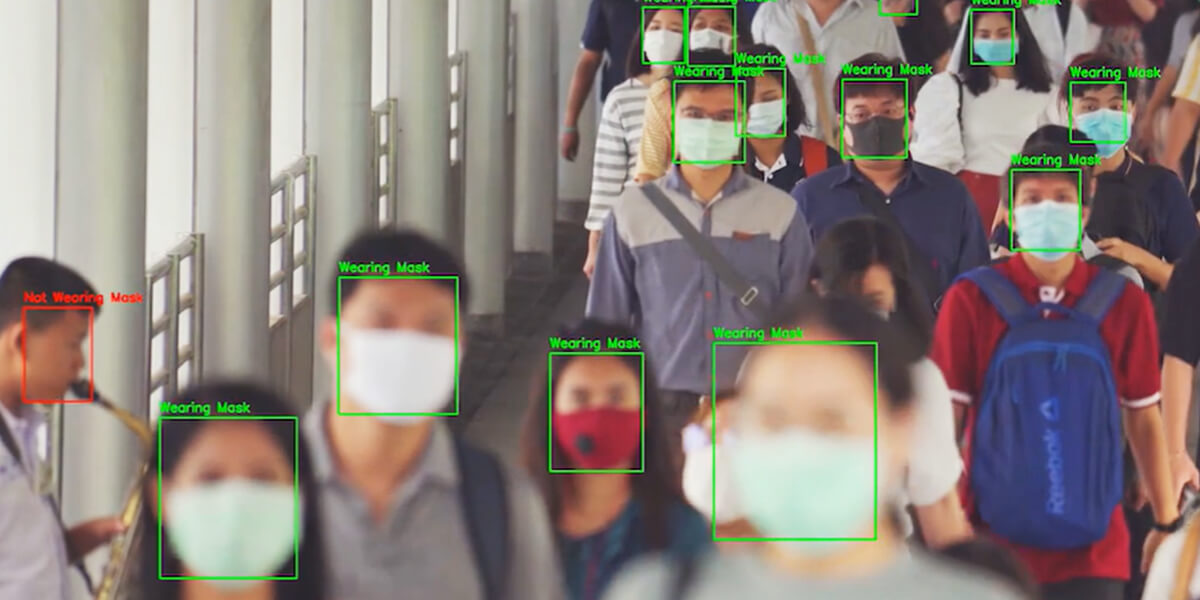
The World Health Organization (WHO) report suggests that respiratory droplets are one of the main routes of transmission of the COVID-19 virus. In a medical study, it was proven that surgical masks can prevent up to 95% of viral transmission caused due to respiratory droplets. This project uses Computer-Vision techniques like Face Detection and CNN classification to detect whether a person is wearing a mask in real-time.
To detect whether the person is wearing a face mask in real-time, the app needs to keep track of individual faces per frame. OpenCV comes with many pre-trained DNN models for facial detection. Once faces are detected with high confidence, they are sent to a CNN classifier that detects face masks.
- Loading images and preparing data for the CNN classifier
- Building and training CNN classifier
- Evaluating the CNN Classifier
- Capturing video frames and detecting faces
- Performing predictions and displaying results
Firstly, execute the below commands in the terminal for setting up the virtual environment and installing packages:
- Create a virtual environment
python3 -m venv env
- Activate newly created virtual environment
env
env/Scripts/activate.bat
- Execute the below command to install python packages used in this project
pip install requirement.txt
- After installing all dependencies execute below command to run
main_app.py.
python main_app.py
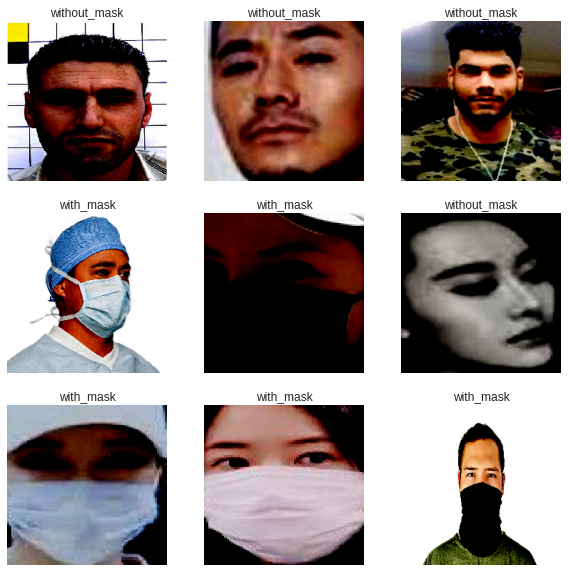
To training our CNN classifier, images are present inside the data.zip file. Once unzipped, below will be the folder structure.
data
├── with_mask - this folder contains images of people with mask
└── without_mask - this folder contains images of people without the mask
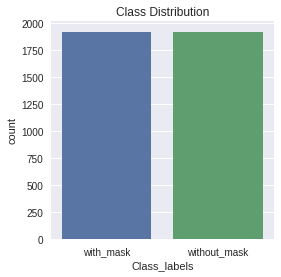
The below bar plot shows that labels are uniformly distributed. As there is a minimal class imbalance, 'accuracy' can be used as an evaluation metric for the classifier.
Once images are loaded, they are resized to a fixed size of 224x224 pixels.
The resized images are then normalized and passed through a data augmentation phase so that the model can generalize. Finally, 20% of the data is spared for testing the final model.
For building, the CNN classifier architecture transfer learning has been used to reduce the number of epochs to train the model. The MobileNet model was used as its base architecture, due to its high performance and smaller footprint. As the model will be capturing similar abstract features present in the Imagenet dataset, the trainable parameters of the Conv-Maxpool blocks are set to False. The top layers of MobileNet are chopped off and custom fully connected layers are added.
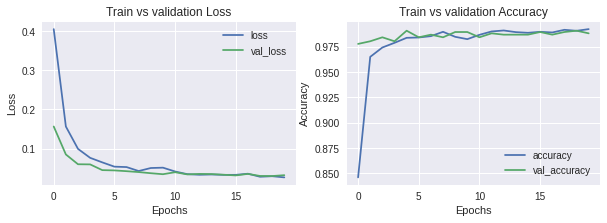
On, training the model for 20 epochs below are the loss and Accuracy curves for our train and test data.
After model completion, it is trained for 20 epochs to achieve an accuracy of 97.5% on the train and test data. Below are the accuracy and loss of the trained model.
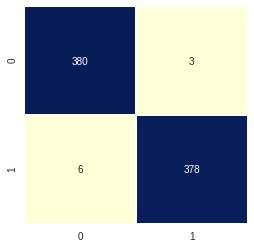
The trained model is evaluated on the test data. The below confusion matrix shows that the model fares pretty well on unseen data.
For capturing video frames, the VideoCapture module of OpenCV has been used. Then individual frames are passed through an OpenCV pre-trained DNN model for detecting faces present inside a frame. Faces that are above a certain threshold are saved and the rest are discarded. The model returns the pixel coordinates of detected faces. These coordinates are then used to extract faces and form the bounding box.
The faces captured by the face detector are resized and preprocessed so that they can be fed to the CNN model to classify whether the person is wearing a mask or not. Finally, the bounding and the resulting predictions are displayed on the captured frame.
Socials : Linkedin
E-mail : rppradhan310@gmail.com