Check the documentation to install and use OpenCVE.
We also provide a running instance on https://www.opencve.io if you don't want to host it yourself.
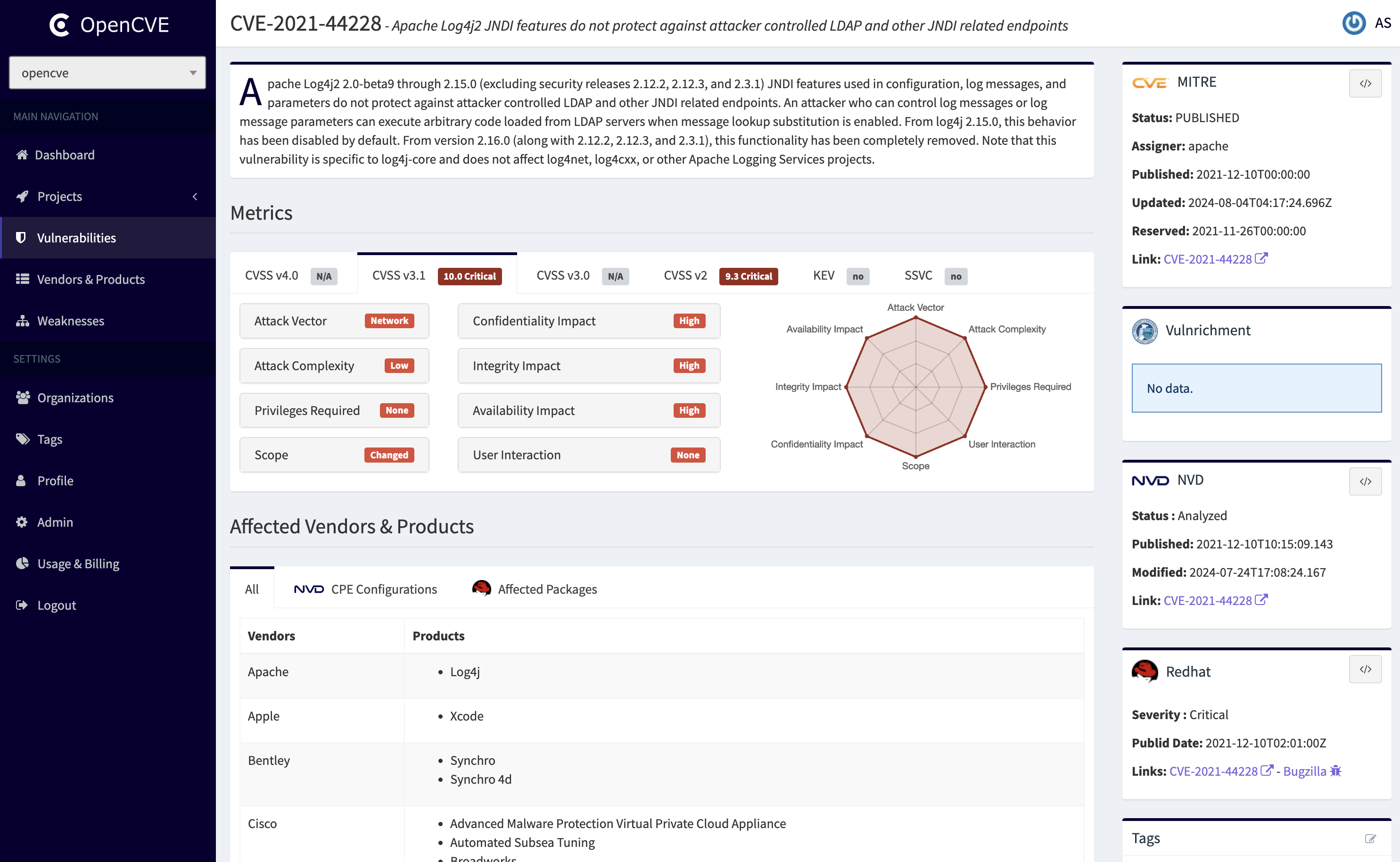
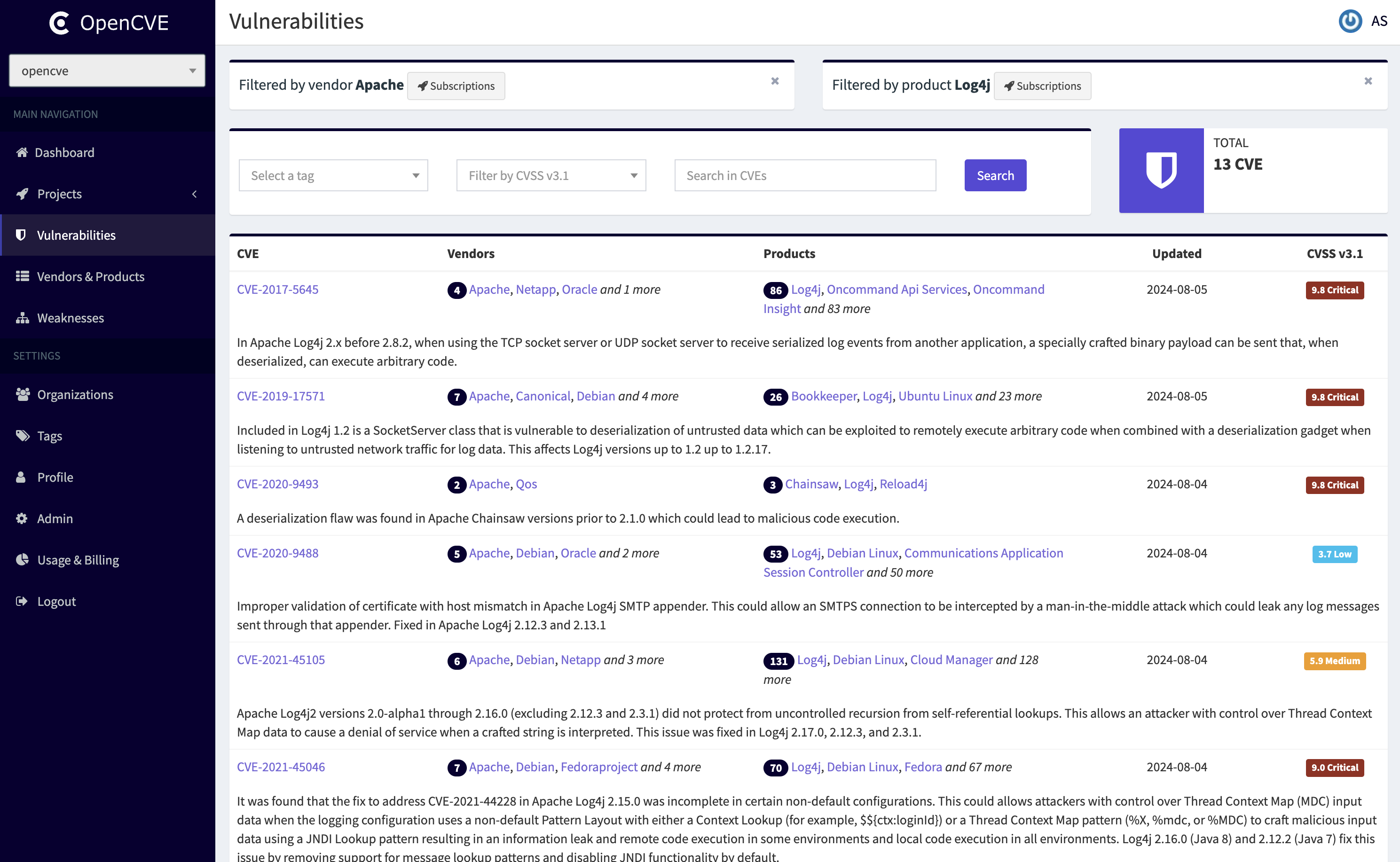
OpenCVE is a platform used to locally import the list of CVEs and perform searches on it (by vendors, products, CVSS, CWE...).
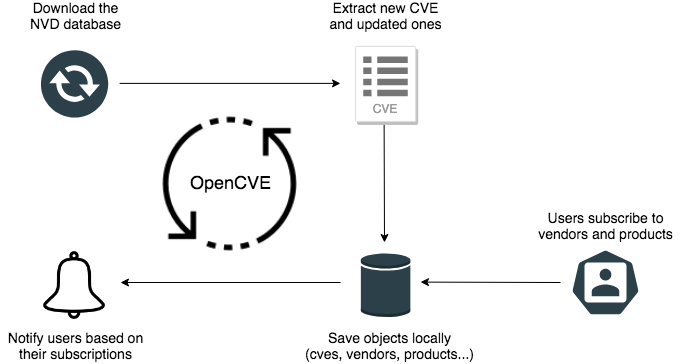
Users subscribe to vendors or products, and OpenCVE alerts them when a new CVE is created or when an update is done in an existing CVE.
OpenCVE uses the JSON feed provided by the NVD to update the local list of CVEs.
After an initial import, a background task is regularly executed to synchronize the local copy with the NVD feed. If a new CVE is added, or if a change is detected, the subscribers of the related vendors and products are alerted.
OpenCVE works with Python >=3.6.
It uses the JSONB feature for performance, so you will need a PostgreSQL instance to store the data (CVE, Users, Vendors, Products, Subscriptions, ...). Other engines are not supported.
The pg_trgm module of PostgreSQL is required to let you search in the CVEs list. The upgrade-db command will enable it for you, but you can also do it yourself if you prefer (CREATE EXTENSION pg_trgm). From PostgreSQL 13 this module is considered as trusted, meaning it can be installed by non-superusers with the CREATE privilege.
Celery is used to periodically fetch the NVD database and update the list of CVEs. For that you will need a broker : we recommend you Redis for the ease of installation. Futhermore it is possible that future versions of OpenCVE will use a cache feature, in that case the Redis requirement will already be filled for you.
During the import of initial data OpenCVE will download and parse huge files, like the CPE dictionnary. For that we recommend you 3.5G RAM at least.
We provide 2 methods to install OpenCVE :
The second method can be useful if you don't want to manage the dependencies (like PostgreSQL, Redis or Celery).
Check these documentations for the details of each step (initial import, admin creation, etc).