The WiDS Datathon challenged us to uncover the mysteries of the female brain, particularly the unique sex patterns observed in ADHD. By diving deep into functional connectivity and neural interactions, our research aims to reveal how the female brain differs in its response to ADHD. These insights could pave the way for more personalized, sex-specific approaches in ADHD diagnosis and treatment, ultimately demystifying the complex neural underpinnings that contribute to behavioral differences.
- Team Members
- Project Highlights
- Setup and Execution
- Project Overview
- Data Exploration
- Model Development
- Results and Key Findings
- Impact Narrative
- Next Steps & Future Improvements
- References & Additional Resources
The Mysteries of the Female Brain: Sex Patterns in ADHD
WiDS Datathon 2025 Kaggle Competition
| Name | GitHub Handle | Contribution |
|---|---|---|
| Mariia Nikitash | @MariiaNikitash | Data Understanding & Preprocessing, Feature Engineering, Model Development & Implementation |
| Shubhangi Waldiya | @shubhangibw | Data Understanding & Preprocessing, Model Development, Implementation & Evaluation |
| Ami Rajesh | @Arajesh03 | Data Preprocessing, Feature Engineering, Model Development & Evaluation |
| Itzalen Lopez | @Itz-creator07 | Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA), Data Visualization, Model Development, & GitHub README Project Implementation |
- Babu Swagath
- We (UCLA_WiDS_Team_2) placed 1 out of 26 teams from Break Through Tech AI at UCLA program.
- Ranked 157 (out of 1075) on the final official Kaggle leaderboard.
- Developed a multi-outcome machine learning model to predict ADHD diagnosis and sex differentiation in females.
- Used functional MRI connectome matrices and socio-demographic data to improve ADHD diagnostic processes.
- Aimed to better understand brain activity patterns for personalized treatment of ADHD.
- Researched various models with a focus on binary classification.
- Collaboratively analyzed the datasets for key insights.
- Executed similar preprocessing steps tailored to individual workflows.
-
Decision Trees:
- Highest Accuracy: 0.69
-
Random Forest:
- Accuracy = 0.66
- Cross-validation scores: [0.67489712, 0.68312757, 0.62139918, 0.66528926, 0.6322314]
- Mean accuracy = 0.6554
-
Logistic Regression:
- Accuracy = 0.74
- Detailed Metrics:
precision recall f1-score support False 0.64 0.11 0.18 65 True 0.75 0.98 0.85 178 accuracy 0.74 243 macro avg 0.69 0.54 0.52 243 weighted avg 0.72 0.74 0.67 243 - Cross-validation scores: [0.74485597, 0.70781893, 0.66666667, 0.69421488, 0.65289256]
- Mean accuracy = 0.6933
-
XGBoost:
- Accuracy = 0.7582
- F1 Score = 0.8174
-
K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN):
- Highest Accuracy: 0.55
-
Best Performing Model: Highest Accuracy = 76.031%
-
Key Details:
- COMBINED.ipynb: Central notebook for final experiments.
- Best Decision Tree model predicted the ADHD column.
- Optimized Random Forest model predicted the SEX column.
- Extensive parameter tuning was performed.
- Graphical representations of model performance were included.

|
Kaggle is a collaborative platform where data scientist share datasets, build models and compete in machine learning challenges. |
|
|
🔗 WiDS Datathon 2025 Kaggle Competition Page |
Follow these step-by-step instructions to run this repository on Google Colab and GitHub.
-
Open Google Colab, start a new notebook, and run the following command to download the repository:
!git clone https://github.com/UCLA-WiDS-Team/adhd-brain-prediction.git %cd adhd-brain-prediction
-
This will copy all code files from GitHub into your Colab environment.
-
Install the required libraries manually using the following command. This includes libraries such as pandas, numpy, matplotlib, seaborn, scikit-learn, and others necessary for running the code:
!pip install pandas numpy matplotlib seaborn scikit-learn
✅ Automate installation of all required libraries, ensure version consistency across different setups, and save time by avoiding missing dependencies.
The datasets are hosted on Kaggle, and it must be downloaded from the competition page:
🔗 WiDS Datathon 2025 Dataset
-
First, install Kaggle API:
!pip install kaggle
-
Upload your Kaggle API key (
kaggle.json). You can generate this key from your Kaggle account under Account Settings:from google.colab import files files.upload() # Upload kaggle.json
-
Move the API key to the correct directory and set permissions:
!mkdir -p ~/.kaggle !mv kaggle.json ~/.kaggle/ !chmod 600 ~/.kaggle/kaggle.json
-
Run the following command to download the dataset:
!kaggle competitions download -c widsdatathon2025
-
Extract the dataset:
!unzip widsdatathon2025.zip
-
Load the dataset into a pandas DataFrame:
import pandas as pd df = pd.read_csv("train.csv") # Adjust filename if needed df.head()
The Kaggle API key is required to programmatically download datasets from Kaggle directly into Google Colab. Without it, you would need to manually download the dataset from Kaggle and upload it to Colab. The key helps with:
- Authentication – Kaggle restricts dataset access to registered users, so an API key verifies your identity.
