文章首发:Spring Cloud OpenFeign入门和实战
Feign是一个声明式的Web Service客户端,是一种声明式、模板化的HTTP客户端。而OpenFeign是Spring Cloud 在Feign的基础上支持了Spring MVC的注解,如@RequesMapping等等。 OpenFeign的@FeignClient可以解析SpringMVC的@RequestMapping注解下的接口,并通过动态代理的方式产生实现类,实现类中做负载均衡并调用其他服务。 Feign可以把Rest的请求进行隐藏,伪装成类似SpringMVC的Controller一样。你不用再自己拼接url,拼接参数等等操作,一切都交给Feign去做。
- 可插拔的注解支持,包括Feign注解和JSX-RS注解
- 支持可插拔的HTTP编码器和解码器
- 支持Hystrix和它的Fallback
- 支持Ribbon的负载均衡
- 支持HTTP请求和响应的压缩。
此工程用于存放所有关于openfeign的示例。
pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.msr.better</groupId>
<artifactId>cloud-openfeign-practice</artifactId>
<version>1.0</version>
<packaging>pom</packaging>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.2.3.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
<spring.cloud-version>Hoxton.SR3</spring.cloud-version>
</properties>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring.cloud-version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>pom.xml
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>配置文件
application.xml
server:
port: 8010
spring:
application:
name: openfeign-hello
# 日志
logging:
level:
com.msr.better.feign.service.HelloFeignService: debug
配置类
@Configuration
public class HelloFeignServiceConfig {
/**
* Logger.Level 的具体级别如下:
* NONE:不记录任何信息
* BASIC:仅记录请求方法、URL以及响应状态码和执行时间
* HEADERS:除了记录 BASIC级别的信息外,还会记录请求和响应的头信息
* FULL:记录所有请求与响应的明细,包括头信息、请求体、元数据
*/
@Bean
Logger.Level feignLoggerLevel() {
return Logger.Level.FULL;
}
}serivce
@FeignClient(name = "github-client", url = "https://api.github.com", configuration = HelloFeignServiceConfig.class)
public interface HelloFeignService {
/**
* content:
* {
* "message":"Validation Failed",
* "errors":[{"resource":"Search","field":"q","code":"missing"}],
* "documentation_url":"https://developer.github.com/v3/search"
* }
*
* @param queryStr
* @return
*/
@GetMapping(value = "/search/repositories")
String searchRepo(@RequestParam("q") String queryStr);
}在上面的HelloFeignService中通过@FeignClient注解手动指定了该接口要访问的URL(https://api.github.com),调用searchGithubRepoByStr方法时,最终会发起GET请求https://api.github.com/search/repositories?q=输入的参数。
controller
@RestController
public class HelloFeignController {
@Autowired
private HelloFeignService helloFeignService;
@GetMapping(value = "/search/github")
public String searchGithubRepoByStr(@RequestParam("searchStr") String searchStr) {
return helloFeignService.searchRepo(searchStr);
}
}启动类
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableFeignClients
public class OpenFeignHelloApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(OpenFeignHelloApplication.class, args);
}
}@EnableFeignClients包扫描时,扫描所有@FeignClient。
运行启动类之后,在浏览器或者PostMan之类的工具访问http://localhost:8010/search/github?searchStr=spring-cloud
- 添加@EnableFeignClients注解开启对@FeignClient注解的扫描加载处理。根据Feign Client的开发规范,定义接口并添加@FeiginClient注解
- 当程序启动之后,会进行包扫描,扫描所有@FeignClient注解的接口,并将这些信息注入到IOC容器中。当定义的Feign接口被调用时,通过JDK的代理的方式生成具体的RequestTemplate。Feign会为每个接口方法创建一个RequestTemplate对象。该对象封装了HTTP请求需要的所有信息,例如请求参数名、请求方法等信息。
- 然后由RequestTemplate生成Request,把Request交给Client去处理,这里的Client可以是JDK原生的URLConnection、HttpClient或Okhttp。最后Client被封装到LoadBalanceClient类,看这个类的名字既可以知道是结合Ribbon负载均衡发起服务之间的调用,因为在OpenFeign中默认是已经整合了Ribbon了。
