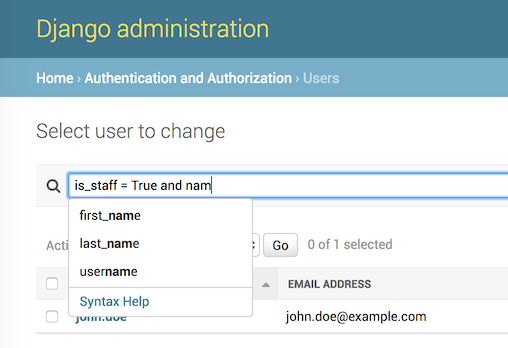
Advanced search language for Django, with auto-completion. Supports logical operators, parenthesis, table joins, works with any Django models. Tested vs. Python 2.7, 3.5 - 3.7, Django 1.8 - 2.1. Auto-completion feature tested in Chrome, Firefox, Safari, IE9+.
See a video: DjangoQL demo
- Installation
- Add it to your Django admin
- Using together with a standard Django admin search
- Saved Queries with Advanced Search with DjangoQL
- Language reference
- DjangoQL Schema
- Custom search fields
- Can I use it outside of Django admin?
- Using completion widget outside of Django admin
$ pip install djangoqlAdd 'djangoql' to INSTALLED_APPS in your settings.py:
INSTALLED_APPS = [
...
'djangoql',
...
]Add DjangoQLSearchMixin to your model admin, and it will replace standard
Django search functionality with DjangoQL search. Example:
from django.contrib import admin
from djangoql.admin import DjangoQLSearchMixin
from .models import Book
@admin.register(Book)
class BookAdmin(DjangoQLSearchMixin, admin.ModelAdmin):
passIf you define search_fields on your ModelAdmin class, DjangoQL integration
would automatically recognize this and let users choose between a standard
Django search (that you specified with search_fields) and Advanced Search
with DjangoQL. Example:
@admin.register(Book)
class BookAdmin(DjangoQLSearchMixin, admin.ModelAdmin):
search_fields = ('title', 'author__name')For the example above, a checkbox that controls search mode would appear near
the search input. If you don't want two search modes, simply remove
search_fields from your ModelAdmin class.
If you add DjangoQLSearchMixin to your model admin,
you will get button "Save query" near textarea.
You can write your query, save it in modal window.
You can select auto-completion or saved queries in popup.
You can select, edit or delete your or public saved query.
DjangoQL is shipped with comprehensive Syntax Help, which is available in Django admin (see Syntax Help link in auto-completion popup). Here's a quick summary:
DjangoQL looks close to Python syntax, however there're some minor differences. Basically you just reference model fields like you do it in Python code, apply comparison and logical operators and parenthesis. DjangoQL is case-sensitive.
- model fields: exactly as they are defined in Python code. Access
nested properties via
., for exampleauthor.last_name; - strings must be double-quoted. Single quotes are not supported.
To escape a double quote use
\"; - boolean and null values:
True,False,None. Please note that they can be combined with equality operators only, so you can writepublished = False or date_published = None, butpublished > Falsewill cause an error; - logical operators:
and,or; - comparison operators:
=,!=,<,<=,>,>=- work as you expect.~and!~- test that a string contains or not contains a substring (translated into__icontains); - test a value vs. list:
in,not in. Example:pk in (2, 3).
Schema defines limitations - what you can do with a DjangoQL query. If you don't specify any schema, DjangoQL will provide a default schema for you. It would recursively walk though all model fields and relations and include everything it could find in the schema, so users would be able to search through everything. However sometimes this is not what you want, either due to DB performance or security concerns. If you'd like to limit search models or fields, you should define a schema. Here's an example:
class UserQLSchema(DjangoQLSchema):
exclude = (Book,)
suggest_options = {
Group: ['name'],
}
def get_fields(self, model):
if model == Group:
return ['name']
return super(UserQLSchema, self).get_fields(model)
@admin.register(User)
class CustomUserAdmin(DjangoQLSearchMixin, UserAdmin):
djangoql_schema = UserQLSchemaIn the example above we created a schema that does 3 things:
- excludes Book model from search via
excludeoption. Instead ofexcludeyou may also useinclude, it would limit search to listed models only; - limits available search fields for Group model to
namefield only, in.get_fields()method; - enables completion options for Group names via
suggest_options.
Important note about suggest_options: it looks for choices model field
parameter first, and if it's not specified - it synchronously pulls all values
for given model fields, so you should avoid large querysets there. If you'd like
to define custom suggestion options, see below.
