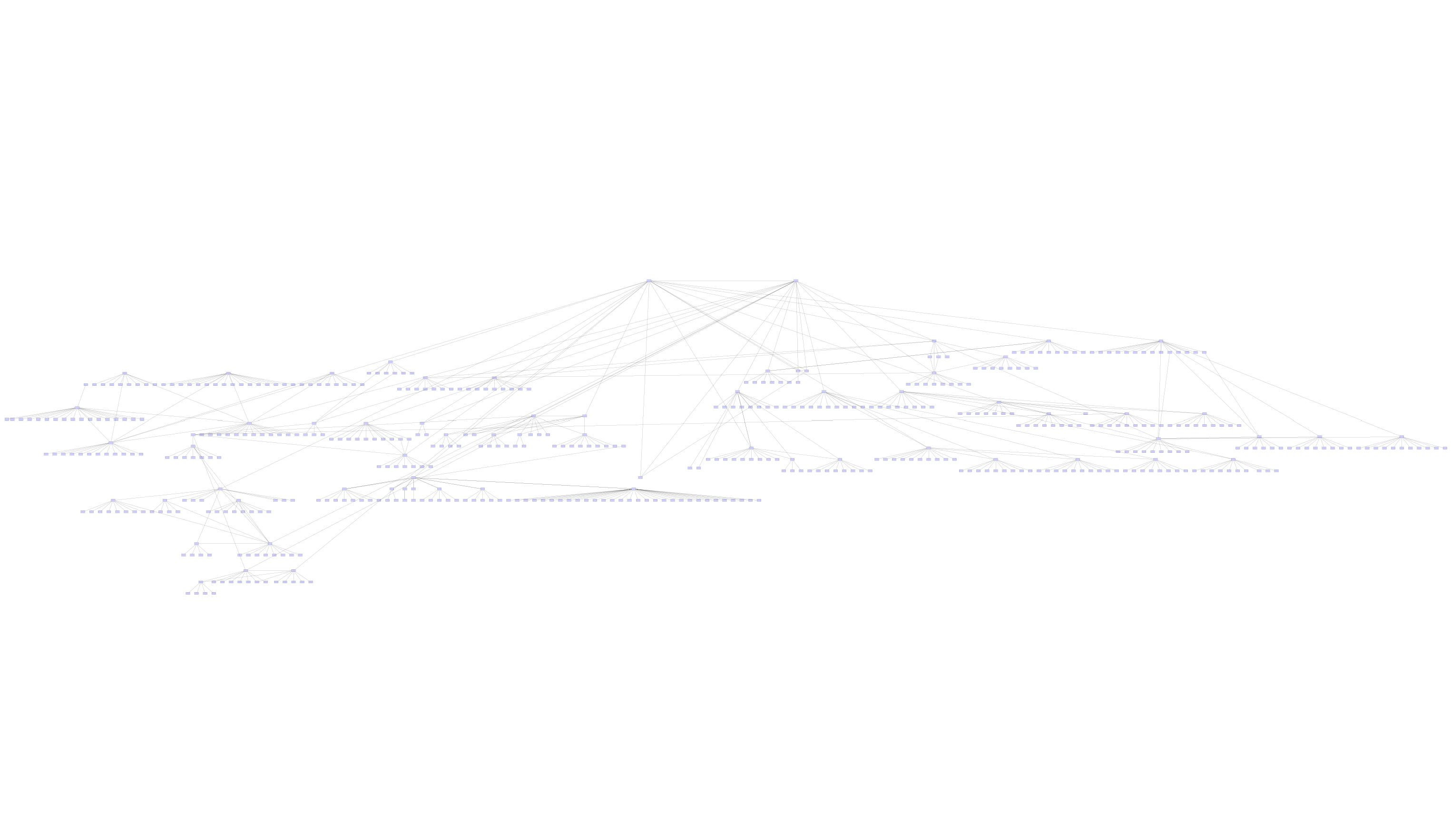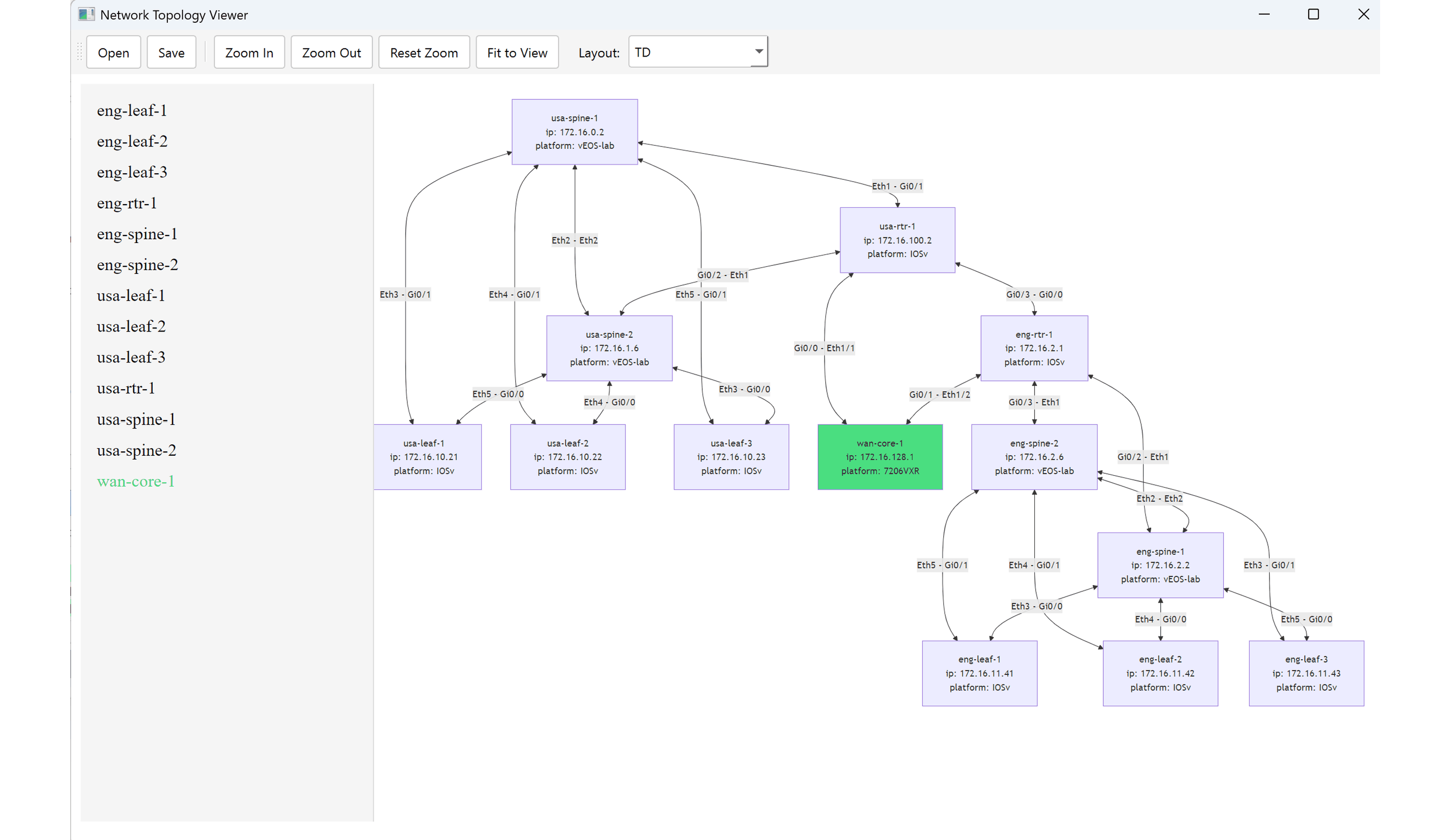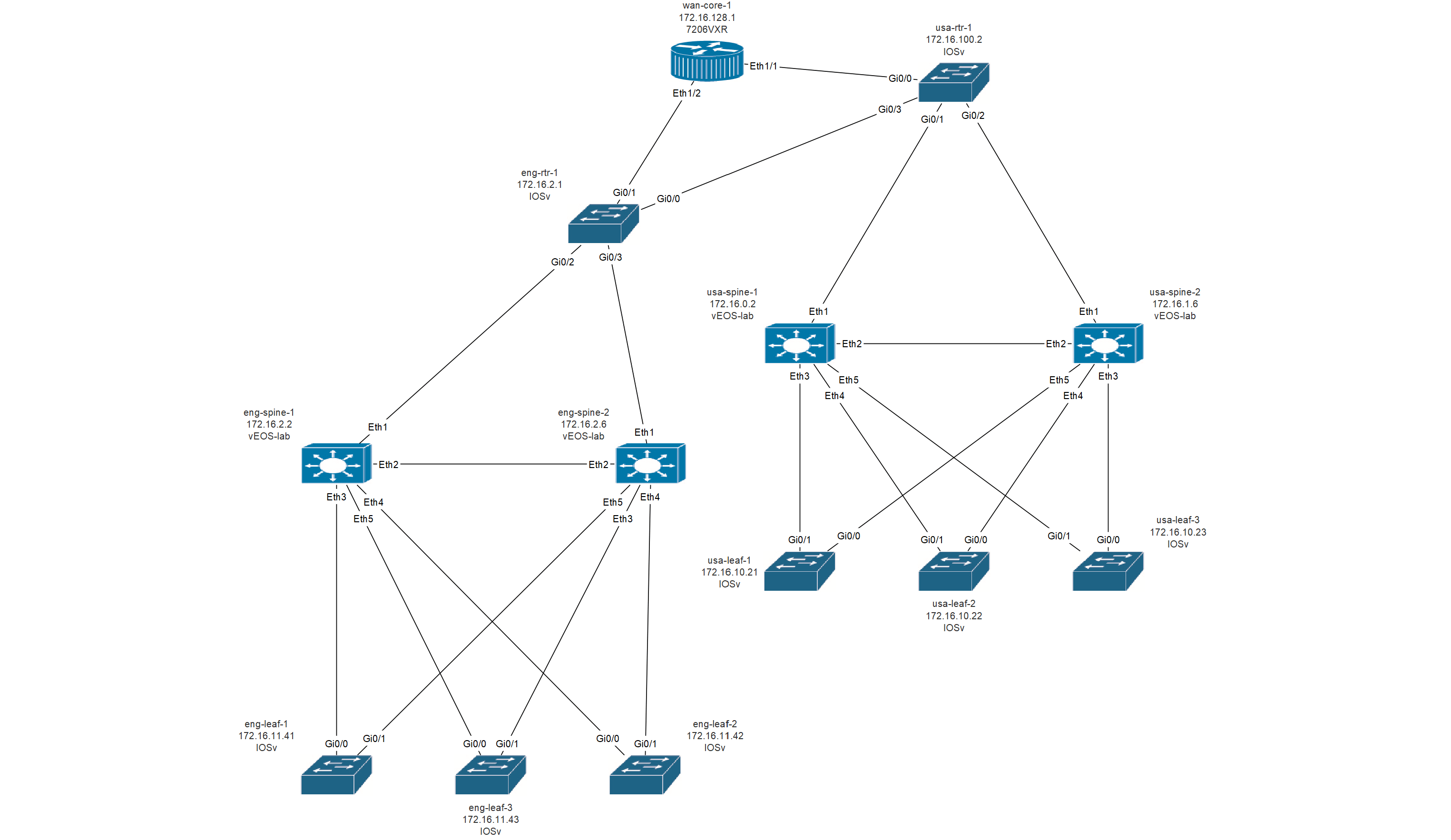