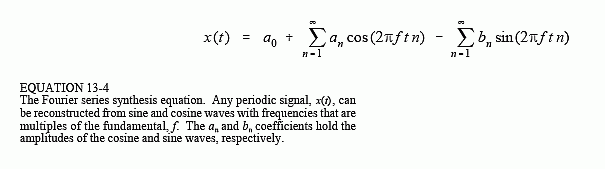This project is experimental in nature. You should view this implementation simply as a proof of concept. This "framework" gives you the possibility to define/reveal a function that interpolates a given set of points in terms of sinusoids/harmonics. It implements in a way, "lazily", symbolic regression. This is an exploration of the frequency space practically.
As the mathematician Joseph Fourier proved, any given function, no matter how irregular in variation, could be expressed as a weighted summation of sinusoids. I was intrigued beyound measure by this fact while I was still in college, concluding that sinusoids play a special and important part in the grand scheme of the universe. This affirmation can be expressed as fallows:
In the considered discrete case, obviously, the summation will not have infinity as a limit, but the number of points given to be interpolated(sample frequency) divided by 2; refering to nyquist limit(the formula implies some other adjustments for the discrete case). The problem that needs to be solved is that of finding the coeficients an, bn, a0; such that the overall obtained function x(t) interpolates as accurately as possible the given set of points. The intention is to avoid the conventional way of determining the values of the parameters(by the means of Fourier Transform), proposing a different aproach by viewing this conundrum as an optimization problem. The implementation is based on a genetic algorithm, as expected. Therefore, the genotype is defined as fallows:
[a1, a2, ..., an, b1, b2, ..., bn, a0]
where n = ((number_of_samples_of_function - 1) / 2 ) -1) * 2 and ai, bj = coeficients_of_sinusoids
Where the corresponding fenotype, given the genotype defined above is obtained as fallows:
a1*cos(2 * pi * 1 * x/T) + a2*cos(2 * pi * 2 * x/T) + ... + an*cos(2 * pi * n * x/T) + b1*sin(2 * pi * 1 * x/T) + b2*sin(2 * pi * 2 * x/T) + ... + bn*sin(2 * pi * n * x/T) + a0
where T = number_of_samples_of_function - 1 or nr_of_target_points - 1
Regarding the fitness function, it is based on the RMSD in the fallowing manner:
fitness_function(fenotype) = 100 / (1 + RMSD)
where y = set_target_points_to_be_interpolated, ŷ = set_points_obtained_after_fenotype_evaluation and T = nr_of_target_points
As a first example, in order to test the validaity of the implementation, it is used as points to be interpolated, the points obtained of a simple sinusoidal of frequency 1Hz, sampled at 6hz. Therefore, it is visualized as fallows:
Where the actual points to be interpolated viewd separately:
The gentic algorithm behind Harmonica is executed with the fallowing parameters: generations = 100, population = 50
Revealing the function that interpolates the above given points:
obtained_function(x) = 0.002758497956727668*cos(2*pi*1*x/5)+0.001460710938479326*cos(2*pi*2*x/5)+0.00045249072318997996*cos(2*pi*3*x/5)+0.999134478010111*sin(2*pi*1*x/5)+0.609025912138845*sin(2*pi*2*x/5)+0.6093149935194077*sin(2*pi*3*x/5)+(0.023094772686164333) .
This function visualized: :
As it can be seen, the simple/plain sinusoidal is not revealed/defined; but a more complex function that interpolates nevertheless the given points successfully.
As a second example, it is used a more "sofisticated" arrangement of points to be interpolated, 21 in number:
As expected, the function that is revealed is "sofisticated" also: :
obtained_function(x) = 0.013938328067339523 * cos(2 * pi * 1 * x /20 ) + 0.8985585752502332 * cos(2 * pi * 2 * x /20 ) + 0.017119131042009128 * cos(2 * pi * 3 * x /20 ) + 0.017038282873673927 * cos(2 * pi * 4 * x /20 ) + 0.005686950072323227 * cos(2 * pi * 5 * x /20 ) + 0.04034219080962831 * cos(2 * pi * 6 * x /20 ) + 0.0026083865261755657 * cos(2 * pi * 7 * x /20 ) + 0.002114542073817338 * cos(2 * pi * 8 * x /20 ) + 0.034423936824864 * cos(2 * pi * 9 * x /20 ) + 0.7948683810739523 * sin(2 * pi * 1 * x /20 ) + 0.011037098606327178 * sin(2 * pi * 2 * x /20 ) + 0.28941776818615894 * sin(2 * pi * 3 * x /20 ) + 0.7580725650630825 * sin(2 * pi * 4 * x /20 ) + 0.01249286865336785 * sin(2 * pi * 5 * x /20 ) + 0.0028725353123258968 * sin(2 * pi * 6 * x /20 ) + 0.02661288338791712 * sin(2 * pi * 7 * x /20 ) + 0.003988475386816903 * sin(2 * pi * 8 * x /20 ) + 0.027508077252014762 * sin(2 * pi * 9 * x /20 ) + (0.007537662639844456) .
This function visualized:
Don't retain yourself from participating, from developing further this intriguing project. Thank you!