Sometimes you may want deeper customization, and here custom search fields
come into play. You may use them to search by annotations, or to define
custom suggestion options, or define fully custom search logic. DjangoQL
defines the following base field classes in djangoql.schema that you may
subclass to define your own behavior:
IntFieldFloatFieldStrFieldBoolFieldDateFieldDateTimeFieldRelationField
Here are examples for common use cases:
Search by queryset annotations:
from djangoql.schema import DjangoQLSchema, IntField
class UserQLSchema(DjangoQLSchema):
def get_fields(self, model):
fields = super(UserQLSchema, self).get_fields(model)
if model == User:
fields = [IntField(name='groups_count')] + fields
return fields
@admin.register(User)
class CustomUserAdmin(DjangoQLSearchMixin, UserAdmin):
djangoql_schema = UserQLSchema
def get_queryset(self, request):
qs = super(CustomUserAdmin, self).get_queryset(request)
return qs.annotate(groups_count=Count('groups'))Let's take a closer look what's happening in the example above. First, we
add groups_count annotation to queryset that is used by Django admin
in CustomUserAdmin.get_queryset() method. It would contain no. of groups
user belongs to. As our queryset now pulls this column, we can now filter by
it, we just need to include it into the schema. In
UserQLSchema.get_fields() we define a custom integer search field for
User model. It's name should match the name of the column in our queryset.
Custom suggestion options
from djangoql.schema import DjangoQLSchema, StrField
class GroupNameField(StrField):
model = Group
name = 'name'
suggest_options = True
def get_options(self):
return super(GroupNameField, self).get_options().\
annotate(users_count=Count('user')).\
order_by('-users_count')
class UserQLSchema(DjangoQLSchema):
def get_fields(self, model):
if model == Group:
return ['id', GroupNameField()]
return super(UserQLSchema, self).get_fields(model)
@admin.register(User)
class CustomUserAdmin(DjangoQLSearchMixin, UserAdmin):
djangoql_schema = UserQLSchemaIn this example we've defined a custom GroupNameField that sorts suggestions for group names by popularity (no. of users in a group) instead of default alphabetical sorting.
Custom search lookup
DjangoQL base fields provide two basic methods that you can override to
substitute either search column, or search value, or both -
.get_lookup_name() and .get_lookup_value(value):
class UserDateJoinedYear(IntField):
name = 'date_joined_year'
def get_lookup_name(self):
return 'date_joined__year'
class UserQLSchema(DjangoQLSchema):
def get_fields(self, model):
fields = super(UserQLSchema, self).get_fields(model)
if model == User:
fields = [UserDateJoinedYear()] + fields
return fields
@admin.register(User)
class CustomUserAdmin(DjangoQLSearchMixin, UserAdmin):
djangoql_schema = UserQLSchemaIn this example we've defined custom date_joined_year search field for
users, and used built-in Django __year filter option in
.get_lookup_name() to filter by date year only. Similarly you can use
.get_lookup_value(value) hook to modify search value before it's used in
the filter.
Fully custom search lookup
.get_lookup_name() and .get_lookup_value(value) hooks can cover many
simple use cases, but sometimes they're not enough and you want fully custom
search logic. In such cases you can override main .get_lookup() method of
a field. Example below demonstrates User age search:
from djangoql.schema import DjangoQLSchema, IntField
class UserAgeField(IntField):
"""
Search by given number of full years
"""
model = User
name = 'age'
def get_lookup_name(self):
"""
We'll be doing comparisons vs. this model field
"""
return 'date_joined'
def get_lookup(self, path, operator, value):
"""
The lookup should support with all operators compatible with IntField
"""
if operator == 'in':
result = None
for year in value:
condition = self.get_lookup(path, '=', year)
result = condition if result is None else result | condition
return result
elif operator == 'not in':
result = None
for year in value:
condition = self.get_lookup(path, '!=', year)
result = condition if result is None else result & condition
return result
value = self.get_lookup_value(value)
search_field = '__'.join(path + [self.get_lookup_name()])
year_start = self.years_ago(value + 1)
year_end = self.years_ago(value)
if operator == '=':
return (
Q(**{'%s__gt' % search_field: year_start}) &
Q(**{'%s__lte' % search_field: year_end})
)
elif operator == '!=':
return (
Q(**{'%s__lte' % search_field: year_start}) |
Q(**{'%s__gt' % search_field: year_end})
)
elif operator == '>':
