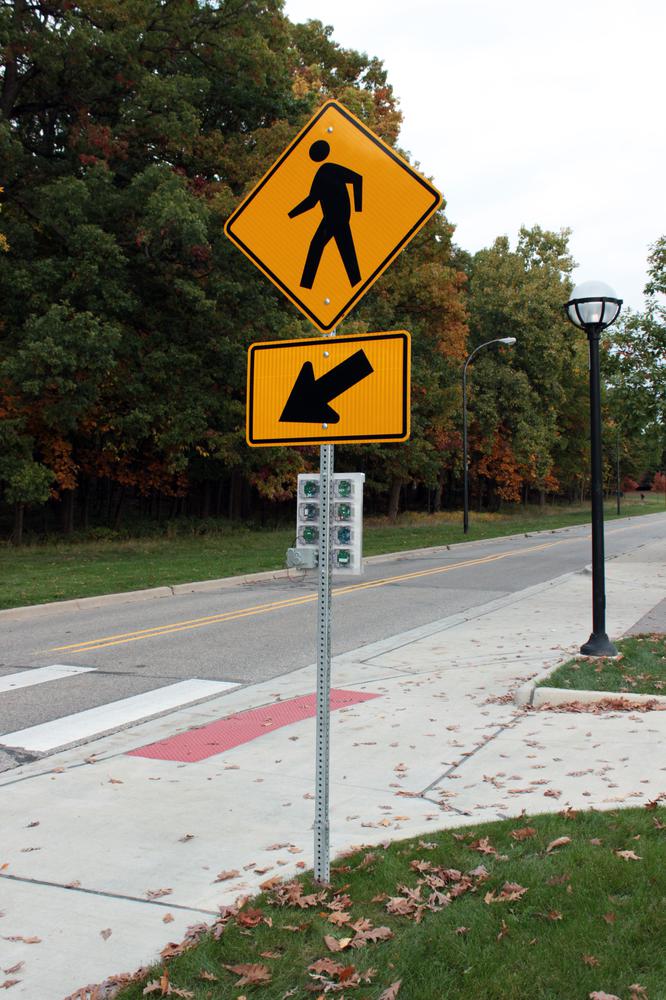
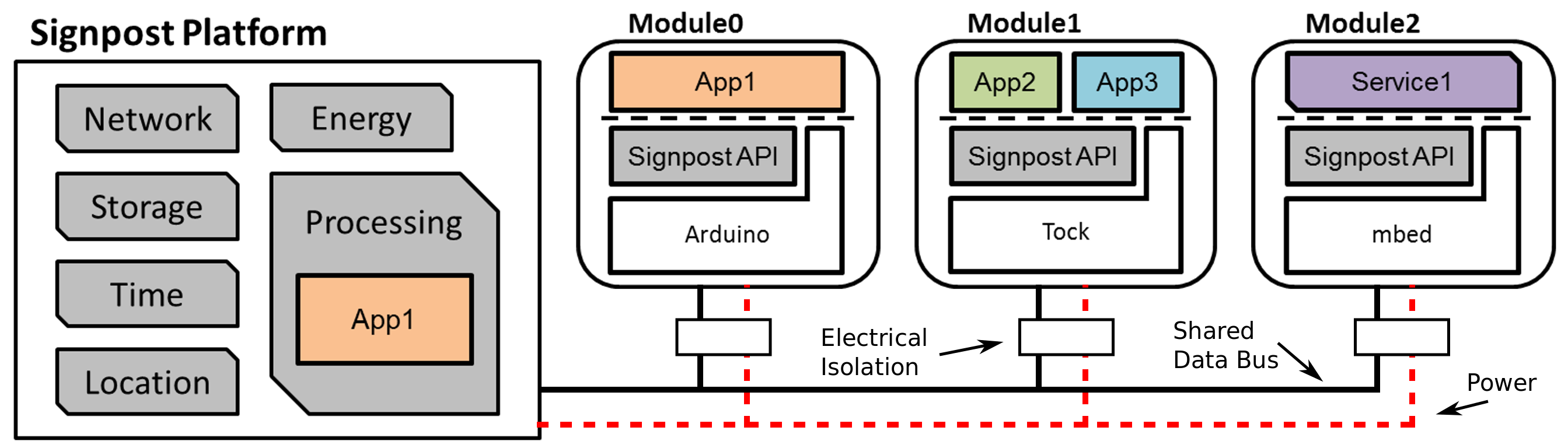
The Signpost project is a modular city-scale sensing platform that is designed to be installed on existing signposts. It is powered through solar energy harvesting, and provides six slots for generic sensing tasks. Modules have access to a set of shared platform resources including power, communication, gps-based location and time, storage, and higher-performance computation, and they use a Signpost-specific software API that enables not only use of these resources, but also supports the development of inter-module applications.
