Krumo is a debugging tool, which displays structured information about any PHP variable.
It is a nice replacement for print_r() or var_dump() which are used by a lot of PHP developers.
To put it simply, Krumo is a replacement for print_r() and var_dump(). By definition Krumo
is a debugging tool, which displays structured information about any PHP variable.
A lot of developers use print_r() and var_dump() in the means of debugging
tools. Although they were intended to present human readable information about a
variable, we can all agree that in general they are not. Krumo is an
alternative: it does the same job, but it presents the information beautified
using CSS/JS/HTML.
This library can be installed in autoloadable way using Composer as kktsvetkov/krumo.
php composer.phar require kktsvetkov/krumoIn the rare occasion that you are dealing with some legacy code that
has not yet embraced Composer, you can also download this package,
and include class.krumo.php in your project, or make it accessible
somewhere in your INCLUDE_PATH:
include 'class.krumo.php';More or less, that's it.
Here's a basic example, which will return a report on the array variable passed as argument to it:
krumo(array('a1'=> 'A1', 3, 'red'));You can dump simultaneously more then one variable - here's another example:
krumo($_SERVER, $_REQUEST);You probably saw from the examples above that some of the nodes are expandable, so if you want to inspect the nested information, click on them and they will expand; if you do not need that information shown simply click again on it to collapse it. Here's an example to test this:
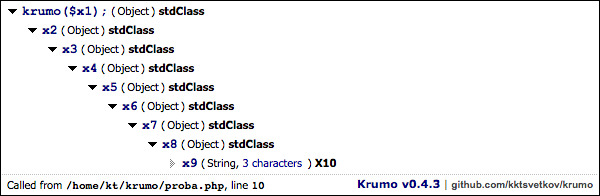
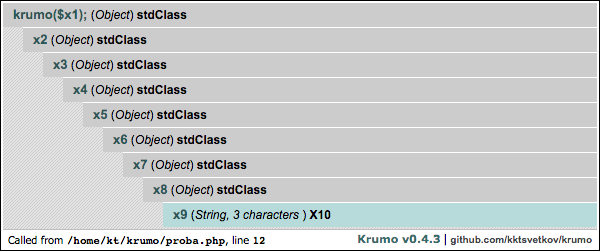
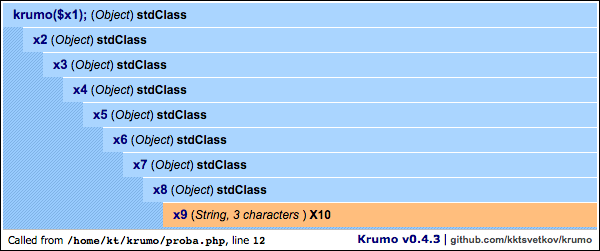
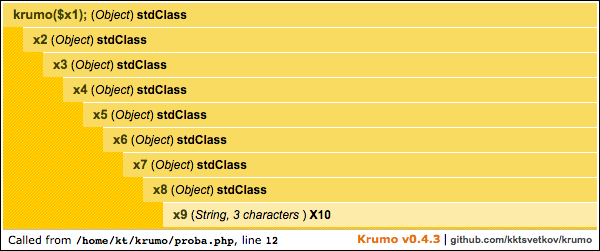
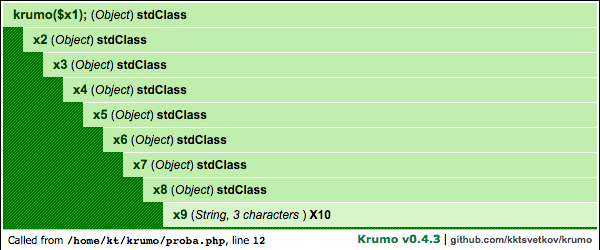
$x1->x2->x3->x4->x5->x6->x7->x8->x9 = 'X10';
krumo($x1);The krumo() is the only standalone function from the package, and this is
because basic dumps about variables (like print_r() or var_dump()) are the most
common tasks such functionality is used for. The rest of the functionality can
be called using static calls to the Krumo class. Here are several more examples:
// print a debug backgrace
krumo::backtrace();
// print all the included(or required) files
krumo::includes();
// print all the included functions
krumo::functions();
// print all the declared classes
krumo::classes();
// print all the defined constants
krumo::defines();... and so on, etc.
Please note that the first time you call Krumo the dump it produces also
prints the CSS and the JS code used to expand/collapse the dump nodes.
If you want to get the output returned instead of printed, you can use
the krumo::fetch() method for that:
$a = krumo::fetch($app, $env);It's been a valid complain that sometimes Krumo output is called in the middle
of some opened HTML tag, and that breaks the output of both that tag and Krumo
itself. You can use krumo::queue() instead of krumo::dump() to solve that
problem, since krumo::queue() will print its output at the end of the script:
krumo::queue($request);There are several skins pre-installed with this package, but if you wish you can create skins of your own. The skins are simply CSS files that are prepended to the result that Krumo prints.
To the Krumo skin, you have to set it at krumo::$skin:
krumo::$skin = 'blue';Here is a list of the pre-installed skins in Krumo
This is the new default theme, kaloyan.info. It is not as color heavy as the other skins
// set up using the "kaloyan.info" skin
krumo::$skin = 'kaloyan.info';As the name suggests, this is the old "default" theme.
// set up using the "default" skin
krumo::$skin = 'default';This is a blue version of the old default theme
// set up using the "blue" skin
krumo::$skin = 'blue';This is an orange version of the old default theme
// set up using the "orange" skin
krumo::$skin = 'orange';This is a green version of the old default theme
// set up using the "green" skin
krumo::$skin = 'green';This project is released under GNU Lesser General Public License v2.1 opensource.org/licenses/LGPL-2.1
The project was first hosted and maintained at sourceforge.net/projects/krumo/.