- Automated Downloads – Fetch datasets directly without manual intervention.
- Colab Integration – Since Colab runs in the cloud, it doesn’t store your Kaggle login credentials.
- Reproducibility – Ensures others running your code can fetch the exact dataset without extra steps.
- Open the Google Colab notebook from the cloned repository.
- Run all cells sequentially to reproduce results.
-
If executing a standalone Python script, use the following command:
!python your_script.py
This guide ensures a smooth setup process by covering:
- ✅ Cloning the GitHub repository
- ✅ Installing dependencies (e.g., pandas, numpy, etc.)
- ✅ Downloading the WiDS Datathon 2025 dataset from Kaggle
- ✅ Explaining the need for the Kaggle API key
- ✅ Running the notebook or script for execution
This structured approach ensures users:
- ✅ Properly clone the repository before proceeding
- ✅ Understand the code's source and execution process
- ✅ Follow a clear flow: cloning → installing dependencies → downloading data → executing the code 🚀
The Women in Data Science (WiDS) Datathon 2025 is a Kaggle competition aimed at encouraging women in AI and data science. This initiative is part of the Break Through Tech AI Program that seeks to bridge the gender gap in AI by offering real-world machine learning challenges.
Our team is analyzing The Mysteries of the Female Brain: Sex Patterns in ADHD, a project designed to identify differences in ADHD diagnosis and manifestations in females using AI-driven predictions. The model predicts:
- ADHD diagnosis (1 = ADHD, 0 = No ADHD)
- Sex (1 = Female, 0 = Male)
ADHD diagnosis can be challenging, especially in females, due to symptom presentations. Our model aims to:
- Improve diagnostic accuracy for ADHD in females
- Investigate brain activity patterns and their correlation with ADHD across genders
- Contribute to personalized treatment options for ADHD
Our project leverages data from the Healthy Brain Network (HBN), which includes:
- Functional MRI connectome matrices
- Socio-demographic data
- Behavioral and parenting assessments
- ADHD diagnostic labels
- Analyze distributions and relationships within the data (e.g., socio-demographic variables and MRI metrics).
- Process categorical data and combine it with the functional connectome matrices.
- Identify outliers, missing values, and noise to inform feature engineering and preprocessing strategies.
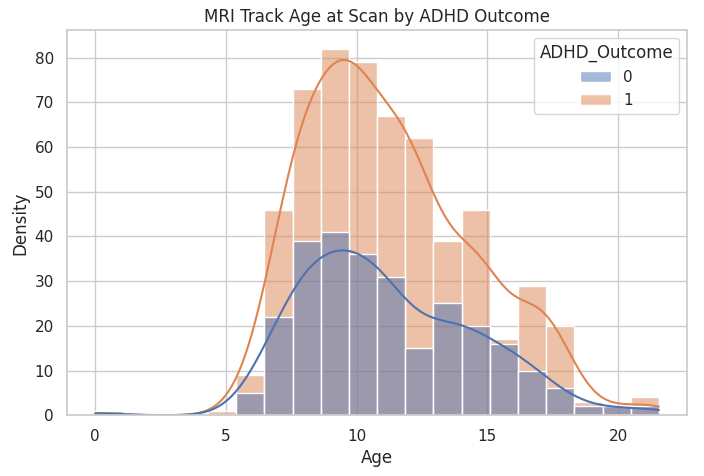
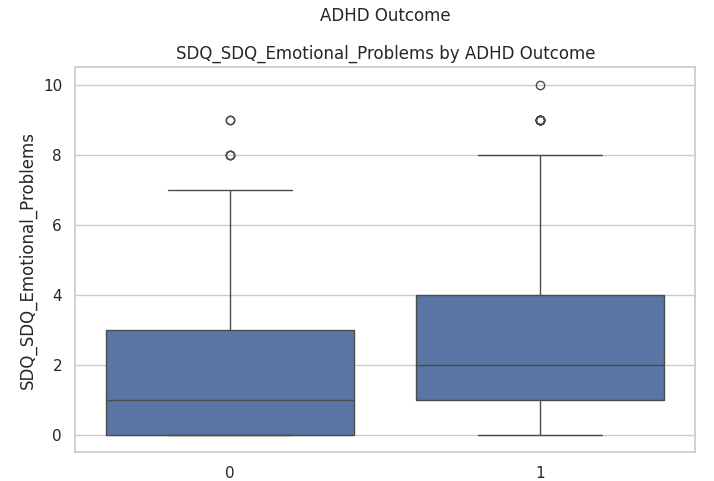
Visualizations - Visualized brain activity patterns and their link to ADHD - Examined demographic distributions and ADHD correlations - Assessed feature importance in model development
-
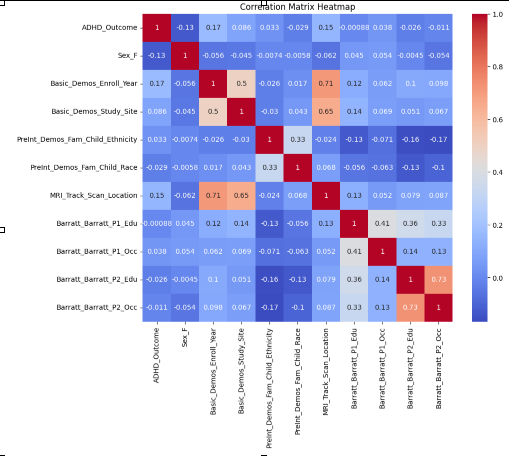
Feature Correlation Matrix Heatmap for Multiple Brain Regions
-
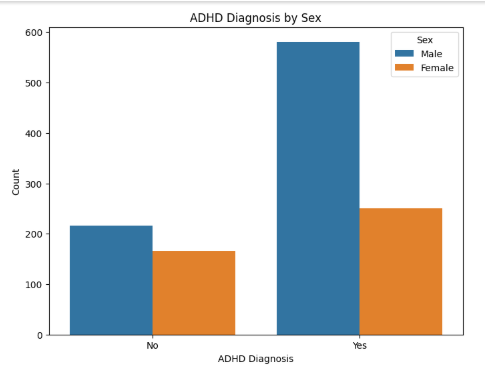
Distribution of ADHD vs. Non-ADHD Participants by Demographics
-
Model(s) Used:
- Experiments included Decision Trees, Random Forest, Logistic Regression, XGBoost, and K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN).