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface FeignClient {...}从FeignClient的注解可以看得出,ElementType.TYPE说明FeignClient的作用目标是接口。其常用的属性如下:
- name:执行FeignClient的名称,如果项目中使用Ribbon,name属性会作为微服务的名称,用作服务发现。
- url:url一般用于调试,可以手动指定@FeignClient调用的地址
- decode404:当发生404错误时,如果该字段为true,会调用decoder进行解码,否则抛出FeignException。
- configuration:Feigin配置类,可自定义Feign的Encode,Decode,LogLevel,Contract。
- fallback:定义容错的类,当远程调用的接口失败或者超时的时候,会调用对应接口的容错罗杰,fallback执行的类必须实现@FeignClient标记的接口。在OpenFeign的依赖中可以发现,集成Hystrix。
- fallbackFactory:工厂类,用于生成fallback类实例,通过此属性可以实现每个接口通用的容错逻辑,以达到减少重复的代码。
- path:定义当前FeignClient的统一前缀。
OpenFeign支持对请求和响应进行GZIP压缩,以此来提供通信效率。只需在配置文件中配置即可,比较简单。
server:
port: 8011
spring:
application:
name: openfeign-gzip
logging:
level:
com.msr.better.feign.service.HelloFeignService: debug
feign:
# 压缩配置
compression:
request:
enabled: true
# 配置压缩支持的MIME TYPE
mime-types: text/xml,application/xml,application/json
min-request-size: 2048 # 配置压缩数据大小的下限
response:
enabled: true # 配置响应GZIP压缩
等价的properties配置
feign.compression.request.enabled=true
# 配置压缩支持的MIME TYPE
feign.compression.request.mime-types=text/xml,application/xml,application/json
# 配置压缩数据大小的下限
feign.compression.request.min-request-size=2048
# 配置响应GZIP压缩
feign.compression.response.enabled=true@FeignClientde的配置信息可以通过配置文件的方式来配置
server:
port: 8011
spring:
application:
name: openfeign-gzip
logging:
level:
com.msr.better.feign.service.HelloFeignService: debug
feign:
# 压缩配置
compression:
request:
enabled: true
# 配置压缩支持的MIME TYPE
mime-types: text/xml,application/xml,application/json
min-request-size: 2048 # 配置压缩数据大小的下限
response:
enabled: true # 配置响应GZIP压缩
client:
config:
# 需要配置的FeignName
github-client:
# 连接超时时间
connectTimout: 5000
# 读超时时间
readTimeut: 5000
# Feign的日志级别
loggerLevel: full
# Feign的错误解码器
errorDecode: com.example.SimpleErrorDecoder
# 设置重试
retryer: com.example.SimpleRetryer
# 拦截前
requestInterceptors:
- com.example.FirstInterceptor
- com.example.SecondInterceptor
decode404: false
# Feign的编码器
encoder: com.example.SimpleEncoder
# Feign的解码器
decoder: com.example.SimpleDecoder
# Feign的contract配置
contract: com.example.SimpleContract在@EnableFeignClients注解上有一个defaultConfiguration属性,可以将默认设置写成一个配置类,例如这个类叫做DefaultFeignClientConfiguration。
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableFeignClients(defaultConfiguration = DefaultFeignClientConfiguration.class)
public class FeignClientConfigApplication{
SpringApplication.run(FeignClientConfigApplication.class, args);
}同时也可以在配置文件中配置
feign:
client:
config:
default:
# 连接超时时间
connectTimout: 5000
# 读超时时间
readTimeut: 5000
# Feign的日志级别
loggerLevel: full
...但是如果以上两种方式(在配置文件和在注解中配置FeignClient的全局配置),最后配置文件会覆盖注解上执行配置类的方式。但是可以在配置文件中添加feign.client.default-to-properties=false来改变Feigin配置的优先级。
其实在上面的就已经是配置了FeignClient的日志了。Feign为每一个Feign都提供了一个fegin.Logger实例。可以在配置中开启日志输出,开启的步骤也很简单。
第一步:在配置文件中配置日志输出
logging:
level:
# 指定那个FeignClient接口的请求需要输出日志,以及日志级别
com.msr.better.feign.service.HelloFeignService: debug第二步:通过Java代码的方式在主程序入口配置日志Bean
@Bean
Logger.Level feignLoggerLevel() {
return Logger.Level.FULL;
}又或者通过配置类配置,并在@FeignClient注解中执行改配置类。
@Configuration
public class HelloFeignServiceConfig {