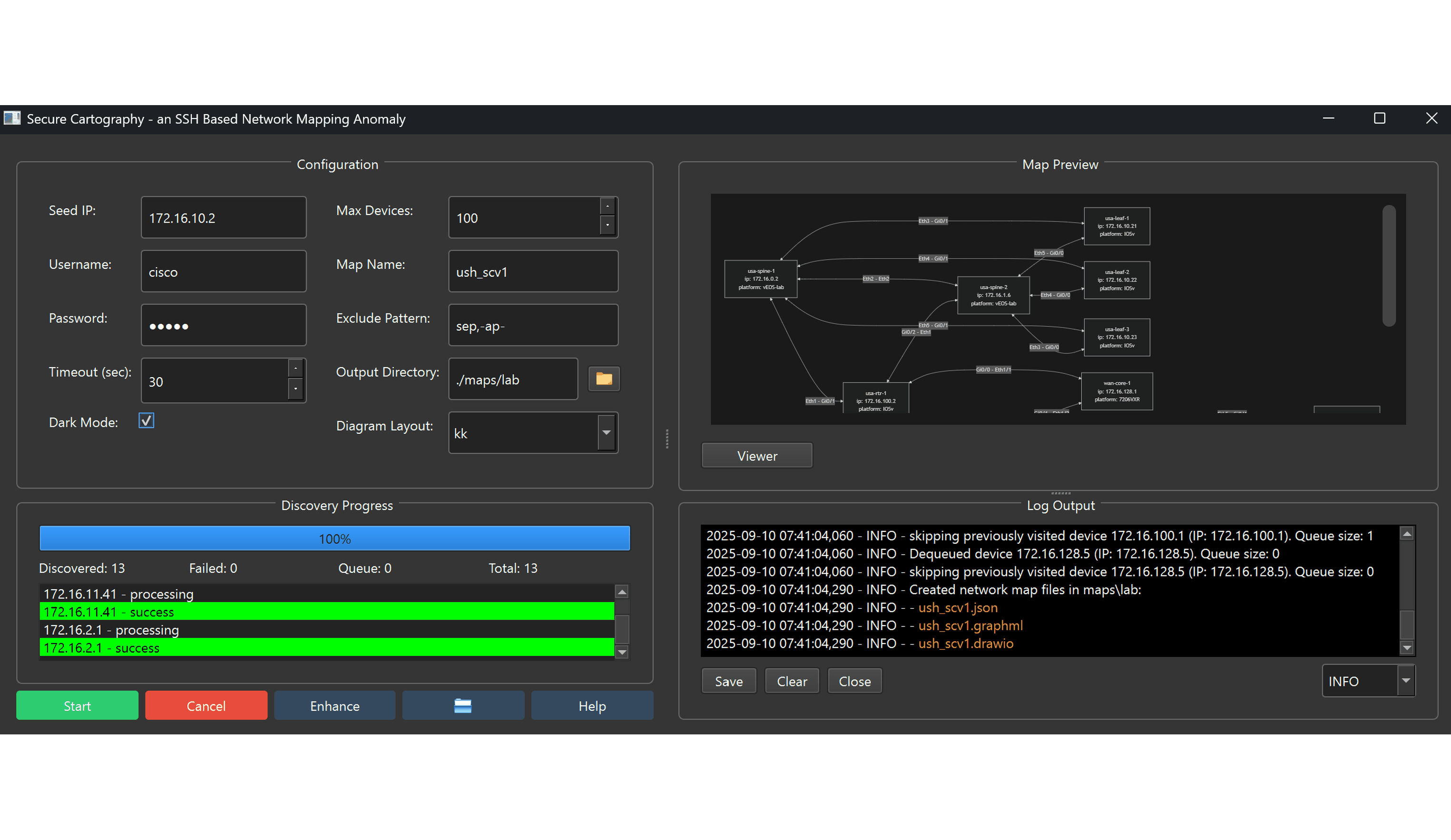
Secure Cartography is a comprehensive network discovery and mapping tool that automates the process of documenting network topologies through SSH-based device interrogation. The system leverages CDP/LLDP protocols to discover device relationships and generates professional-grade network diagrams with customizable device icons and multiple export formats.
