ||
| } |
54 changes: 54 additions & 0 deletions
54
src/main/kotlin/g3401_3500/s3417_zigzag_grid_traversal_with_skip/readme.md
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,54 @@ | ||
| 3417\. Zigzag Grid Traversal With Skip | ||
|
|
||
| Easy | ||
|
|
||
| You are given an `m x n` 2D array `grid` of **positive** integers. | ||
|
|
||
| Your task is to traverse `grid` in a **zigzag** pattern while skipping every **alternate** cell. | ||
|
|
||
| Zigzag pattern traversal is defined as following the below actions: | ||
|
|
||
| * Start at the top-left cell `(0, 0)`. | ||
| * Move _right_ within a row until the end of the row is reached. | ||
| * Drop down to the next row, then traverse _left_ until the beginning of the row is reached. | ||
| * Continue **alternating** between right and left traversal until every row has been traversed. | ||
|
|
||
| **Note** that you **must skip** every _alternate_ cell during the traversal. | ||
|
|
||
| Return an array of integers `result` containing, **in order**, the value of the cells visited during the zigzag traversal with skips. | ||
|
|
||
| **Example 1:** | ||
|
|
||
| **Input:** grid = [[1,2],[3,4]] | ||
|
|
||
| **Output:** [1,4] | ||
|
|
||
| **Explanation:** | ||
|
|
||
| **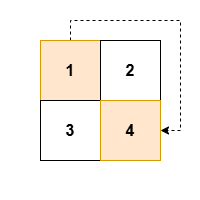** | ||
|
|
||
| **Example 2:** | ||
|
|
||
| **Input:** grid = [[2,1],[2,1],[2,1]] | ||
|
|
||
| **Output:** [2,1,2] | ||
|
|
||
| **Explanation:** | ||
|
|
||
| 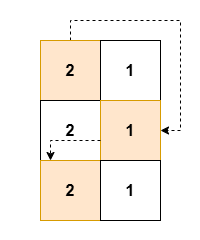 | ||
|
|
||
| **Example 3:** | ||
|
|
||
| **Input:** grid = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]] | ||
|
|
||
| **Output:** [1,3,5,7,9] | ||
|
|
||
| **Explanation:** | ||
|
|
||
| 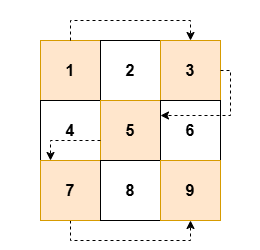 | ||
|
|
||
| **Constraints:** | ||
|
|
||
| * `2 <= n == grid.length <= 50` | ||
| * `2 <= m == grid[i].length <= 50` | ||
| * `1 <= grid[i][j] <= 2500` |
58 changes: 58 additions & 0 deletions
58
src/main/kotlin/g3401_3500/s3418_maximum_amount_of_money_robot_can_earn/Solution.kt
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,58 @@ | ||
| package g3401_3500.s3418_maximum_amount_of_money_robot_can_earn | ||
|
|
||
| // #Medium #Array #Dynamic_Programming #Matrix #2025_01_14_Time_60_(81.82%)_Space_84.66_(81.82%) | ||
|
|
||
| import kotlin.math.max | ||
|
|
||
| class Solution { | ||
| fun maximumAmount(coins: Array<IntArray>): Int { | ||
| val m = coins.size | ||
| val n = coins[0].size | ||
| val dp = Array<IntArray>(m) { IntArray(n) } | ||
| val dp1 = Array<IntArray>(m) { IntArray(n) } | ||
| val dp2 = Array<IntArray>(m) { IntArray(n) } | ||
| dp[0][0] = coins[0][0] | ||
| for (j in 1..<n) { | ||
| dp[0][j] = dp[0][j - 1] + coins[0][j] | ||
| } | ||
| for (i in 1..<m) { | ||
| dp[i][0] = dp[i - 1][0] + coins[i][0] | ||
| } | ||
| for (i in 1..<m) { | ||
| for (j in 1..<n) { | ||
| dp[i][j] = max(dp[i][j - 1], dp[i - 1][j]) + coins[i][j] | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| dp1[0][0] = max(coins[0][0], 0) | ||
| for (j in 1..<n) { | ||
| dp1[0][j] = max(dp[0][j - 1], (dp1[0][j - 1] + coins[0][j])) | ||
| } | ||
| for (i in 1..<m) { | ||