/**
* Logger.Level 的具体级别如下:
* NONE:不记录任何信息
* BASIC:仅记录请求方法、URL以及响应状态码和执行时间
* HEADERS:除了记录 BASIC级别的信息外,还会记录请求和响应的头信息
* FULL:记录所有请求与响应的明细,包括头信息、请求体、元数据
*/
@Bean
Logger.Level feignLoggerLevel() {
return Logger.Level.FULL;
}
}Feign的调用分为两层,Ribbon的调用和Hystrix的调用。但是高版本的Hystrix默认是关闭的。一般出现想这样的异常:Read timed out executing POST http://***,是由Ribbon引起,这样可以适当得调大一下Ribbon的超时时间
ribbon:
ConnectTimeout: 2000
ReadTimeout: 5000HystrixRuntimeException: XXX timed -out and no fallback available .这就是Hystrix的超时报错
feign:
hystrix:
enabled: true
# 设置hystrix超时时间
hystrix:
shareSecurityContext: true
command:
default:
circuitBreaker:
sleepWindowinMilliseconds: 10000
forceClosed: true
execution:
isolation:
thread:
timeoutinMilliseconds: 10000Feign默认是使用JDK原生的URLConnection发送HTTP请求,没有连接池,但是对每个地址会保持一个长连接,就是利用HTTP的persistence connection.。这样可以使用其他优秀的Client去替换。这样可以设置连接池,超时时间等对服务之间的调用调优。下面介绍使用Http Client和Okhttp替换Feign默认的Client。步骤也很简单。
pom.xml
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring Cloud OpenFeign的Starter的依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 使用Apache HttpClient替换Feign原生httpclient -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.httpcomponents</groupId>
<artifactId>httpclient</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.github.openfeign</groupId>
<artifactId>feign-httpclient</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>application.yml
server:
port: 8010
spring:
application:
name: openfeign-httpclient
feign:
httpclient:
enabled: true关于Http Client的一些配置也是可以在配置文件中配置的
在org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.clientconfig.HttpClientFeignConfiguration中是关于HttpClient的配置:
@Configuration(
proxyBeanMethods = false
)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean({CloseableHttpClient.class})
public class HttpClientFeignConfiguration {
private final Timer connectionManagerTimer = new Timer("FeignApacheHttpClientConfiguration.connectionManagerTimer", true);
private CloseableHttpClient httpClient;
@Autowired(
required = false
)
private RegistryBuilder registryBuilder;
public HttpClientFeignConfiguration() {
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean({HttpClientConnectionManager.class})
public HttpClientConnectionManager connectionManager(ApacheHttpClientConnectionManagerFactory connectionManagerFactory, FeignHttpClientProperties httpClientProperties) {
final HttpClientConnectionManager connectionManager = connectionManagerFactory.newConnectionManager(httpClientProperties.isDisableSslValidation(), httpClientProperties.getMaxConnections(), httpClientProperties.getMaxConnectionsPerRoute(), httpClientProperties.getTimeToLive(), httpClientProperties.getTimeToLiveUnit(), this.registryBuilder);
this.connectionManagerTimer.schedule(new TimerTask() {
public void run() {
connectionManager.closeExpiredConnections();
}
}, 30000L, (long)httpClientProperties.getConnectionTimerRepeat());
return connectionManager;
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnProperty(
value = {"feign.compression.response.enabled"},
havingValue = "true"
)
public CloseableHttpClient customHttpClient(HttpClientConnectionManager httpClientConnectionManager, FeignHttpClientProperties httpClientProperties) {
