Table of Contents
Break down large Salesforce metadata files (XML) into smaller, more manageable files (XML/JSON/YAML/JSON5) for version control and then recreate deployment-compatible files.
- Install plugin using
sf
sf plugins install sf-decomposer@x.y.z- Decompose the metadata type(s) in your Salesforce DX project
sf decomposer decompose -m "flow" -m "labels"- Add decomposed files to
.forceignore
This is REQUIRED to avoid errors when running
sfcommands
-
Stage decomposed files in version control
-
Recompose the metadata type(s) before deployment
sf decomposer recompose -m "flow" -m "labels"- Deploy recomposed metadata
Why should you consider using sf-decomposer over Salesforce's decomposition?
- Broad Metadata Support: Unlike Salesforce's decomposition,
sf-decomposersupports most metadata types available in the Metadata API. - Selective Decomposition:
sf-decomposerallows you to decompose only the metadata you need instead of Salesforce's all-or-nothing approach. - Complete Decomposition: Partially decomposed metadata types (e.g., Salesforce's
decomposePermissionSetBeta2) can be fully decomposed bysf-decomposer. - Consistent Sorting:
sf-decomposerrecomposition ensures elements are always sorted consistently for better version control. - Multiple Decompose Formats:
sf-decomposerallows you to decompose the original XML file into smaller XML, JSON, JSON5, or YAML files depending on your preference. - CI/CD Friendly: Hooks allow for seamless decomposition and recomposition in CI/CD workflows.
- Better Version Control: Smaller files make pull requests more readable and reduce merge conflicts.
In general, sf-decomposer helps Salesforce Admins do a few things with their source deployments:
- Enhance peer reviews of large metadata in CI/CD platforms like GitHub, i.e. easier-to-review diffs in pull requests
- Make deployments safer by ensuring only the intended changes are deployed, improving the overall version control process
The sf-decomposer supports 2 commands:
sf decomposer decomposesf decomposer recompose
Decomposes the original metadata files in all local package directories into smaller files for version control.
USAGE
$ sf decomposer decompose -m <value> -f <value> -i <value> [--prepurge --postpurge --debug --json]
FLAGS
-m, --metadata-type=<value> The metadata suffix to process, such as 'flow', 'labels', etc.
Can be declared multiple times.
-f, --format=<value> The file type for the decomposed files.
Must match what format you provide for recompose.
Options: ['xml', 'yaml', 'json', 'json5']
[default: 'xml']
-i, --ignore-package-directory=<value> Package directory to ignore.
Should be as they appear in the "sfdx-project.json".
Can be declared multiple times.
--prepurge Purgd directories of pre-existing decomposed files.
[default: false]
--postpurge Purge the original files after decomposing them.
[default: false]
--debug Log debugging results to a text file (disassemble.log).
[default: false]
GLOBAL FLAGS
--json Format output as json.
EXAMPLES
Decompose all flows in XML format:
$ sf decomposer decompose -m "flow" -f "xml" --prepurge --postpurge --debug
Decompose all flows and custom labels in YAML format
$ sf decomposer decompose -m "flow" -m "labels" -f "yaml" --prepurge --postpurge --debug
Decompose flows except for those in the "force-app" package directory.
$ sf decomposer decompose -m "flow" -i "force-app"
Recompose decomposed files into deployment-compatible files.
USAGE
$ sf decomposer recompose -m <value> -f <value> -i <value> [--postpurge --debug --json]
FLAGS
-m, --metadata-type=<value> The metadata suffix to process, such as 'flow', 'labels', etc.
Can be declared multiple times.
-f, --format=<value> The file format for the decomposed files.
Must match what format you provide for decompose.
Options: ['xml', 'yaml', 'json', 'json5']
[default: 'xml']
-i, --ignore-package-directory=<value> Package directory to ignore.
Should be as they appear in the "sfdx-project.json".
Can be declared multiple times.
--postpurge Purge the decomposed files after recomposing them.
[default: false]
--debug Log debugging results to a text file (disassemble.log).
[default: false]
GLOBAL FLAGS
--json Format output as json.