- The final model combined Decision Trees and Random Forest, achieving the highest accuracy.
-
Feature Selection & Hyperparameter Tuning Strategies:
- Feature selection was guided by exploratory data analysis (e.g., correlation analysis using functional MRI connectome matrices).
- Hyperparameter tuning (e.g., grid search for maximum tree depth, regularization parameters) was performed to optimize model performance.
-
Training Setup:
- Data was split into training and validation sets.
- Evaluation metrics included accuracy and F1 score, with baseline performance established using Logistic Regression.
-
Performance Metrics:
- Overall, the model achieved a Kaggle leaderboard accuracy of 76.031%.
- Detailed metrics (e.g., F1 scores, cross-validation scores) are provided for each model variant.
-
Overall Model Performance:
- The combined Decision Trees and Random Forest approach delivered the best performance among the models explored.
Potential Visualizations to Include:
- Confusion Matrix
- Precision-Recall Curve
- Feature Importance Plot
- Prediction Distribution
- Outputs from Fairness or Explainability Tools
WiDS Challenge:
-
What brain activity patterns are associated with ADHD; are they different between males and females, and, if so, how?
Our analysis of functional connectivity suggests that individuals with ADHD exhibit distinct neural activity patterns compared to those without ADHD. In particular, disruptions in the communication between regions responsible for attention, executive control, and emotional regulation were observed. Furthermore, preliminary results indicate potential sex-specific differences, where females may show alternative connectivity patterns or varying levels of activation in certain brain networks compared to males. These differences could be influenced by developmental, hormonal, or genetic factors, emphasizing the need for tailored approaches when studying ADHD.
-
How could your work help contribute to ADHD research and/or clinical care?
By applying advanced machine learning techniques to functional MRI connectome data alongside socio-demographic variables, our work enhances the understanding of ADHD’s neural underpinnings. This improved insight can aid in:
- Early Diagnosis: Providing biomarkers based on brain connectivity that may support earlier and more accurate identification of ADHD.
- Personalized Treatment: Informing the development of targeted therapies that account for individual differences, including sex-specific neural profiles.
- Research Advancement: Offering a framework for integrating complex neuroimaging data with clinical metrics, thereby contributing to a more comprehensive model of ADHD that can be validated in larger studies.
Overall, our findings aim to bridge the gap between neuroscience research and clinical practice, ultimately improving the diagnostic and therapeutic landscape for ADHD.
-
Model Limitations:
- The current model, despite its high accuracy, may be sensitive to noise and outliers in the functional MRI data.
- Limited demographic diversity in the training data might affect the model’s fairness and generalizability.
-
Improvements with More Time/Resources:
- Perform extensive hyperparameter tuning and explore advanced deep learning architectures to capture more complex patterns.
- Implement robust cross-validation techniques (e.g., nested cross-validation) to better assess model performance.
- Enhance data preprocessing and feature engineering to reduce noise and improve feature representation.
-
Additional Datasets/Techniques to Explore:
- Integrate external neuroimaging datasets to validate model generalizability across different populations.
- Investigate model explainability methods (e.g., SHAP, LIME) to gain insights into feature importance and decision-making processes.
- Explore transfer learning approaches to leverage pre-trained models for similar neuroimaging tasks.
- Kaggle Competition: WiDS Datathon 2025
-
GitHub: GitHub
-
Notion: Notion
-
Google Colab: Google Colab
-
Jupyter: Jupyter
-
NumPy: NumPy
-
Pandas: Pandas
-
Matplotlib: Matplotlib
-
scikit-learn: scikit-learn
-
Conda: Conda