HttpClientBuilder builder = HttpClientBuilder.create().disableCookieManagement().useSystemProperties();
this.httpClient = this.createClient(builder, httpClientConnectionManager, httpClientProperties);
return this.httpClient;
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnProperty(
value = {"feign.compression.response.enabled"},
havingValue = "false",
matchIfMissing = true
)
public CloseableHttpClient httpClient(ApacheHttpClientFactory httpClientFactory, HttpClientConnectionManager httpClientConnectionManager, FeignHttpClientProperties httpClientProperties) {
this.httpClient = this.createClient(httpClientFactory.createBuilder(), httpClientConnectionManager, httpClientProperties);
return this.httpClient;
}
private CloseableHttpClient createClient(HttpClientBuilder builder, HttpClientConnectionManager httpClientConnectionManager, FeignHttpClientProperties httpClientProperties) {
RequestConfig defaultRequestConfig = RequestConfig.custom().setConnectTimeout(httpClientProperties.getConnectionTimeout()).setRedirectsEnabled(httpClientProperties.isFollowRedirects()).build();
CloseableHttpClient httpClient = builder.setDefaultRequestConfig(defaultRequestConfig).setConnectionManager(httpClientConnectionManager).build();
return httpClient;
}
@PreDestroy
public void destroy() throws Exception {
this.connectionManagerTimer.cancel();
if (this.httpClient != null) {
this.httpClient.close();
}
}
}很明显当没有CloseableHttpClient这个bean的时候,就是会由这个类来生成Http Client的默认配置。所以说对于HttpClient的自定义配置可以通过自己注入CloseableHttpClient。还有HttpClientConnectionManager管理连接的bean。其实OpenFeign对HttpClient的支持很好,因为它的一些属性可以在配置文件中配置。
其实和Http Client一样的配置,也是在配置文件中开启
pom.xml
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring Cloud OpenFeign的Starter的依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.github.openfeign</groupId>
<artifactId>feign-okhttp</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>application.yml
server:
port: 8011
spring:
application:
name: openfeign-okhttp
feign:
okhttp:
enabled: true
# 日志
logging:
level:
com.msr.better.feign.service.HelloFeignService: debug这样开启之后,Client就被替换了。同理在org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.clientconfig包下,也有一个关于Okhttp的配置类。
@Configuration(
proxyBeanMethods = false
)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean({OkHttpClient.class})
public class OkHttpFeignConfiguration {
private OkHttpClient okHttpClient;
public OkHttpFeignConfiguration() {
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean({ConnectionPool.class})
public ConnectionPool httpClientConnectionPool(FeignHttpClientProperties httpClientProperties, OkHttpClientConnectionPoolFactory connectionPoolFactory) {
Integer maxTotalConnections = httpClientProperties.getMaxConnections();
Long timeToLive = httpClientProperties.getTimeToLive();
TimeUnit ttlUnit = httpClientProperties.getTimeToLiveUnit();
return connectionPoolFactory.create(maxTotalConnections, timeToLive, ttlUnit);
}
@Bean
public OkHttpClient client(OkHttpClientFactory httpClientFactory, ConnectionPool connectionPool, FeignHttpClientProperties httpClientProperties) {