- Automated Network Discovery: SSH-based multi-vendor device discovery
- Enhanced Visualization: Customizable device icons for professional diagrams
- Multiple Output Formats: JSON, GraphML (yEd), Draw.io, and SVG
- Security-First Design: Encrypted credential storage with master password protection
- TextFSM Integration: Advanced parsing engine for accurate device data extraction
- Map Enhancement Tools: Interactive icon mapping and diagram customization
- pip install secure-cartography
- scart
- if from source python -m secure_cartography.scart
- Master Password Protection: All credentials encrypted with user-defined master password
- System Keyring Integration: Leverages OS-native secure storage (Windows Credential Manager, macOS Keychain, Linux Secret Service)
- PBKDF2 Key Derivation: Strong cryptographic key generation from master password
- Fernet Encryption: Industry-standard symmetric encryption for credential storage
class NetworkMapperWidget(QWidget):
"""Primary GUI widget handling discovery and visualization"""
def __init__(self, creds_manager: SecureCredentials, parent=None):
self.setup_ui() # Initialize interface components
self.load_settings() # Load encrypted credentials and preferences
self.set_dark_mode() # Apply theme preferencesThe interface provides comprehensive configuration through organized sections:
- Discovery Parameters: Seed IP, credentials, timeout settings
- Scope Control: Maximum devices, exclusion patterns, domain filtering
- Output Options: Directory selection, map naming, layout algorithms
- Real-time Monitoring: Progress tracking, device status, queue management
- Credential Authentication: Master password entry with secure credential loading
- Configuration Setup: Network parameters and discovery options via organized forms
- Discovery Execution: Multi-threaded processing with real-time progress monitoring
- Result Visualization: Interactive preview with multiple export options
class NetworkDiscoveryWorker(QThread):
"""Non-blocking discovery execution"""
device_discovered = pyqtSignal(str, str) # Real-time device status
discovery_complete = pyqtSignal(dict) # Final statistics
progress_update = pyqtSignal(dict) # Queue and progress stats
log_message = pyqtSignal(str) # Detailed loggingThe GUI maintains responsive interaction during discovery through:
- Separate Worker Thread: Discovery runs independently of UI thread
- Real-time Updates: Progress signals update interface components
- Cancellation Support: User can abort long-running discovery operations
- Status Monitoring: Device-by-device progress with color-coded results
The interface provides comprehensive discovery feedback:
- Progress Bar: Overall completion percentage
- Device List: Real-time device status (processing, success, failed)
- Statistics Panel: Discovered, failed, queued, and total device counts
- Log Output: Detailed discovery events with configurable verbosity levels
def save_settings(self):
"""Secure settings storage with credential encryption"""
# Non-sensitive settings to QSettings
self.settings.setValue('seed_ip', self.seed_ip.text())
# Encrypted credential storage
if self.creds_manager.is_unlocked():
cred = {
'primary_password': self.creds_manager.encrypt_value(self.password.text()),
'alternate_password': self.creds_manager.encrypt_value(self.alt_password.text())
}
self.creds_manager.save_credentials([cred], credentials_path)The GUI initiates discovery through a worker thread that manages the core NetworkDiscovery class:
# GUI creates discovery configuration from form inputs
discovery_config = {
'seed_ip': self.seed_ip.text(),
'username': self.username.text(),
'password': self.password.text(),
'max_devices': self.max_devices.value(),
'output_dir': Path(self.output_dir.text()),
'layout_algo': self.layout_algo.currentText()
}
# Initialize discovery engine with GUI-provided configuration
discovery = NetworkDiscovery(DiscoveryConfig(**discovery_config))Key components initialized:
- Queue System - Device processing queue
- Tracking Sets - Visited IPs, failed devices, unreachable hosts
- Logger - Progress and debug logging with GUI callback
- Driver Discovery - Multi-vendor device support
# Initialize with seed device from GUI configuration
seed_device = DeviceInfo(
hostname=config.seed_ip,
ip=config.seed_ip,
username=config.username,
password=config.password,
timeout=config.timeout
)
queue.put(seed_device)The main discovery loop operates with real-time GUI feedback:
# GUI receives progress updates through Qt signals
def _handle_progress(self, progress_data):
"""Handle progress updates from NetworkDiscovery"""
ip = progress_data.get('ip')
status = progress_data.get('status')
# Update GUI elements in real-time
if ip and status:
self.device_discovered.emit(ip, status) # Updates device list
# Update progress statistics
self.progress_update.emit({
'devices_discovered': progress_data.get('devices_discovered', 0),
'devices_failed': progress_data.get('devices_failed', 0),
'devices_queued': progress_data.get('devices_queued', 0)
})The discovery process maintains the same core logic while providing GUI integration:
# Each device triggers GUI updates
while not queue.empty() and devices_discovered < max_devices:
current_device = queue.get()
# GUI shows "processing" status
self.emit_device_discovered(current_device.hostname, "processing")
