MashMap implements a fast and approximate algorithm for computing local alignment boundaries between long DNA sequences. It can be useful for mapping genome assembly or long reads (PacBio/ONT) to reference genome(s). Given a minimum alignment length and an identity threshold for the desired local alignments, Mashmap computes alignment boundaries and identity estimates using k-mers. It does not compute the alignments explicitly, but rather estimates an unbiased k-mer based Jaccard similarity using a combination of minmers (a novel winnowing scheme) and MinHash. This is then converted to an estimate of sequence identity using the Mash distance. An appropriate k-mer sampling rate is automatically determined using the given minimum local alignment length and identity thresholds.
As an example, Mashmap can map a human genome assembly to the human reference genome in about one minute total execution time and < 4 GB memory using just 8 CPU threads, achieving more than an order of magnitude improvement in both runtime and memory over alternative methods. We describe the algorithms associated with Mashmap, and report on speed, scalability, and accuracy of the software in the publications listed below. Unlike traditional mappers, MashMap does not compute exact sequence alignments. In future, we plan to add an optional alignment support to generate base-to-base alignments.
- The automatic sampling rate has increased slightly relative to MashMap2, resulting in more accurate mappings and ANI prediction at the cost of more RAM. For a more dense sampling rate, users can provide the
--denseflag. - The default output file format is now PAF, but the MashMap2 output format can be obtained with the
--legacyflag. Theidtag in the PAF output corresponds to the predicted ANI. - More details of the MashMap3 changes can be found in the v3.0.1 changelog.
Follow INSTALL.txt to compile and install MashMap. We also provide dependency-free linux and OSX binaries for user convenience through the latest release.
-
Map set of query sequences against a reference genome:
mashmap -r reference.fna -q query.fa
The output is space-delimited with each line consisting of query name, length, 0-based start, end, strand, target name, length, start, end and mapping nucleotide identity.
-
Map set of query seqences against a list of reference genomes:
mashmap --rl referenceList.txt -q query.fa
File 'referenceList.txt' containing the list of reference genomes should contain path to the reference genomes, one per line.
For most of the use cases, default values should be appropriate. However, different parameters and their purpose can be checked using the help page mashmap -h. Important ones are mentioned below:
-
Identity threshold (
--perc_identity,--pi) : By default, it is set to 85, implying mappings with 85% or more identity should be reported. For example, it can be set to 80% to account for more noisy long-read datasets or 95% for mapping human genome assembly to human reference. -
Minimum segment length (
-s,--segLength) : Default is 5,000 bp. Sequences below this length are ignored. Mashmap provides guarantees on reporting local alignments of length twice this value. -
Filtering options (
-f,--filter_mode) : Mashmap implements a plane-sweep based algorithm to perform the alignment filtering. Similar to delta-filter in nucmer, different filtering options are provided that are suitable for long read or assembly mapping. Option-f mapis suitable for reporting the best mappings for long reads, whereas-f one-to-oneis suitable for reporting orthologous mappings among all computed assembly to genome mappings. -
Sketch size (
-J,--sketchSize) : This parameter sets the seed density of the winnowing scheme, gauranteeing that the minhash will be calculated from a sample ofsketchSizek-mers for each segment. It is set automatically based on--pibut can be manually set as well. -
Dense sketching (
--dense) : This flag will increase the seed density substantially, resulting in a density of roughly0.02 * (1 + (1 - pi) / .05)wherepiis theperc_identitythreshold. This leads to longer runtimes and higher RAM usage, but significantly more accurate estimates of ANI.
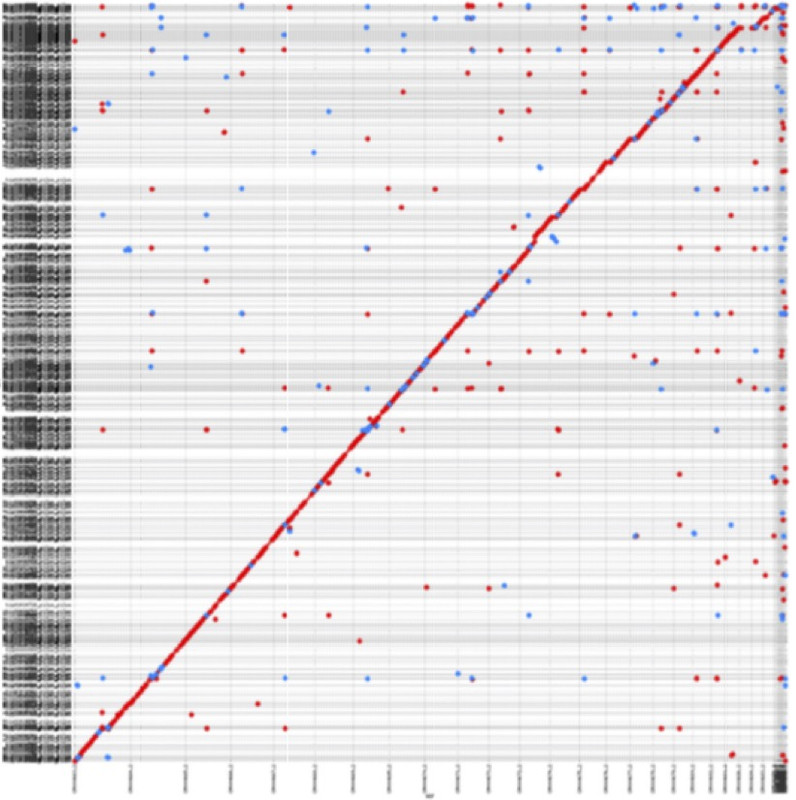
We provide a perl script for generating dot-plots to visualize mappings. It takes Mashmap's mapping output as its input. This script requires availability of gnuplot. Below is an example demonstrating mapping of canu NA12878 human genome assembly (y-axis) to hg38 reference (x-axis).
Use the latest release for a stable version.
-
Bryce Kille, Erik Garrison, Todd Treangen, and Adam M Phillippy "Minmers are a generalization of minimizers that enable unbiased local Jaccard estimation". bioRxiv (2023).
-
Chirag Jain, Sergey Koren, Alexander Dilthey, Adam M. Phillippy, and Srinivas Aluru. "A Fast Adaptive Algorithm for Computing Whole-Genome Homology Maps". Bioinformatics (ECCB issue), 2018.
-
Chirag Jain, Alexander Dilthey, Sergey Koren, Srinivas Aluru, and Adam M. Phillippy. "A fast approximate algorithm for mapping long reads to large reference databases." In International Conference on Research in Computational Molecular Biology, Springer, Cham, 2017.