Boolean followRedirects = httpClientProperties.isFollowRedirects();
Integer connectTimeout = httpClientProperties.getConnectionTimeout();
this.okHttpClient = httpClientFactory.createBuilder(httpClientProperties.isDisableSslValidation()).connectTimeout((long)connectTimeout, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS).followRedirects(followRedirects).connectionPool(connectionPool).build();
return this.okHttpClient;
}
@PreDestroy
public void destroy() {
if (this.okHttpClient != null) {
this.okHttpClient.dispatcher().executorService().shutdown();
this.okHttpClient.connectionPool().evictAll();
}
}
}很明显OkHttpClient是核心功能执行的类。因为OpenFeign中有一个类FeignHttpClientProperties,有了这个类关于HttpClient的属性就可以在配置文件中设置了。但是Okhttp没有这一个类似的类,所以一般可以自己注入一个OkHttpClient去设置这些属性
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass(Feign.class)
@AutoConfigureBefore(FeignAutoConfiguration.class)
public class OkHttpConfig {
@Bean
public okhttp3.OkHttpClient okHttpClient() {
return new okhttp3.OkHttpClient.Builder()
//设置连接超时
.connectTimeout(60, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
//设置读超时
.readTimeout(60, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
//设置写超时
.writeTimeout(60, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
//是否自动重连
.retryOnConnectionFailure(true)
.connectionPool(new ConnectionPool())
//构建OkHttpClient对象
.build();
}
}关于自定义OkHttpClient的配置,可以参考OpenFeign里OkHttpFeignConfiguration的配置,例如ConnectionPool这个bean。
在使用OpenFeign实现服务之间的调用时,很多时候是要传递多个参数。
Eureka Server注册中心
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-server</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- springboot web -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<!--不用Tomcat,使用undertow -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-undertow</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.undertow</groupId>
<artifactId>undertow-servlet</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>配置文件application.yml
server:
port: 8761
eureka:
instance:
hostname: localhost
server :
enable-self-preservation: false
client:
registerWithEureka: false
fetchRegistry: false
serviceUrl:
defaultZone: http://${eureka.instance.hostname}:${server.port}/eureka/启动类
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaServer
public class EurekaApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(EurekaApplication.class, args);
}
}服务提提供者
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>配置文件application.yml
server:
port: 8012
spring:
application:
name: openfeign-provider
eureka:
client:
serviceUrl:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eureka/
#eureka.instance.prefer-ip-address 表示将自己的IP注册到Eureka Server上,
#如果不配置,会将当前服务提供者所在的主机名注册到Eureka Server上。
instance:
prefer-ip-address: true实体类和控制器
public class Order {
private Long id;
private String name;
private int age;
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}@RestController
@RequestMapping("/order")
public class OrderController {
@GetMapping(value = "/add")
public String addUser(Order order, HttpServletRequest request) {
String token = request.getHeader("oauthToken");
return "hello," + order.getName();
}
@PostMapping(value = "/update")
