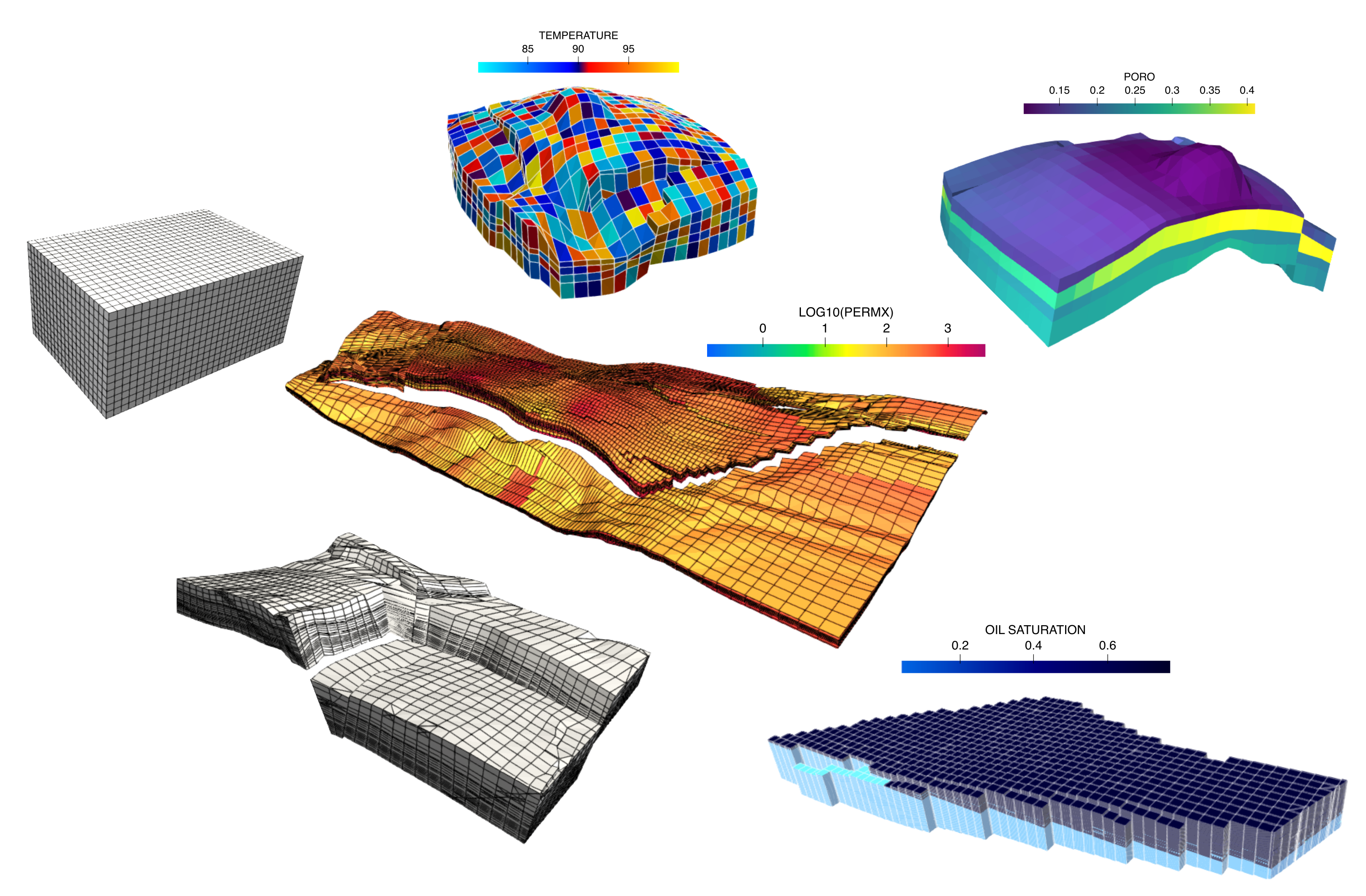
This artwork comprises examples of a few Cartesian and non-Cartesian petroleum 3D reservoirs grid models post-processed by APyCe.
Mateus Tosta (@mt2312) 1,* (mateustosta@outlook.com.br), Bin Wang (@BinWang0213) 2 (bin.wang@cup.edu.cn), and Gustavo P. Oliveira (@gcpeixoto) 1 (gustavo.oliveira@ci.ufpb.br)
1 TRIL Lab, Center of Informatics, Federal University of Paraíba, João Pessoa, Brazil
2 State Key Laboratory of Petroleum Resources and Prospecting, China University of Petroleum-Beijing, Beijing 102249, P. R. China
* Currently at Gaudium Corp., Brazil
APyCE (pronounced as "ah-pees") is an enhanced version of the early project PyGRDECL (by @BinWang0213), developed to handle Schlumberger Eclipse© deck files for visualization. APyCE is multi-platform, object-oriented, and easy to use, being prepared to fulfill its objectives with only 4 lines of Python code to be run by whoever with a minimum background in programming. It is recommended for researchers who need to render high-quality figures for inclusion into scientific papers, reports, presentations, handouts, interactive notebooks, and general documents for teaching purposes, or auxiliary tools for data analysis within reservoir modeling or related domains.
APyCE was developed to allow quick analysis and visualization of 3D oil and gas reservoirs, so that the tool can be used by people in academia or industry. It is an open-source tool maintained on GitHub platform, fully accessible to any developer interested to contribute via pull requests. Given its object-oriented structure, the code can be extended and improved for further applications.
All the components of APyCE are briefly described below.
