The apriori algorithm has been implemented based on the algorithm provided in the textbook Data Mining by Tan et al.(Second Edition). for candidate generation and pruning, frequent itemset generation and rule generation. It is present in the notebook in the github repository.
The algorithm followed is
Both the f(k-1)*f1 and f(k-1)*f(k-1) approaches have been implemented and it is observed that the f(k-1)*f(k-1) method has provided a lot of savings on the number of candidate sets generated as compared to f(k-1)*f1 which is better compared to the brute force method.
To illustrate this we used the example in the textbook and the kaggle dataset provided.
For the textbook example:
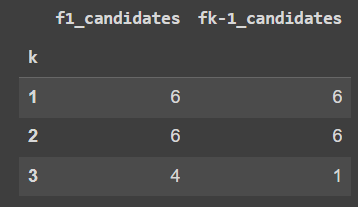
For min_sup = 0.6 and min_conf = 0.9
f(k-1)*f(k-1) produced 3 candidate sets less than f(k-1)*f1
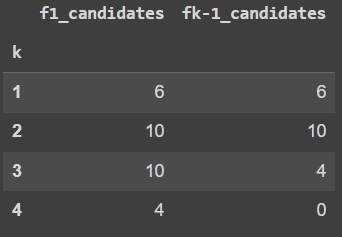
For min_sup = 0.4 and min_conf = 0.9
f(k-1)*f(k-1) produced 10 candidate sets less than f(k-1)*f1
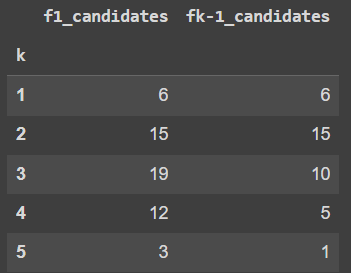
For min_sup = 0.2 and min_conf = 0.8
f(k-1)*f(k-1) produced 18 candidate sets less than f(k-1)*f1
So we can say that there are a lot of savings when we use f(k-1)*f(k-1) method even if it is a small dataset.