EXAMPLES
Recompose all flows:
$ sf decomposer recompose -m "flow" -f "xml" --postpurge --debug
Recompose all decomposed flows and custom labels YAMLs into XMLs
$ sf decomposer recompose -m "flow" -m "labels" -f "yaml" --postpurge --debug
Recompose flows except for those in the "force-app" package directory.
$ sf decomposer recompose -m "flow" -i "force-app"
When the original metadata files are decomposed, this structure is followed for all metadata types except for custom labels:
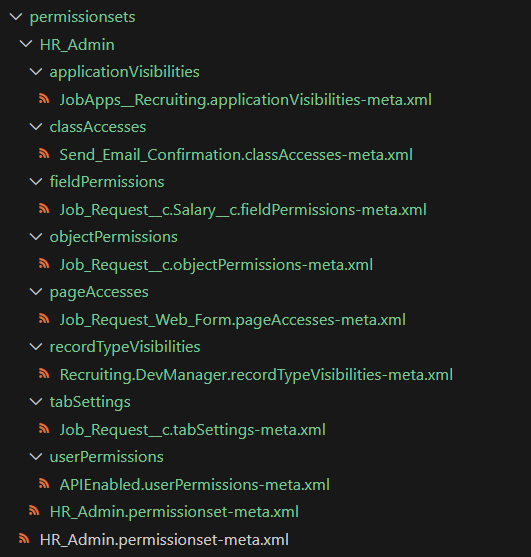
- Leaf elements (i.e.
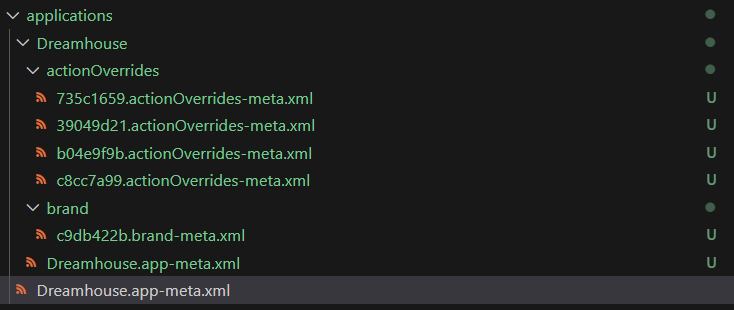
<userLicense>Salesforce</userLicense>) will be decomposed in the same file in the root of the decomposed directory. The leaf file-name will match the original file-name. - Nested elements will be decomposed into their own files under sub-directories by the element type, i.e. custom permissions in a permission set will have their own decomposed file under a custom permissions sub-folder.
- If unique ID elements are found, the decomposed nested files will be named using them.
- Otherwise, the decomposed nested files will be named with the SHA-256 hash of the element contents.
- See Contributing for more information on unique ID elements.
Decomposed Permission Sets named using unique ID elements
Decomposed Application named using SHA-256 hashes of elements
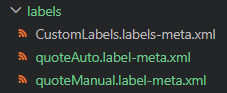
When custom labels are decomposed, each custom label will have its own file in the original labels directory.
Decomposed Custom Labels
All parent metadata types imported from this plugin's version of @salesforce/source-deploy-retrieve (SDR) toolkit are supported except for certain types.
The --metadata-type/-m flag should be the metadata's suffix value as listed in the metadataRegistry.json. You can also infer the suffix by looking at the original XML file-name, i.e. *.{suffix}-meta.xml.
Here are some examples:
- Custom Labels (
--metadata-type "labels") - Workflows (
--metadata-type "workflow") - Profiles (
--metadata-type "profile") - Permission Sets (
--metadata-type "permissionset") - AI Scoring Model Definition (
--metadata-type "aiScoringModelDefinition") - Decision Matrix Definition (
--metadata-type "decisionMatrixDefinition") - Bot (
--metadata-type "bot") - Marketing App Extension (
--metadata-type "marketingappextension")
botVersionis blocked from being ran directly. Please use thebotmeta suffix to decompose and recompose bots and bot versions.Error (1): `botVersion` suffix should not be used. Please use `bot` to decompose/recompose bot and bot version files.- Custom Objects are not supported by this plugin as they already are decomposed by default.
