In this capstone, will predict if the Falcon 9 first stage will land successfully. SpaceX advertises Falcon 9 rocket launches on its website with a cost of 62 million dollars; other providers cost upward of 165 million dollars each, much of the savings is because SpaceX can reuse the first stage. Therefore if we can determine if the first stage will land, we can determine the cost of a launch. This information can be used if an alternate company wants to bid against SpaceX for a rocket launch. In this lab, will collect and make sure the data is in the correct format from an API. The following is an example of a successful and launch.
Several examples of an unsuccessful landing are shown here:
Most unsuccessful landings are planned. Space X performs a controlled landing in the oceans.
In this lab, will make a get request to the SpaceX API. You will also do some basic data wrangling and formating.
- Request to the SpaceX API
- Clean the requested data
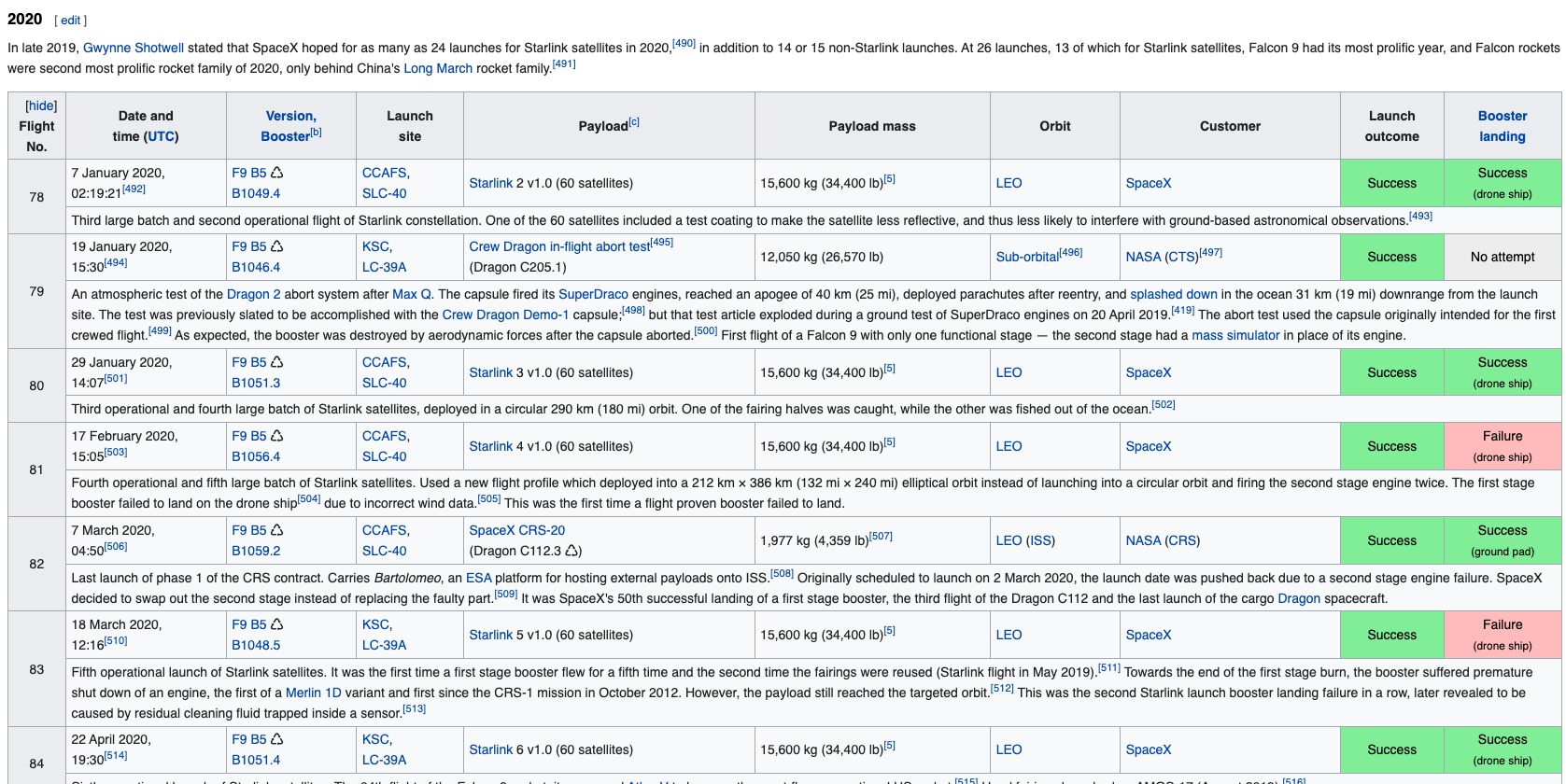
In this lab, you will be performing web scraping to collect Falcon 9 historical launch records from a Wikipedia page titled List of Falcon 9 and Falcon Heavy launches
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_Falcon_9_and_Falcon_Heavy_launches
Falcon 9 first stage will land successfully
Several examples of an unsuccessful landing are shown here:
More specifically, the launch records are stored in a HTML table shown below:
Web scrap Falcon 9 launch records with BeautifulSoup:
- Extract a Falcon 9 launch records HTML table from Wikipedia
- Parse the table and convert it into a Pandas data frame
In this lab, we will perform some Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA) to find some patterns in the data and determine what would be the label for training supervised models.