public String updateUser(@RequestBody Order order) {
return "hello," + order.getName();
}
}启动类
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient
public class ProviderApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ProviderApplication.class, args);
}
}消费者服务
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 使用Apache HttpClient替换Feign原生httpclient -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.httpcomponents</groupId>
<artifactId>httpclient</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.github.openfeign</groupId>
<artifactId>feign-httpclient</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>配置文件application.yml
server:
port: 8011
spring:
application:
name: openfeign-consumer
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eureka
feign:
httpclient:
enabled: true实体类
package com.msr.better.feign.model;
public class Order {
private Long id;
private String name;
private int nums;
// 此处省略了getter和setter
}FeignClient接口
@FeignClient("openfeign-provider")
public interface OrderApiService {
@GetMapping(value = "/order/add")
String addUser(@SpringQueryMap Order order);
@PostMapping(value = "/order/update")
String updateUser(@RequestBody Order order);
}此处的Client接口中对于GET请求传递实体类使用了注解@SpringQueryMap。OpenFeign@QueryMap批注支持将POJO用作GET参数映射。但是默认的OpenFeign QueryMap注释与Spring不兼容,因为它缺少value属性。
Spring Cloud OpenFeign提供了等效的@SpringQueryMap注释,该注释用于将POJO或Map参数注释为查询参数映射。
在一些资料中说什么OpenFeign的什么GET不能传递POJO,写了个拦截器把实体类转换了,估计是OpenFeign的版本低,在新的OpenFeign中是有了对QueryMap的支持了。
配置类
@Configuration
public class CoreAutoConfiguration {
@Autowired
private HttpClient httpClient;
@Bean
public HttpComponentsClientHttpRequestFactory httpComponentsClientHttpRequestFactory() {
HttpComponentsClientHttpRequestFactory factory = new HttpComponentsClientHttpRequestFactory();
factory.setHttpClient(httpClient);
factory.setReadTimeout(3000);
factory.setConnectTimeout(3000);
factory.setConnectionRequestTimeout(3000);
return factory;
}
/**
* {@link RestTemplate }的setRequestFactory方法支持HttpClient和Okhttp等Client
* 默认是使用{@link SimpleClientHttpRequestFactory } Http的请求是使用原生的URLConnection
*
* @return RestTemplate的bean
*/
@LoadBalanced
@Bean
public RestTemplate restTemplate() {
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
restTemplate.setRequestFactory(httpComponentsClientHttpRequestFactory());
return restTemplate;
}
}上面是替换了RestTemplate的Client。因为RestTemplate默认是使用URLConnection。这里是使用HttpClient替换了。
控制器
@RestController
@RequestMapping("api")
public class OrderController {
@Autowired
private OrderApiService orderApiService;
/**
* @param order
* @return
*/
@PostMapping("/get/pojo")
public String getPojo(@RequestBody Order order) {
return orderApiService.addUser(order);
}
@PostMapping("/post/pojo")
String postPojo(@RequestBody Order order){
return orderApiService.updateUser(order);
}
}最后就可以测试http://localhost:8011/get/pojo和http://localhost:8011/post/pojo了。
继续使用上一节创建的Eureka Server。然后创建一下两个模块用作文件上传。
想要实现文件上传功能,需要编写Encoder去实现文件上传。现在OpenFeign提供了子项目feign-form(https://github.com/OpenFeign/feign-form)
文件上传接口的提供者
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>配置文件application.yml
server:
port: 8012
spring:
application:
name: openfeign-file-server
eureka:
server:
enableSelfPreservation: false
client:
serviceUrl:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eureka/
instance:
prefer-ip-address: true启动类
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient
public class UploadServerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(UploadServerApplication.class, args);
}
}上传接口
@RestController
public class FileController {
@PostMapping(value = "/uploadFile/server", consumes = MediaType.MULTIPART_FORM_DATA_VALUE)
public String fileUploadServer(MultipartFile file) {
// save file and return file address
return "http://localhost/" + file.getOriginalFilename();
}
}文件上传接口的调用者
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring Cloud OpenFeign的Starter的依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Feign文件上传依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.github.openfeign.form</groupId>
<artifactId>feign-form</artifactId>
<version>3.8.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.github.openfeign.form</groupId>
<artifactId>feign-form-spring</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>配置文件application.yml
server:
port: 8011
spring:
application:
name: openfeign-upload-client
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eureka启动类:
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient
@EnableFeignClients
public class UploadClientApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(UploadClientApplication.class, args);
}
}配置类
@Configuration
public class FeignMultipartSupportConfig {
@Bean
@Primary
@Scope("prototype")
public Encoder multipartFormEncoder() {
return new SpringFormEncoder();
}
}控制器
@RestController
@RequestMapping("file")
public class FeignUploadController {
@Autowired
private FileUploadApiService fileUploadApiService;
@PostMapping(value = "/upload", consumes = MediaType.MULTIPART_FORM_DATA_VALUE)
public String imageUpload(MultipartFile file) throws Exception {
return fileUploadApiService.fileUpload(file);
}
}FeignClient
@FeignClient(value = "openfeign-file-server", configuration = FeignMultipartSupportConfig.class)
public interface FileUploadApiService {
/***
* 1.produces,consumes必填
* 2.注意区分@RequestPart和RequestParam,不要将
* @RequestPart(value = "file") 写成@RequestParam(value = "file")
* @param file
* @return
*/
@PostMapping(value = "/uploadFile/server",
produces = {MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8_VALUE},
consumes = MediaType.MULTIPART_FORM_DATA_VALUE)
String fileUpload(@RequestPart(value = "file") MultipartFile file);
}- 先启动cloud-openfeign-eureka-server
- 后启动cloud-openfeign-fileupload-server和cloud-openfeign-fileupload-client
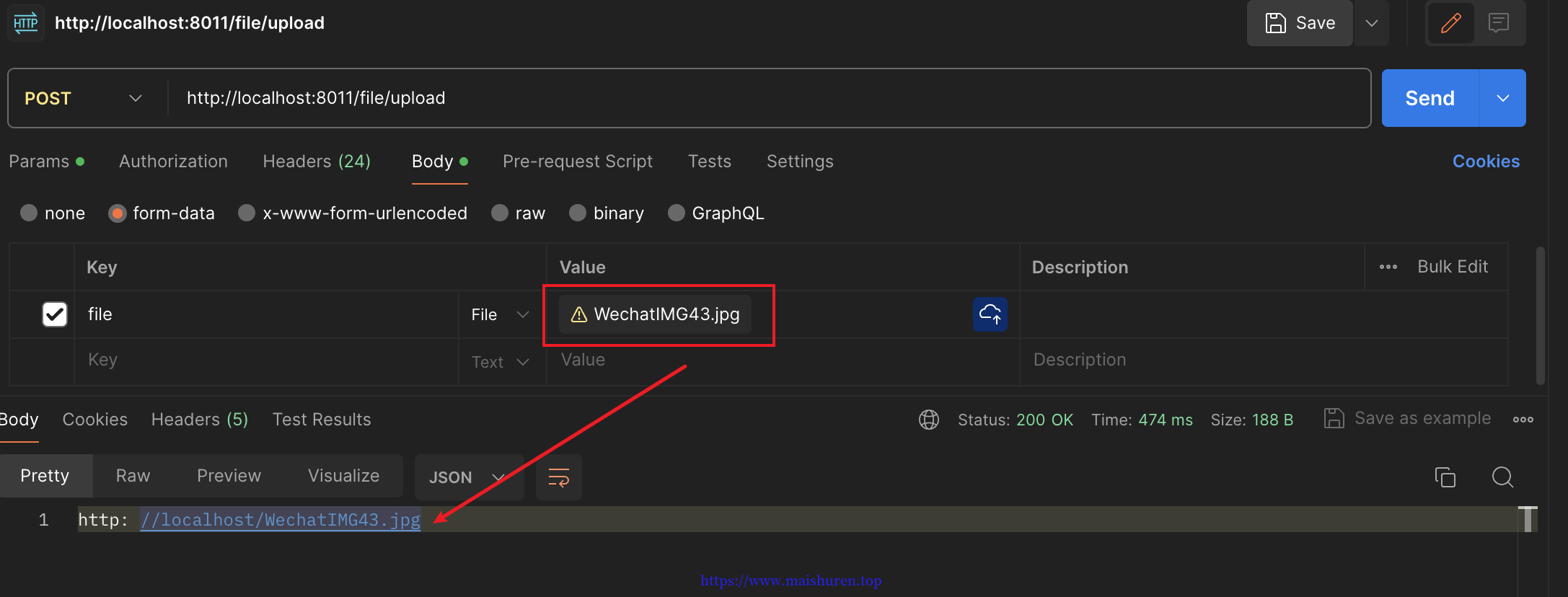
- 使用PostMan进行测试。最后成功返回文件的名字,文件成功的上传到server上了。如下图:
由于OpenFeign整合了Ribbon和Hystrix,可能会出现首次调用失败的问题。
主要原因是:Hystrix默认的超时时间是1秒,如果超过这个时间没有响应,就会进入fallback代码。由于Bean的装配和懒加载的机制,Feign首次请求都会比较慢。如此一来当响应时间大于1秒就会进入fallback而导致请求失败。解决方法:
-
将Hystrix的超时时间调大,此方法比较好
hystrix: command: default: execution: isolation: thread: timeoutInMillseconds: 5000 # 5秒
-
禁用Hystrix的超时时间
hystrix: command: default: execution: timout: enable: false
-
使用Feign的时候关闭Hystrix,这是不推荐的
feign: hystrix: enable: false