# Apply exclusion patterns from GUI configuration
exclude_patterns = self.config.exclude_string.split(',')
if matches_exclude_pattern(current_device.hostname):
continueThe GUI provides rich visual feedback during each discovery phase:
- Device List Widget: Real-time device status with color coding (green=success, red=failed)
- Progress Statistics: Live counters for discovered, failed, queued, and total devices
- Log Output: Detailed discovery events with user-selectable log levels
- Cancellation Control: User can abort discovery with immediate cleanup
Upon discovery completion, the GUI automatically:
def on_discovery_complete(self, stats):
"""Handle discovery completion with immediate visualization"""
# Load generated network map
json_map_path = Path(config['output_dir']) / f"{config['map_name']}.json"
self.preview_widget.load_topology(json_map_path)
# Enable enhancement and viewer tools
self.enhance_button.setEnabled(True)
self.viewer_button.setEnabled(True)For each discovered neighbor, the system processes both CDP and LLDP data:
for protocol in ['cdp', 'lldp']:
protocol_neighbors = neighbors.get(protocol, {})
for neighbor_id, data in protocol_neighbors.items():
# Normalize hostname
normalized_neighbor_id = _normalize_hostname(neighbor_id)
# Process connections
for connection in data.get('connections', []):
local_port = InterfaceNormalizer.normalize(connection[0])
remote_port = InterfaceNormalizer.normalize(connection[1])For Cisco IOS devices, the system performs enhanced CDP parsing using the TextFSM Fire engine:
if capabilities['platform'] == "ios":
get_ios_cdp(current_device, capabilities)This addresses NAPALM's limitations by using TextFSM templates to parse show cdp neighbors detail output directly:
# Use TextFSMAutoEngine for accurate parsing
engine = TextFSMAutoEngine("secure_cartography/tfsm_templates.db")
template_name, parsed_data, score = engine.find_best_template(cdp_output, "cdp_neighbors_detail")The TextFSM Fire engine provides:
- Template Auto-Selection: Automatically finds the best matching template
- Scoring Algorithm: Evaluates parsing quality based on data completeness
- Thread-Safe Operations: Supports concurrent device processing
- Error Recovery: Graceful handling of parsing failures
Each connection is stored with:
- Local Port - Normalized interface name (e.g., "Gi0/1")
- Remote Port - Normalized interface name on neighbor
- Neighbor IP - Management IP address
- Platform - Device platform type
- Protocol - Discovery protocol (CDP/LLDP)
New devices are queued for discovery if:
- Device has a valid IP address
- Device hasn't been visited or queued
- Device doesn't match exclusion patterns
- Maximum device limit hasn't been reached
if neighbor_ip and not _is_known_device(neighbor_ip):
neighbor_device = DeviceInfo(
hostname=neighbor_ip,
ip=neighbor_ip,
username=config.username,
password=config.password,
timeout=config.timeout
)
queue.put(neighbor_device)Raw device objects are transformed into the standard mapping format:
transformed_map = transform_map(network_map)
# Result format:
{
"device_hostname": {
"node_details": {
"ip": "192.168.1.1",
"platform": "ios"
},
"peers": {
"neighbor_hostname": {
"ip": "192.168.1.2",
"platform": "eos",
"connections": [["Gi0/1", "Eth1"]]
}
}
}
}The system enriches peer data by cross-referencing discovered devices:
enriched_map = enrich_peer_data(transformed_map)This updates peer platform information using actual discovered device data when available.
Final hostname normalization ensures consistency:
- Removes domain suffixes (e.g., "router.domain.com" → "router")
- Handles special cases (Nexus devices reporting "Kernel" hostname)
- Merges duplicate entries
The GUI's "Enhance" button launches the TopologyEnhanceWidget, providing professional diagram customization:
def open_enhance_widget(self):
"""Open the Topology Enhance Widget in a non-modal window"""
self.enhance_window = QDialog(self)
self.enhance_window.setWindowTitle("Topology Enhance")
# Add the enhance widget
self.enhance_widget = TopologyEnhanceWidget()
layout.addWidget(self.enhance_widget)
self.enhance_window.resize(600, 400)
self.enhance_window.show()The enhancement tool transforms basic network diagrams into professional visualizations:
Icon Customization Features:
- Interactive Icon Editor: Map discovered device platforms to custom icons
- Vendor-Specific Shapes:
- Cisco devices: Router and switch icons with IOS/NX-OS variants
- Arista devices: EOS-specific switch representations
- HP/Aruba devices: ProCurve switch icons
- Generic devices: Configurable fallback icons
Multi-Format Icon Support:
# GraphML enhancement for yEd compatibility
if device_platform == 'ios':
node_style = 'cisco_router_icon'
elif device_platform == 'eos':
node_style = 'arista_switch_icon'
elif device_platform == 'nxos_ssh':
node_style = 'cisco_nexus_icon'Draw.io Integration:
- Custom Stencils: Network device shape libraries
- Automatic Styling: Platform-based icon assignment
- Collaborative Editing: Maintains compatibility with Draw.io web editor
- Professional Templates: Pre-configured icon sets for enterprise networks
The main interface provides multiple visualization options:
Map Preview Widget:
class TopologyPreviewWidget:
"""Embedded network map preview with theme support"""
def load_topology(self, json_path):