| dp1[i][0] = max(dp[i - 1][0], (dp1[i - 1][0] + coins[i][0])) | ||
| } | ||
| for (i in 1..<m) { | ||
| for (j in 1..<n) { | ||
| dp1[i][j] = max( | ||
| max(dp[i][j - 1], dp[i - 1][j]), | ||
| (max(dp1[i][j - 1], dp1[i - 1][j]) + coins[i][j]), | ||
| ) | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| dp2[0][0] = max(coins[0][0], 0) | ||
| for (j in 1..<n) { | ||
| dp2[0][j] = max(dp1[0][j - 1], (dp2[0][j - 1] + coins[0][j])) | ||
| } | ||
| for (i in 1..<m) { | ||
| dp2[i][0] = max(dp1[i - 1][0], (dp2[i - 1][0] + coins[i][0])) | ||
| } | ||
| for (i in 1..<m) { | ||
| for (j in 1..<n) { | ||
| dp2[i][j] = max( | ||
| max(dp1[i][j - 1], dp1[i - 1][j]), | ||
| (max(dp2[i][j - 1], dp2[i - 1][j]) + coins[i][j]), | ||
| ) | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| return dp2[m - 1][n - 1] | ||
| } | ||
| } |
54 changes: 54 additions & 0 deletions
54
src/main/kotlin/g3401_3500/s3418_maximum_amount_of_money_robot_can_earn/readme.md
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,54 @@ | ||
| 3418\. Maximum Amount of Money Robot Can Earn | ||
|
|
||
| Medium | ||
|
|
||
| You are given an `m x n` grid. A robot starts at the top-left corner of the grid `(0, 0)` and wants to reach the bottom-right corner `(m - 1, n - 1)`. The robot can move either right or down at any point in time. | ||
|
|
||
| The grid contains a value `coins[i][j]` in each cell: | ||
|
|
||
| * If `coins[i][j] >= 0`, the robot gains that many coins. | ||
| * If `coins[i][j] < 0`, the robot encounters a robber, and the robber steals the **absolute** value of `coins[i][j]` coins. | ||
|
|
||
| The robot has a special ability to **neutralize robbers** in at most **2 cells** on its path, preventing them from stealing coins in those cells. | ||
|
|
||
| **Note:** The robot's total coins can be negative. | ||
|
|
||
| Return the **maximum** profit the robot can gain on the route. | ||
|
|
||
| **Example 1:** | ||
|
|
||
| **Input:** coins = [[0,1,-1],[1,-2,3],[2,-3,4]] | ||
|
|
||
| **Output:** 8 | ||
|
|
||
| **Explanation:** | ||
|
|
||
| An optimal path for maximum coins is: | ||
|
|
||
| 1. Start at `(0, 0)` with `0` coins (total coins = `0`). | ||
| 2. Move to `(0, 1)`, gaining `1` coin (total coins = `0 + 1 = 1`). | ||
| 3. Move to `(1, 1)`, where there's a robber stealing `2` coins. The robot uses one neutralization here, avoiding the robbery (total coins = `1`). | ||
| 4. Move to `(1, 2)`, gaining `3` coins (total coins = `1 + 3 = 4`). | ||
| 5. Move to `(2, 2)`, gaining `4` coins (total coins = `4 + 4 = 8`). | ||
|
|
||
| **Example 2:** | ||
|
|
||
| **Input:** coins = [[10,10,10],[10,10,10]] | ||
|
|
||
| **Output:** 40 | ||
|
|
||
| **Explanation:** | ||
|
|
||
| An optimal path for maximum coins is: | ||
|
|
||
| 1. Start at `(0, 0)` with `10` coins (total coins = `10`). | ||
| 2. Move to `(0, 1)`, gaining `10` coins (total coins = `10 + 10 = 20`). | ||
| 3. Move to `(0, 2)`, gaining another `10` coins (total coins = `20 + 10 = 30`). | ||
| 4. Move to `(1, 2)`, gaining the final `10` coins (total coins = `30 + 10 = 40`). | ||
|
|
||
| **Constraints:** | ||