对于返回的是图片,一般都是字节数组。但是Contrller不能直接返回byte,所以被调用的API返回的类型应该使用Response。
使用上面的文件上传创建的模块中添加一个返回图片的接口。以生成一个二维码为例。
添加新的依赖,使用hutool快速生成二维码
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.hutool</groupId>
<artifactId>hutool-all</artifactId>
<version>5.6.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.zxing</groupId>
<artifactId>core</artifactId>
<version>3.3.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.github.openfeign</groupId>
<artifactId>feign-core</artifactId>
</dependency>controller的接口,这里仅简单的生成了一个二维码,二维码还可以添加更加多的信息。这里就不详细介绍,hutool的QrCodeUtil有很多方法,有兴趣的可以自行研究。
@GetMapping(value = "/qrcode")
public byte[] image() {
return generateQrCode();
}
/**
* 先简单的生成一个url的二维码,指向百度
* @return
*/
private byte[] generateQrCode() {
return QrCodeUtil.generatePng("https://www.baidu.cn/", 300, 300);
}添加新依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-io</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-io</artifactId>
<version>2.6</version>
</dependency>
feignclient添加新接口
@GetMapping("/qrcode")
Response getQrCode();controller的修改,对于要在前端页面显示图片,一般用的最多的是返回页面一个url,但是这都是存储好的图片,但是每次生成验证码和二维码这些,服务端可能并不会存储起来。所以并不能返回一个url地址,对于验证码用的返回前端Base64编码。二维码的话可以基于HttpServletResponse,produces返回字节流和Base64图片。
这里使用HttpServletResponse,添加方法:
@GetMapping("/qrcode")
public void getQrCode(HttpServletResponse response) {
Response res = fileUploadApiService.getQrCode();
try {
InputStream inputStream = res.body().asInputStream();
response.setContentType(MediaType.IMAGE_PNG_VALUE);
IOUtils.copy(inputStream,response.getOutputStream());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}浏览器访问:http://localhost:8011/file/qrcode,结果
正常的来说,系统都是有认证鉴权的功能,不管是JWT还是security,在外部请求到A服务时,是带有token过来的,但是此请求在A服务内部通过Feign调用B服务时,就会发生token的丢失。
解决方法也是不难,就是在使用Feign远程调用时,在请求头里携带一下token,一般token是放在请求头里面。
Feign提供的拦截器RequestInterceptor,这样可以拦截Feign的请求,在请求头里添加token。对于这部分代码,在cloud-openfeign-consumer和cloud-openfeign-provider上进行添加。
修改一下方法,便于展示结果
@PostMapping(value = "/update")
public String updateOrder(@RequestBody Order order, HttpServletRequest request) {
String token = request.getHeader("token");
return "hello," + order.getName() + " " + "haha!I get a token: " + token;
}添加拦截器实现feign.RequestInterceptor
@Component
public class FeignTokenInterceptor implements RequestInterceptor {
@Override
public void apply(RequestTemplate requestTemplate) {
if (null == getHttpServletRequest()) {
//此处可以记录一些日志
return;
}
//将获取Token对应的值往下面传
requestTemplate.header("token", getHeaders(getHttpServletRequest()).get("token"));
}
private HttpServletRequest getHttpServletRequest() {
try {
return ((ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes()).getRequest();
} catch (Exception e) {
return null;
}
}
/**
* Feign拦截器拦截请求获取Token对应的值
*
* @param request
* @return
*/
private Map<String, String> getHeaders(HttpServletRequest request) {
Map<String, String> map = new LinkedHashMap<>();
Enumeration<String> enumeration = request.getHeaderNames();
while (enumeration.hasMoreElements()) {
String key = enumeration.nextElement();
String value = request.getHeader(key);
map.put(key, value);
}
return map;
}
}最后启动服务就可以开始测试了,测试结果:
本文介绍了一些Feign的用法,后续如果有关于Feign新的东西将会新开文章述说。