In the data set, there are several different cases where the booster did not land successfully. Sometimes a landing was attempted but failed due to an accident; for example, True Ocean means the mission outcome was successfully landed to a specific region of the ocean while False Ocean means the mission outcome was unsuccessfully landed to a specific region of the ocean. True RTLS means the mission outcome was successfully landed to a ground pad False RTLS means the mission outcome was unsuccessfully landed to a ground pad.True ASDS means the mission outcome was successfully landed on a drone ship False ASDS means the mission outcome was unsuccessfully landed on a drone ship.
In this lab we will mainly convert those outcomes into Training Labels with 1 means the booster successfully landed 0 means it was unsuccessful.
Falcon 9 first stage will land successfully
Several examples of an unsuccessful landing are shown here:
Using this Python notebook you will:
- Understand the Spacex DataSet
- Load the dataset into the corresponding table in a Db2 database
- Execute SQL queries to answer assignment questions
SpaceX has gained worldwide attention for a series of historic milestones. It is the only private company ever to return a spacecraft from low-earth orbit, which it first accomplished in December 2010. SpaceX advertises Falcon 9 rocket launches on its website with a cost of 62 million dollars wheras other providers cost upward of 165 million dollars each, much of the savings is because Space X can reuse the first stage.
- Therefore if we can determine if the first stage will land, we can determine the cost of a launch.
- This information can be used if an alternate company wants to bid against SpaceX for a rocket launch.
- This dataset includes a record for each payload carried during a SpaceX mission into outer space.
This task requires to load the spacex dataset. In many cases the dataset to be analyzed is available as a .CSV (comma separated values) file, perhaps on the internet. Click on the link below to download and save the dataset (.CSV file): Spacex DataSet
In this task, i will predict if the Falcon 9 first stage will land successfully. SpaceX advertises Falcon 9 rocket launches on its website with a cost of 62 million dollars; other providers cost upward of 165 million dollars each, much of the savings is due to the fact that SpaceX can reuse the first stage. In this lab, you will perform Exploratory Data Analysis and Feature Engineering.
Perform exploratory Data Analysis and Feature Engineering using Pandas and Matplotlib
- Exploratory Data Analysis
- Preparing Data Feature Engineering
The launch success rate may depend on many factors such as payload mass, orbit type, and so on. It may also depend on the location and proximities of a launch site, i.e., the initial position of rocket trajectories. Finding an optimal location for building a launch site certainly involves many factors and hopefully we could discover some of the factors by analyzing the existing launch site locations.
In the previous exploratory data analysis labs, you have visualized the SpaceX launch dataset using matplotlib and seaborn and discovered some preliminary correlations between the launch site and success rates. In this lab, you will be performing more interactive visual analytics using Folium.
This lab contains the following tasks:
- TASK 1: Mark all launch sites on a map
- TASK 2: Mark the success/failed launches for each site on the map
- TASK 3: Calculate the distances between a launch site to its proximities
After completed the above tasks, you should be able to find some geographical patterns about launch sites.
Space X advertises Falcon 9 rocket launches on its website with a cost of 62 million dollars; other providers cost upward of 165 million dollars each, much of the savings is because Space X can reuse the first stage. Therefore if we can determine if the first stage will land, we can determine the cost of a launch. This information can be used if an alternate company wants to bid against space X for a rocket launch. In this lab, you will create a machine learning pipeline to predict if the first stage will land given the data from the preceding labs.
Perform exploratory Data Analysis and determine Training Labels
- create a column for the class
- Standardize the data
- Split into training data and test data
-Find best Hyperparameter for SVM, Classification Trees and Logistic Regression
- Find the method performs best using test data