This repository implements the Intersection over Union (IoU) metric from scratch using PyTorch. IoU is a crucial metric in object detection tasks, where it is used to evaluate the accuracy of predicted bounding boxes against ground truth bounding boxes.
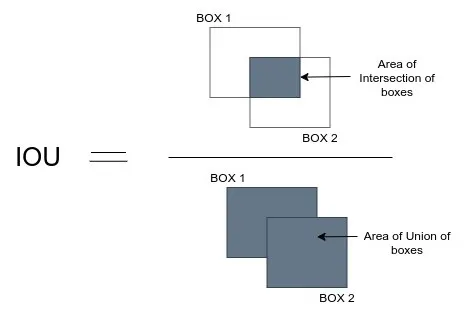
Intersection over Union (IoU) is a metric used to measure the overlap between two bounding boxes. It is defined as the area of the intersection divided by the area of the union of the two boxes.
In the above image:
- The red box represents the predicted bounding box.
- The blue box represents the ground truth bounding box.
- The purple area is the intersection between the two boxes.
- The union is the combined area of both boxes.
IoU is widely used in computer vision tasks, particularly in object detection and segmentation. Here are some of its common use cases:
-
Object Detection: In object detection, IoU is used to compare the predicted bounding boxes with the ground truth boxes to determine the accuracy of the predictions. A higher IoU indicates a better match between the predicted and actual bounding boxes.
-
Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS): In object detection algorithms like YOLO or SSD, IoU is used in the NMS step to eliminate redundant bounding boxes that overlap too much, keeping only the most confident predictions.
-
Image Segmentation: IoU is also used in semantic and instance segmentation tasks to evaluate how well the predicted segmentation masks match the ground truth masks.
IoU.py: Contains theintersection_over_unionfunction, which computes the IoU for two bounding boxes.IoU_tests.py: Contains unit tests to verify the correctness of the IoU implementation.
To use this code, you'll need Python 3.x and PyTorch installed. You can install the required dependencies using pip:
pip install torchYou can calculate the IoU between two bounding boxes by importing the intersection_over_union function from IoU.py.
import torch
from IoU import intersection_over_union
box1 = torch.tensor([.5, .5, .2, .2])
box2 = torch.tensor([.6, .6, .2, .2])
iou = intersection_over_union(box1, box2, box_format='midpoint')
print(f'IoU: {iou.item():.4f}')This will run all the unit tests defined in IoU_tests.py and print the results.
Here's an example of the IoU calculation for different scenarios:
# Example 1: Partial overlap
box1 = torch.tensor([.8, .1, .2, .2])
box2 = torch.tensor([.9, .2, .2, .2])
iou = intersection_over_union(box1, box2, box_format='midpoint')
print(f'IoU: {iou.item():.4f}') # Expected IoU: 0.1429
# Example 2: Complete overlap
box1 = torch.tensor([.5, .5, .2, .2])
box2 = torch.tensor([.5, .5, .2, .2])
iou = intersection_over_union(box1, box2, box_format='midpoint')
print(f'IoU: {iou.item():.4f}') # Expected IoU: 1.0000The IoU_tests.py file contains a variety of unit tests that cover different scenarios for the IoU calculation. Here’s a breakdown of the types of tests included:
-
Test for Overlapping Boxes (
test_both_inside_cell_shares_area):- Scenario: Tests the IoU when both boxes partially overlap.
- Example: A small overlap between two boxes centered at different points.
- Expected Outcome: IoU is a positive value less than 1.
-
Test for Partial Overlap (
test_partially_outside_cell_shares_area):- Scenario: Checks the IoU when one box is slightly outside the boundary of the other.
- Example: Boxes share some area but not completely overlapping.
- Expected Outcome: IoU is a positive value that accounts for the shared area.
-
Test for No Overlap (
test_both_inside_cell_shares_no_area):- Scenario: Verifies IoU calculation when there is no overlap between the boxes.
- Example: Boxes are positioned such that they do not touch each other.
- Expected Outcome: IoU is 0.
-
Test for Complete Overlap (
test_both_inside_cell_shares_entire_area):- Scenario: Tests the IoU when one box is exactly the same as the other.
- Example: Two identical boxes in the same location.
- Expected Outcome: IoU is 1.
-
Test for Midpoint Format (
test_midpoint_outside_cell_shares_area):- Scenario: Ensures correct IoU calculation when boxes are defined using the midpoint format.
- Example: Boxes defined by their center coordinates and width/height.
- Expected Outcome: Accurate IoU calculation based on the midpoint representation.
-
Test for Corner Coordinates Format (
test_box_format_x1_y1_x2_y2):- Scenario: Validates IoU calculation when boxes are defined using corner coordinates (x1, y1, x2, y2).
- Example: Boxes represented by the coordinates of their top-left and bottom-right corners.
- Expected Outcome: IoU should be accurately calculated using corner coordinates.
-
Test for Multiple Boxes (Batch Processing) (
test_additional_and_batch):- Scenario: Tests the IoU calculation when dealing with a batch of multiple boxes.
- Example: Multiple predicted and ground truth boxes evaluated in a single function call.
- Expected Outcome: Correct IoU values for each pair of boxes in the batch.
To run the tests and verify the implementation, simply execute:
python IoU_tests.py