The project is driven by several core applications, but also strives to be an upgradeable and adaptable platform that supports new applications for scientists and cities. Modules can be added and removed from the platform after deployment without disassembling the installed Signpost, reprogramming the Signpost, or interrupting the other functions of the Signpost. Additionally, by providing APIs to modules that support common operations, developing and deploying a sensing application in a city is significantly streamlined. A focus of this project is ensuring that domain scientists and researchers interested in city-scale applications can effectively leverage this platform to accelerate their projects.
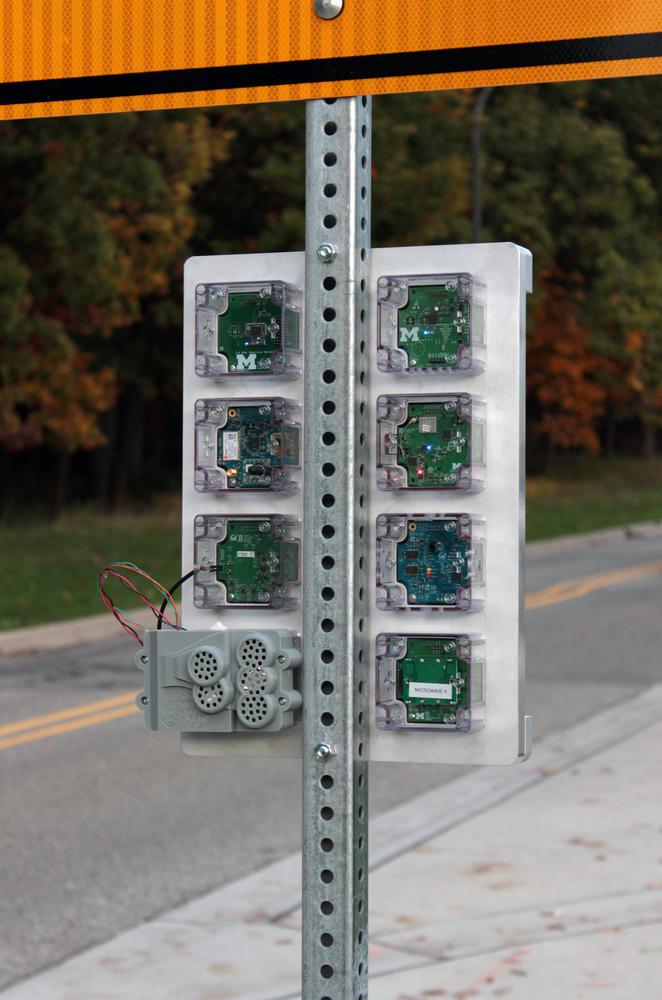
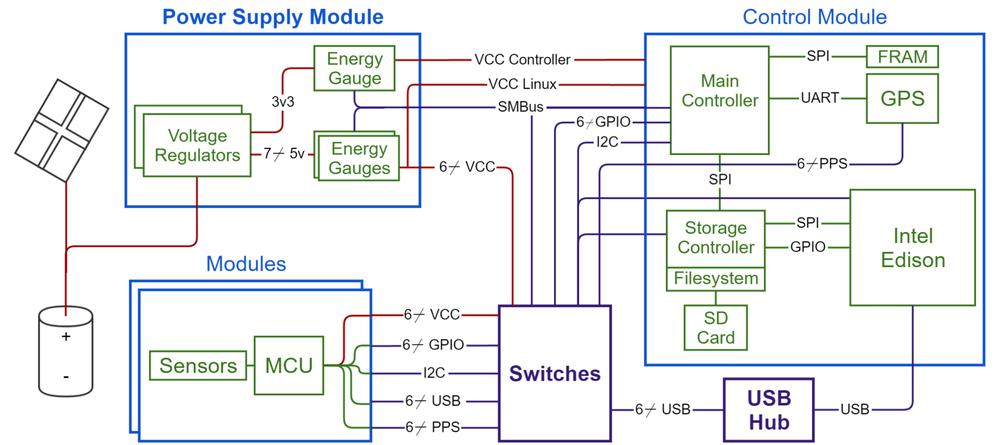
Each Signpost platform includes a power supply that also meters energy usage, a controller that provides storage and computation and manages the operation of the Signpost, and several module slots that support extensible sensor modules for city-scale sensing applications. All modules are connected via an I2C bus, and core system features (e.g. per-module energy metering) are on a SMBus network. For higher bandwidth communication on the Signpost, each module is also attached to a USB 2.0 host.