Error (1): Custom Objects are not supported by this plugin. - Metadata types such as Apex Classes, Apex Components, Triggers, etc. with certain SDR adapter strategies (
matchingContentFile,digitalExperience,mixedContent,bundle) are not supported by this plugin.Error (1): Metadata types with [matchingContentFile, digitalExperience, mixedContent, bundle] strategies are not supported by this plugin. - Children metadata types (i.e. custom fields) are not supported and will result in this general error:
Error (1): Metadata type not found for the given suffix: field.
sf-decomposer searches the current working directory for the sfdx-project.json, and if it's not found in the current working directory, it will search upwards for it until it hits your root drive. If the sfdx-project.json file isn't found, the plugin will fail with:
Error (1): sfdx-project.json not found in any parent directory.
The xml-disassembler package will create a log file, disassemble.log, at all times. By default, the log will only contain XML decomposing/recomposing errors. XML decomposing/recomposing errors do not cause the Salesforce CLI to fail. The CLI will proceed to decompose/recompose all remaining metadata.
The Salesforce CLI will print XML errors as warnings in the terminal:
Warning: C:\Users\matth\Documents\sf-decomposer\test\baselines\flows\Get_Info\actionCalls\Get_Info.actionCalls-meta.xml was unabled to be parsed and will not be processed. Confirm formatting and try again.
To add debugging to the log, provide the --debug flag to the decompose or recompose command.
[2024-03-30T14:28:37.959] [DEBUG] default - Created disassembled file: mock\no-nested-elements\HR_Admin\HR_Admin.permissionset-meta.xml
NOTE: In order to avoid errors when running
sfcommands, you must configure your.forceignorefile to have the Salesforce CLI ignore the decomposed files. See Ignore Files.
sf-decomposer supports automatic decomposition and recomposition by defining a .sfdecomposer.config.json file in your project root.
You can copy and update the sample .sfdecomposer.config.json.
metadataSuffixesis required and should be a comma-separated string of metadata suffixes to decompose and recompose based on the CLI command.ignorePackageDirectoriesis optional and should be a comma-separated string of package directories to ignore.prePurgeis optional and should betrueorfalse. If true, this will delete any existing decomposed files before decomposing the files. This defauls tofalse.postPurgeis optional and should betrueorfalse. If true, this will delete the retrieval file after decomposing it or delete the decomposed files after recomposing them. This defauls tofalse.decomposedFormatis optional and should be eitherxml,json,json5, oryaml, depending on the decomposed file format. This defaults toxml.
If .sfdecomposer.config.json is found, the hooks will run:
- the decompose command after a
sf project retrieve startcommand completes successfully (post-run) - the recompose command before a
sf project deploy [start/validate]command starts (pre-run)
If .sfdecomposer.config.json isn't found, the hooks will be skipped.
The Salesforce CLI must ignore the decomposed files and allow the recomposed files.
You can use the sample .forceignore. Update the decomposed file extensions based on what format you're using (.xml, .json, .json5, or .yaml).
Optionally, you can create a .sfdecomposerignore file in the root of your Salesforce DX project to ignore specific XMLs when decomposing. The .sfdecomposerignore file should follow .gitignore spec 2.22.1.
When you run sf decomposer decompose --debug and it processes a file that matches an entry in .sfdecomposerignore, a warning will be printed to the disassemble.log:
[2024-05-22T09:32:12.078] [WARN] default - File ignored by .sfdecomposerignore: C:\Users\matth\Documents\sf-decomposer\test\baselines\bots\Assessment_Bot\v1.botVersion-meta.xml
.sfdecomposerignore is not read when recomposing metadata.
Optionally, git can ignore the recomposed files so you don't stage those in your repositories. You can also have git ignore the disassemble.log created by the xml-disassembler package.
You can use the sample .gitignore.
If you encounter any bugs or would like to request features, please create an issue.
Contributions are welcome! See Contributing.
This project is licensed under the MIT license. Please see the LICENSE file for details.