# Load network map data
# Apply current theme (dark/light mode)
# Render interactive previewStandalone Topology Viewer:
def open_topology_viewer(self):
"""Launch full-screen interactive topology viewer"""
viewer = TopologyViewer(
topology_data=topology_data,
dark_mode=self.dark_mode,
parent=self
)
viewer.show()The GUI maintains visual consistency across all components:
def set_dark_mode(self, is_dark: bool):
"""Apply theme to entire application"""
if is_dark:
app.setPalette(self.dark_palette)
# Update preview widget theme
self.preview_widget.dark_mode = is_dark
# Regenerate diagrams with dark theme
if hasattr(self, 'current_json_path'):
self.preview_widget.load_topology(self.current_json_path)Theme Features:
- System-wide Dark/Light Mode: Consistent across all interface elements
- Dynamic Theme Switching: Real-time theme changes without restart
- Diagram Theme Sync: Network diagrams automatically match interface theme
- Preference Persistence: Theme choice saved with encrypted settings
The TextFSM Fire engine (tfsm_fire.py) is a sophisticated template matching system that automatically selects the best TextFSM template for parsing network device output. This addresses limitations in existing parsing libraries by providing intelligent template selection and scoring.
class ThreadSafeConnection:
"""Thread-local storage for SQLite connections"""
def __init__(self, db_path: str, verbose: bool = False):
self.db_path = db_path
self._local = threading.local()
@contextmanager
def get_connection(self):
"""Get a thread-local connection"""
if not hasattr(self._local, 'connection'):
self._local.connection = sqlite3.connect(self.db_path)The engine maintains thread-local SQLite connections to support concurrent device processing without database locking issues.
def find_best_template(self, device_output: str, filter_string: Optional[str] = None):
"""Try filtered templates against output and return best match"""
best_score = 0
# Filter templates by command type
templates = self.get_filtered_templates(conn, filter_string)
for template in templates:
# Parse output with current template
parsed = textfsm_template.ParseText(device_output)
score = self._calculate_template_score(parsed_dicts, template, device_output)
if score > best_score:
best_score = score
best_template = template['cli_command']
best_parsed_output = parsed_dictsThe engine evaluates template effectiveness using multiple factors:
-
Record Count Scoring (0-30 points):
- Version commands: 30 points for single record, 15 for multiple
- Other commands: 10 points per record (max 30)
-
Data Completeness Scoring:
- Evaluates field population rates
- Penalizes empty or null values
- Rewards comprehensive data extraction
-
Command Type Matching:
- Exact command matches receive higher scores
- Partial command matches receive moderate scores
- Generic templates receive lower baseline scores
def _calculate_template_score(self, parsed_data: List[Dict], template: sqlite3.Row, raw_output: str) -> float:
score = 0.0
# Record count scoring
num_records = len(parsed_data)
if 'version' in template['cli_command'].lower():
score += 30 if num_records == 1 else 15
else:
score += min(30, num_records * 10)
# Data completeness evaluation
if parsed_data:
populated_fields = sum(1 for record in parsed_data
for value in record.values()
if value and value.strip())
score += populated_fields * 2
return scoreThe SQLite database contains:
- Template Content: TextFSM template definitions
- Command Mappings: CLI commands to template associations
- Metadata: Template descriptions and vendor information
- Performance Metrics: Historical parsing success rates
The TextFSM Fire engine integrates seamlessly with the discovery process:
def get_ios_cdp(self, device, capabilities):
"""Enhanced CDP parsing using TextFSM Fire"""
# Get raw CDP output
cdp_output = net_connect.send_command("show cdp neighbors detail")
# Use TextFSM Fire for parsing
engine = TextFSMAutoEngine("secure_cartography/tfsm_templates.db")
template_name, parsed_data, score = engine.find_best_template(
cdp_output,
"cdp_neighbors_detail"
)
if parsed_data and score > 0:
# Convert to capabilities schema
cdp_neighbors = {}
for entry in parsed_data:
hostname = entry['NEIGHBOR_NAME'].split('.')[0]
cdp_neighbors[hostname] = {
'ip': entry['MGMT_ADDRESS'],
'platform': 'ios' if 'cisco' in entry['PLATFORM'].lower() else 'unknown',
'connections': [[entry['LOCAL_INTERFACE'], entry['NEIGHBOR_INTERFACE']]]
}- Template Filtering: Pre-filters templates based on command context
- Lazy Loading: Templates loaded only when needed
- Connection Pooling: Thread-local database connections
- Scoring Cache: Results cached for repeated parsing operations
- Graceful Degradation: Falls back to NAPALM if TextFSM parsing fails
- Template Validation: Verifies template syntax before execution
- Verbose Logging: Detailed parsing attempts for troubleshooting
- Thread Safety: Isolated error handling per processing thread
While the GUI is the primary interface, a CLI version supports automation scenarios:
The CLI processes configuration from multiple sources with precedence:
- Defaults - Base configuration values
- YAML Config - Configuration file (if provided)
- CLI Arguments - Command-line parameters
- Environment Variables - Highest precedence (SC_USERNAME, SC_PASSWORD, etc.)