|
|
||
| * `m == coins.length` | ||
| * `n == coins[i].length` | ||
| * `1 <= m, n <= 500` | ||
| * `-1000 <= coins[i][j] <= 1000` |
52 changes: 52 additions & 0 deletions
52
src/main/kotlin/g3401_3500/s3419_minimize_the_maximum_edge_weight_of_graph/Solution.kt
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,52 @@ | ||
| package g3401_3500.s3419_minimize_the_maximum_edge_weight_of_graph | ||
|
|
||
| // #Medium #Depth_First_Search #Breadth_First_Search #Binary_Search #Graph #Shortest_Path | ||
| // #2025_01_14_Time_88_(100.00%)_Space_115.26_(83.33%) | ||
|
|
||
| import java.util.LinkedList | ||
| import java.util.Queue | ||
| import kotlin.math.max | ||
|
|
||
| @Suppress("unused") | ||
| class Solution { | ||
| fun minMaxWeight(n: Int, edges: Array<IntArray>, threshold: Int): Int { | ||
| val reversedG: Array<MutableList<IntArray>?> = arrayOfNulls<MutableList<IntArray>?>(n) | ||
| for (i in 0..<n) { | ||
| reversedG[i] = ArrayList<IntArray>() | ||
| } | ||
| for (i in edges) { | ||
| val a = i[0] | ||
| val b = i[1] | ||
| val w = i[2] | ||
| reversedG[b]!!.add(intArrayOf(a, w)) | ||
| } | ||
| val distance = IntArray(n) | ||
| distance.fill(Int.Companion.MAX_VALUE) | ||
| distance[0] = 0 | ||
| if (reversedG[0]!!.isEmpty()) { | ||
| return -1 | ||
| } | ||
| val que: Queue<Int?> = LinkedList<Int?>() | ||
| que.add(0) | ||
| while (que.isNotEmpty()) { | ||
| val cur: Int = que.poll()!! | ||
| for (next in reversedG[cur]!!) { | ||
| val node = next[0] | ||
| val w = next[1] | ||
| val nextdis = max(w, distance[cur]) | ||
| if (nextdis < distance[node]) { | ||
| distance[node] = nextdis | ||
| que.add(node) | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| var ans = 0 | ||
| for (i in 0..<n) { | ||
| if (distance[i] == Int.Companion.MAX_VALUE) { | ||
| return -1 | ||
| } | ||
| ans = max(ans, distance[i]) | ||
| } | ||
| return ans | ||
| } | ||
| } |
64 changes: 64 additions & 0 deletions
64
...ain/kotlin/g3401_3500/s3419_minimize_the_maximum_edge_weight_of_graph/readme.md
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,64 @@ | ||
| 3419\. Minimize the Maximum Edge Weight of Graph | ||
|
|
||
| Medium | ||
|
|
||
| You are given two integers, `n` and `threshold`, as well as a **directed** weighted graph of `n` nodes numbered from 0 to `n - 1`. The graph is represented by a **2D** integer array `edges`, where <code>edges[i] = [A<sub>i</sub>, B<sub>i</sub>, W<sub>i</sub>]</code> indicates that there is an edge going from node <code>A<sub>i</sub></code> to node <code>B<sub>i</sub></code> with weight <code>W<sub>i</sub></code>. | ||
|
|
||
| You have to remove some edges from this graph (possibly **none**), so that it satisfies the following conditions: | ||
|
|
||
| * Node 0 must be reachable from all other nodes. | ||
| * The **maximum** edge weight in the resulting graph is **minimized**. | ||
| * Each node has **at most** `threshold` outgoing edges. | ||
|
|
||
| Return the **minimum** possible value of the **maximum** edge weight after removing the necessary edges. If it is impossible for all conditions to be satisfied, return -1. | ||