return Q(**{'%s__lt' % search_field: year_start})
elif operator == '>=':
return Q(**{'%s__lte' % search_field: year_end})
elif operator == '<':
return Q(**{'%s__gt' % search_field: year_end})
elif operator == '<=':
return Q(**{'%s__gte' % search_field: year_start})
def years_ago(self, n):
timestamp = now()
try:
return timestamp.replace(year=timestamp.year - n)
except ValueError:
# February 29
return timestamp.replace(month=2, day=28, year=timestamp.year - n)
class UserQLSchema(DjangoQLSchema):
def get_fields(self, model):
fields = super(UserQLSchema, self).get_fields(model)
if model == User:
fields = [UserAgeField()] + fields
return fields
@admin.register(User)
class CustomUserAdmin(DjangoQLSearchMixin, UserAdmin):
djangoql_schema = UserQLSchemaSure. You can add DjangoQL search functionality to any Django model using
DjangoQLQuerySet:
from django.db import models
from djangoql.queryset import DjangoQLQuerySet
class Book(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=255)
author = models.ForeignKey('auth.User')
objects = DjangoQLQuerySet.as_manager()With the example above you can perform search like this:
qs = Book.objects.djangoql(
'name ~ "war" and author.last_name = "Tolstoy"'
)It returns a normal queryset, so you can extend it and reuse if necessary. The following code works fine:
print(qs.count())Alternatively you can add DjangoQL search to any existing queryset, even if it's not an instance of DjangoQLQuerySet:
from django.contrib.auth.models import User
from djangoql.queryset import apply_search
qs = User.objects.all()
qs = apply_search(qs, 'groups = None')
print(qs.exists())Schemas can be specified either as a queryset option, or passed
to .djangoql() queryset method directly:
class BookQuerySet(DjangoQLQuerySet):
djangoql_schema = BookSchema
class Book(models.Model):
...
objects = BookQuerySet.as_manager()
# Now, Book.objects.djangoql() will use BookSchema by default:
Book.objects.djangoql('name ~ "Peace") # uses BookSchema
# Overriding default queryset schema with AnotherSchema:
Book.objects.djangoql('name ~ "Peace", schema=AnotherSchema)You can also provide schema as an option for apply_search()
qs = User.objects.all()
qs = apply_search(qs, 'groups = None', schema=CustomSchema)Completion widget is not tightly coupled to Django admin, so you can easily use it outside of admin if you want. Here is an example:
Template code, completion_demo.html:
{% load static %}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>DjangoQL completion demo</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="{% static 'djangoql/css/completion.css' %}" />
<script src="{% static 'djangoql/js/lib/lexer.js' %}"></script>
<script src="{% static 'djangoql/js/completion.js' %}"></script>
</head>
<body>
<form action="" method="get">
<p style="color: red">{{ error }}</p>
<textarea name="q" cols="40" rows="1" autofocus>{{ q }}</textarea>
</form>
<ul>
{% for item in search_results %}
<li>{{ item }}</li>
{% endfor %}
</ul>
<script>
DjangoQL.DOMReady(function () {
DjangoQL.init({
// either JS object with a result of DjangoQLSchema(MyModel).as_dict(),
// or an URL from which this information could be loaded asynchronously
introspections: {{ introspections|safe }},
// css selector for query input. It should be a textarea
selector: 'textarea[name=q]',
// optional, you can provide URL for Syntax Help link here.
// If not specified, Syntax Help link will be hidden.
syntaxHelp: null,
// optional, enable textarea auto-resize feature. If enabled,
// textarea will automatically grow its height when entered text
// doesn't fit, and shrink back when text is removed. The purpose
// of this is to see full search query without scrolling, could be
// helpful for really long queries.
autoResize: true
});
});
</script>
</body>
</html>And in your views.py:
import json
from django.contrib.auth.models import Group, User
from django.shortcuts import render_to_response
from django.views.decorators.http import require_GET
from djangoql.exceptions import DjangoQLError
from djangoql.queryset import apply_search
from djangoql.schema import DjangoQLSchema
class UserQLSchema(DjangoQLSchema):
include = (User, Group)
@require_GET
def completion_demo(request):
q = request.GET.get('q', '')
error = ''
query = User.objects.all().order_by('username')
if q:
try:
query = apply_search(query, q, schema=UserQLSchema)
except DjangoQLError as e:
query = query.none()
error = str(e)
return render_to_response('completion_demo.html', {
'q': q,
'error': error,
'search_results': query,
'introspections': json.dumps(UserQLSchema(query.model).as_dict()),
})MIT