Each module can be individually disconnected from the USB host and/or the I2C bus, as well as entirely powered off.
Signpost sensor modules access platform resources through the Signpost API, which is a library that sits between the user's applications and the Signpost I2C bus. The API is easily ported, only requiring I2C master/slave, GPIO, and timers. It currently is ported Tock and ARM MBed-OS, with a port coming soon for Arduino. Please see the Signpost API documentation.
Signposts are currently being deployed on campus at UC Berkeley. We have 5 Signposts deployed and more than 20 built and awaiting deployment approval. On these signposts we have modules sensing audio amplitude on seven spectrum bands, ambient environmental markers including temperature, pressure, and humidity, RF Spectrum monitoring from 15-2700 MHz, and a microwave-radar based motion sensor. We are working to build applications such as distributed traffic monitoring on the deployed platforms.
Signpost development kits have been designed to facilitate sensor module and software development without requiring a full signpost platform. The development kits have the ability to fully emulate a signpost including energy metering and a Signpost radio module.
We are working to release version 1.0 of the Signpost Software API.
There are several ways to get involved with the Signpost Project! These include building and deploying full signpost platforms, deploying new sensor modules on our existing platforms, or deploying new applications on existing sensor modules. If you would like to deploy city-scale sensing applications using Signpost, please email signpost-admin@eecs.berkeley.edu.
Below are getting started guides for the Signpost platform.
Developing the Signpost platform is an ongoing effort with several primary goals:
- Designing a programming model for running applications across a network of Signposts. This should truly simplify creating interesting and useful applications, and not discourage development by imposing unnecessary hurdles.
- Creating a HW/SW test framework for accelerating module development.
- Deploying several driving applications on the existing signpost deployment.
- Collaborating with other researchers to serve as a foundation for city-scale sensing and wireless research.
- April 2018: We are presenting the signpost paper and an associated demo at IPSN 2018 in Porto, Portugal.
- February 2018: The signpost paper is released on the arXiv.
- January 2018: Signpost accepted to IPSN 2018!
- November 2017: Signpost demo at Sensys 2017!
- Fall 2017: 20 Signposts were built and deployed for the TerraSwarm Annual Review! 5 of these are still deployed on UC Berkeley's campus, and we are awaiting approval to deploy the remaining 15 signposts. We successfully collaborated with researchers from UIUC and UC San Diego to demonstrate audio event detection on Signposts and high-fidelity data backhaul to a drone deployed upon event detection. Check out the video.
- August 2017: Signpost presentation at the Intel Secure Internet of Things Retreat. A Signpost was transported and successfully deployed for the 48 hours of the retreat, becoming operational in less that five minutes.
- Summer 2017: The first Signposts are being deployed on UC Berkeley's campus!
- Winter 2017: Signpost v0.2 released for the TerraSwarm Signpost Workshop. This workshop featured the release of the Debug Backplane, initial API implementations for signpost modules, and tutorials for getting started with the Signpost platform.
- Fall 2016: Signpost v0.1 presented at TerraSwarm Annual Review. The demo included six modules (ambient conditions, 2.4 GHz RF sensing, LoRa/BLE radios, ambient audio level, microwave radar, and air quality sensing from UCSD), data communication over LoRa to a gateway, and a real-time UI.
- Summer 2016: Discussions on physical design yield a prototype enclosure and module form factor.
City-scale sensing platforms are a growing area of research with several emerging approaches:
- Chicago's Array of Things
- NYC's SONYC
We see Signpost as one part of the city-scale sensing ecosystem, and we hope to eventually deploy dynamic applications that can be distributed across high granularity energy-harvesting nodes (Signposts) and powered nodes such as Array of Things. Hopefully applications such as SONYC can lower the cost of deployment by running on Signpost platforms.
Licensed under either of
- Apache License, Version 2.0 (LICENSE-APACHE or http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0)
- MIT license (LICENSE-MIT or http://opensource.org/licenses/MIT)
at your option.
Unless you explicitly state otherwise, any contribution intentionally submitted for inclusion in the work by you, as defined in the Apache-2.0 license, shall be dual licensed as above, without any additional terms or conditions.