# YAML configuration approach
sc --config network.yaml --seed-ip 192.168.1.1 --verbose
# Environment variable approach
SC_USERNAME=admin SC_PASSWORD=secret sc --config base.yaml
# Full CLI specification
sc --seed-ip 10.1.1.1 --max-devices 100 --exclude-string "sep,phone" --output-dir /tmp/maps# Save primary network map
map_path = output_dir / f"{map_name}.json"
with open(map_path, "w") as fh:
json.dump(normalized_map, indent=2, fp=fh)The system generates multiple output formats:
GraphML (.graphml)
- Compatible with yEd Graph Editor
- Supports advanced layout algorithms
- Professional network diagram capabilities
Draw.io (.drawio)
- Web-based collaborative editing
- Multiple export formats
- Custom network device stencils
SVG (.svg)
- Scalable vector graphics
- Direct preview in applications
- Supports both light and dark themes
create_network_diagrams(normalized_map, output_dir, map_name, layout_algo)Multiple layout options are supported:
- Kamada-Kawai (kk) - Force-directed layout for general topologies
- Spring (rt) - Real-time spring layout
- Circular - Circular arrangement for ring topologies
# Create graph from network map
G = nx.Graph()
for node, data in map_data.items():
G.add_node(node, ip=data['node_details']['ip'])
for peer, peer_data in data['peers'].items():
if peer in map_data:
G.add_edge(node, peer, connection=connection_label)The system creates publication-quality SVG diagrams with:
- Balloon Layout - Hierarchical positioning with core devices centered
- Interface Labels - Connection information on edges
- Theme Support - Dark/light mode compatibility
- Device Icons - Vendor-specific visual representations
- Connection Timeouts - Individual device connection limits
- Global Timeouts - Overall discovery process limits
- Retry Logic - Platform detection fallbacks (e.g., IOS → NX-OS)
# Handle Nexus devices misidentified as IOS
if discovered_hostname in ['Kernel', 'Unknown']:
# Retry with nxos_ssh platform
alternate_capabilities = get_device_capabilities(
alternate_device_with_nxos_platform
)Real-time statistics are maintained:
- Devices Discovered - Successfully processed devices
- Devices Failed - Connection or processing failures
- Devices Queued - Pending discovery queue size
- Unreachable Hosts - Network connectivity failures
output_directory/
├── map_name.json # Primary network map data
├── map_name.graphml # yEd-compatible format
├── map_name.drawio # Draw.io format
└── map_name.svg # SVG visualization
- Credentials - Securely encrypted and stored
- Discovery State - Progress and statistics tracking
- Debug Information - Detailed logs for troubleshooting (optional)
seed_ip: 192.168.1.1
max_devices: 500
output_dir: "./network_maps"
verbose: true
map_name: production_network
layout: "kk"
domain: 'company.local'
exclude: 'test-,dev-,phone'
timeout: 60export SC_USERNAME=netadmin
export SC_PASSWORD=secure_password
export SC_ALT_USERNAME=readonly
export SC_ALT_PASSWORD=readonly_passThis comprehensive discovery process enables automated mapping of complex multi-vendor network environments while maintaining security through encrypted credential storage and providing multiple output formats for different use cases.