The grid class houses the main functions of APyCE.
process_grid(): computes grid topology and geometry from pillar grid description.load_cell_data(): reads a file with data and append this data to model.plot_grid(): renders a static plot of the grid through PyVista.export_data(): saves grid data to a single VTU file for interactive visualization in ParaView.
APyCE is developed under Python>=3.8
To get the most current version, install it from Github:
git clone https://github.com/mateustosta/apyce-project.git
cd apyce-project
To setup the development environment, do the following
virtualenv --python=python3.8 venv3
source venv3/bin/activate
pip install -r requirements.txt
pip install .
or use Anaconda:
conda create -f environment.yml
conda activate apyce
A simple APyCe workflow is like this:
import apyce as ap
G = ap.grid.Grid(filename='Data/dome.grdecl', grid_origin='eclipse', verbose=True)
G.process_grid()
G.export_data()
G.plot_grid(filename='Data/Results/dome.vtu', lighting=False, property='PORO', show_edges=True, specular=0.0,
specular_power=0.0, show_scalar_bar=True, cmap='viridis')APyCE produces ready-made visuals for high-quality publications.
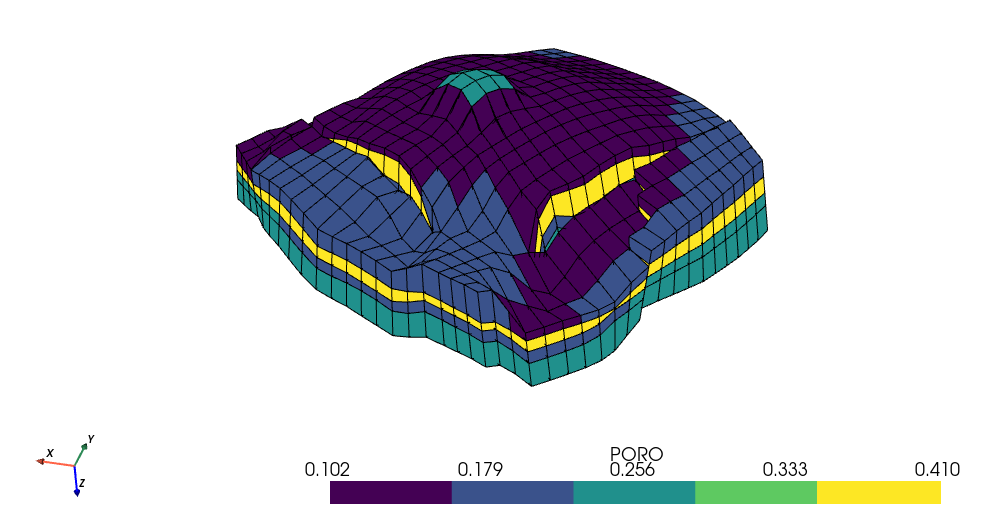
- Output of
Getting_Started.pyexample withdomemodel
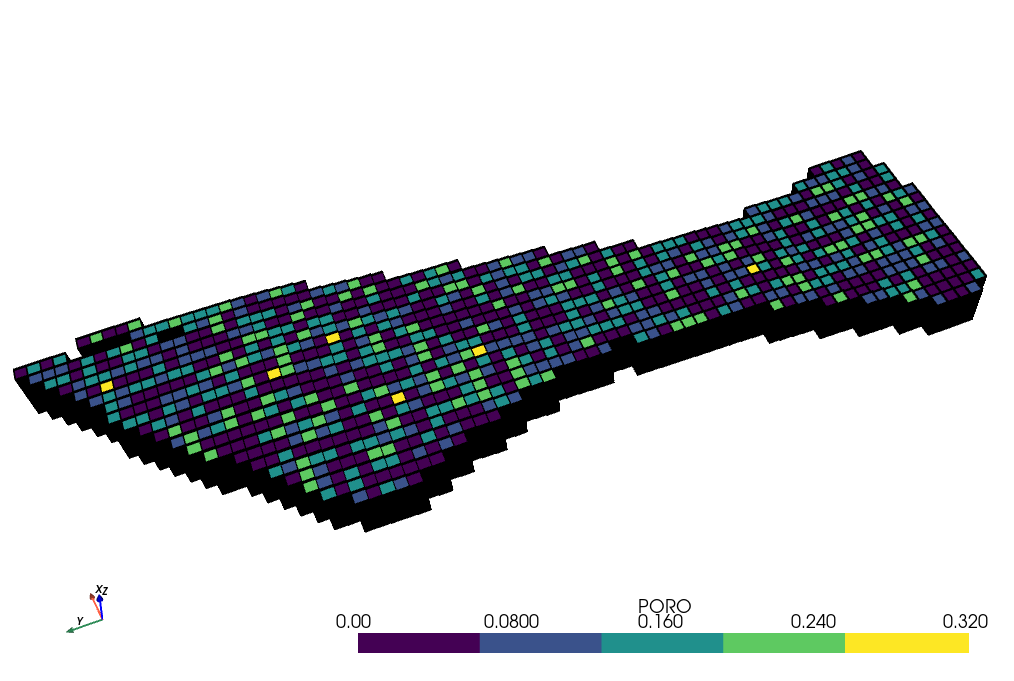
- Output of
Getting_Started.pyexample withPSYmodel
This code is released under the terms of the BSD license, and thus free for commercial and research use. Feel free to use the code into your own project with a PROPER REFERENCE.
Tosta. M, Wang B., Oliveira G.P., APyCE Project: A Python-based Builder/Eclipse wrapper for 3D visualization of reservoir grids, (2020), GitHub repository, https://github.com/mateustosta/apyce-project