Notes on design patterns for future reference.
Note that there are people criticising design patterns as a work-around to hide the defects of the language.
Personally feel the patterns can be grouped as:
- Modify by inheritance
- Factory Method - creator method that can be modified by subclassing
- Template - single branch of inheritance
- Bridge - two separate branches of inheritance
- Repurposing by wrapping
- Middle man
- Object(s) in object
- Object to be passed around and acted upon
- Object that lends functionality to others at run time
- Decorator - accept others to lend functionality
- Abstract Factory - accepted by others to lend object creation functionality
- Strategy - accepted by others to lend functionality
- visitor - accepted by others to lend functionality
- Object that references the next object in a chain-like fashion
- Chain of responsibility - sequentially invoke the next object in chain
- Interpreter - sequentially evaluates a message
- Others
Gist:
- An object creation method that resides in its caller
- Whereas abstract factory is an object with potentially many factory methods and is separate from the caller object
- You can pass a different abstract factory object to the caller to use a different set of factory methods but you can only subclass the caller to change its own factory method
Use cases:
- When you want to encapsulate object creation to a method
Gist:
- An object with potentially many factory methods
- Lends itself to the caller to produce required object
Use cases:
- When you want the flexibility of producing different products at run time
Gist:
- Builds a complex object for someone else.
Use cases:
- When instantiating an object involves assembling multiple components dynamically
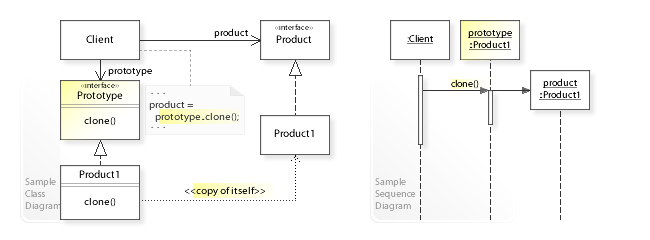
Gist:
- An object that can be cloned to create new object
Use cases:
- When you want to avoid repeatedly defining the same object structure in factory method
Gist:
- Static class to get one and only one instance.
- Only the static class can instantiate and destruct of the instance.
- One of the authors suggested to remove this pattern
Use cases:
- When you do not want to pass a popular object reference everywhere
Gist:
- Basically a wrapper to existing class to adapt to new interface (rewrite method names, parameters, return types ...)
- Can either be adaptor to an object (pass the object as reference to adaptor) or adaptor to a class (subclassing)
Use cases:
- New interface
- Alternative interfaces
Gist:
- Instead of subclassing abstract class into implementor class, let abstract class hold reference to abstract implementor so that both can be independently subclassed and implemented
- Decouples abstraction from implementation
- Abstraction (abstract class)
- defines the abstract interface
- maintains the Implementor reference
- RefinedAbstraction (normal class)
- extends the interface defined by Abstraction
- Implementor (interface)
- defines the interface for implementation classes
- ConcreteImplementor (normal class)
- implements the Implementor interface
- Abstraction (abstract class)
Use cases:
- When both the class and what it does can be modified very often
- No impact on existing abstract-implementation files when you need different class structure and implementation. Just subclass a different pair of abstract-implementation files!
Gist:
- The essence is to use a common interface for both component and composite
- Composite hold references to each component
- Composite distribute client call to each component methods
Use cases:
- Unify client-facing interface for composite and component operations so that you don't have to worry whether you are calling a component or composite
Gist:
- A way of extending object functionality
- In python this can be easily achieved by defining a function that receive other function and extend its functionality
- Structurally the same as chain of responsibility
- Subclass base class
- Receive base class object reference at constructor and save as private property
- Use base class object reference to call base class methods
- Extend base class functionality by add additional operation after calling base class method.
- Decorator can subclass decorator
Use cases:
- When you do not want to create multiple subclasses just to add new functionalities
- When you want to add functionalities at run time to some object instances but not all
Gist:
- A simplified API for complex underlying code structure
Gist:
- Reduce memory usage by sharing common state/data as much as possible
Gist
- A light-weight substitute to another more heavy-weight object
- The proxy and real object share the common interface, otherwise it's an adapter
- The proxy holds a private reference to the real object
- The proxy can add additional logic to control access to the real object
Use cases:
- When the real object is complex
- More often, when access to the real object needs to be controlled (some condition checks in proxy)
Gist:
- Structurally the same as decorator
- Except exactly one of the classes in the chain handles the request, unlike decorator, where all classes handle the request
- Decouples request sender and request handlers
Use cases:
- When you need a chain of receivers to either handle or pass to next receiver at run time
Gist:
- Resembles functional programming
- A command object contains all information needed to execute the command at a later time (can be queued)
- 3 objects are involved to execute an action:
- Invoker: issues a command, only know command interface, does not know the command receiver
- Command: has reference to the receiver and all the parameters needed for the receiver to perform the action
- Receiver: the target object which performs the actual action
Use cases:
- UI action, input replay, undo-redo, transaction, multi-page wizards
Gist:
- Kind of a special case of composite pattern
- A sequence of interpreters completes a task
Should require no explanation
Gist:
- A middle man that handles interaction between objects, like a single point of contact
- Objects calls mediator and pass themselves as parameter
- Mediator then handles the interaction for them
Use cases:
- Tidy up objects interaction
Gist:
- Somewhat a special case of mediator
- Object being observed register/unregister observers in a private list
- Object notifies registered observers when there is a state change
- Observers then inform other relevant objects about the state change event
- Decouples the observed object from the other objects
Use cases:
- Event listener, the middle man of message/event passing
- MVC pattern where observer is the controller
Gist:
- A simple class with setState and getState methods
- But unlike state pattern, it does not act on state, just a data keeper
Use cases:
- Redo/Undo
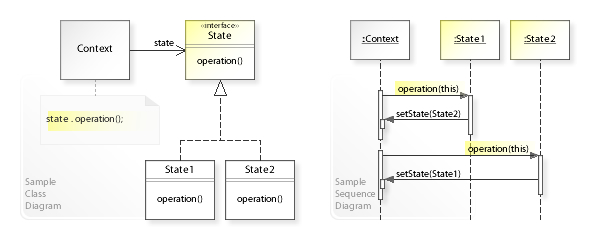
Gist:
- Structurally similar to strategy and visitor
- Context object accepts state object at run time and behave differently based on state
Use cases:
- When you want to change context object's behaviour at run time on different conditions
Gist:
- Structurally similar to state and visitor
- Context object accepts strategy object and calls strategy object to perform operation at run time
Use cases:
- When you want context object to receive and execute differet algorithms at run time
Gist:
- Structurally similar to state and Strategy
- Element object accepts visitor object and calls vistor object to perform operation on element at run time
Use cases:
- When you want element object to receive and execute differet algorithms at run time (very similar to strategy)
Gist:
- Essentially what you always do when you create super-subclass structure
- Provide abstract or shared methods in base class and allow subclass to implement or override the methods
Use cases:
- When you want objects to have shared and custom behaviours