|
|
||
| **Example 1:** | ||
|
|
||
| **Input:** n = 5, edges = [[1,0,1],[2,0,2],[3,0,1],[4,3,1],[2,1,1]], threshold = 2 | ||
|
|
||
| **Output:** 1 | ||
|
|
||
| **Explanation:** | ||
|
|
||
| 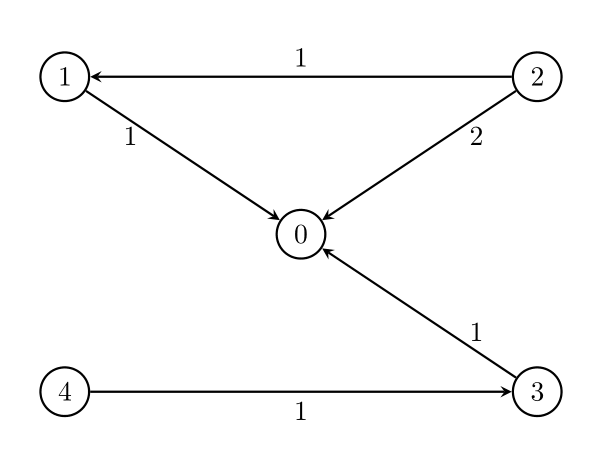 | ||
|
|
||
| Remove the edge `2 -> 0`. The maximum weight among the remaining edges is 1. | ||
|
|
||
| **Example 2:** | ||
|
|
||
| **Input:** n = 5, edges = [[0,1,1],[0,2,2],[0,3,1],[0,4,1],[1,2,1],[1,4,1]], threshold = 1 | ||
|
|
||
| **Output:** \-1 | ||
|
|
||
| **Explanation:** | ||
|
|
||
| It is impossible to reach node 0 from node 2. | ||
|
|
||
| **Example 3:** | ||
|
|
||
| **Input:** n = 5, edges = [[1,2,1],[1,3,3],[1,4,5],[2,3,2],[3,4,2],[4,0,1]], threshold = 1 | ||
|
|
||
| **Output:** 2 | ||
|
|
||
| **Explanation:** | ||
|
|
||
| 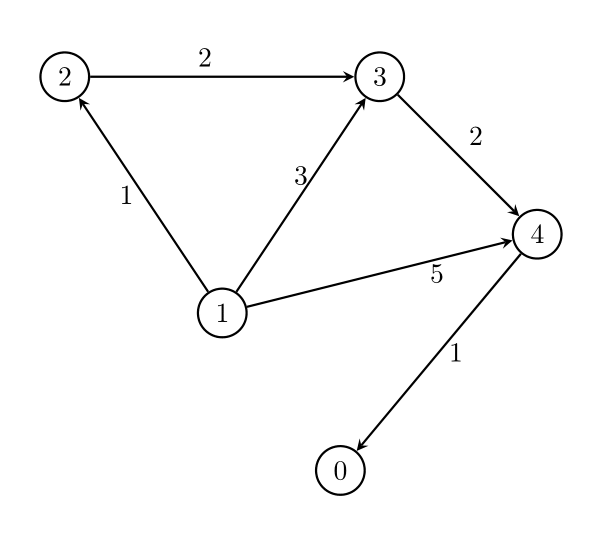 | ||
|
|
||
| Remove the edges `1 -> 3` and `1 -> 4`. The maximum weight among the remaining edges is 2. | ||
|
|
||
| **Example 4:** | ||
|
|
||
| **Input:** n = 5, edges = [[1,2,1],[1,3,3],[1,4,5],[2,3,2],[4,0,1]], threshold = 1 | ||
|
|
||
| **Output:** \-1 | ||
|
|
||
| **Constraints:** | ||
|
|
||
| * <code>2 <= n <= 10<sup>5</sup></code> | ||
| * `1 <= threshold <= n - 1` | ||
| * <code>1 <= edges.length <= min(10<sup>5</sup>, n * (n - 1) / 2).</code> | ||
| * `edges[i].length == 3` | ||
| * <code>0 <= A<sub>i</sub>, B<sub>i</sub> < n</code> | ||
| * <code>A<sub>i</sub> != B<sub>i</sub></code> | ||
| * <code>1 <= W<sub>i</sub> <= 10<sup>6</sup></code> | ||
| * There **may be** multiple edges between a pair of nodes, but they must have unique weights. |
47 changes: 47 additions & 0 deletions
47
...ain/kotlin/g3401_3500/s3420_count_non_decreasing_subarrays_after_k_operations/Solution.kt
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,47 @@ | ||
| package g3401_3500.s3420_count_non_decreasing_subarrays_after_k_operations | ||
|
|
||
| // #Hard #Array #Two_Pointers #Stack #Monotonic_Stack #Queue #Segment_Tree #Monotonic_Queue | ||
| // #2025_01_15_Time_28_(100.00%)_Space_68.93_(88.89%) | ||
|
|
||
| class Solution { | ||
| fun countNonDecreasingSubarrays(nums: IntArray, k: Int): Long { | ||
| val n = nums.size | ||
| reverse(nums) | ||
| var res: Long = 0 | ||
| var t = k.toLong() | ||
| val q = IntArray(n + 1) | ||
| var hh = 0 | ||
| var tt = -1 | ||
| var j = 0 | ||
| var i = 0 | ||
| while (j < n) { | ||
| while (hh <= tt && nums[q[tt]] < nums[j]) { | ||
| val r = q[tt--] | ||
| val l = if (hh <= tt) q[tt] else i - 1 | ||
| t -= (r - l).toLong() * (nums[j] - nums[r]) | ||
| } | ||
| q[++tt] = j | ||
| while (t < 0) { | ||
| t += (nums[q[hh]] - nums[i]).toLong() | ||
| if (q[hh] == i) hh++ | ||
| i++ | ||
| } | ||
| res += (j - i + 1).toLong() | ||
| j++ | ||
| } | ||
| return res | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| private fun reverse(nums: IntArray) { | ||
| val n = nums.size | ||
| var i = 0 | ||
| var j = n - 1 | ||
| while (i < j) { | ||
| val t = nums[i] | ||
| nums[i] = nums[j] | ||
| nums[j] = t | ||
| i++ | ||
| j-- | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| } |
Oops, something went wrong.