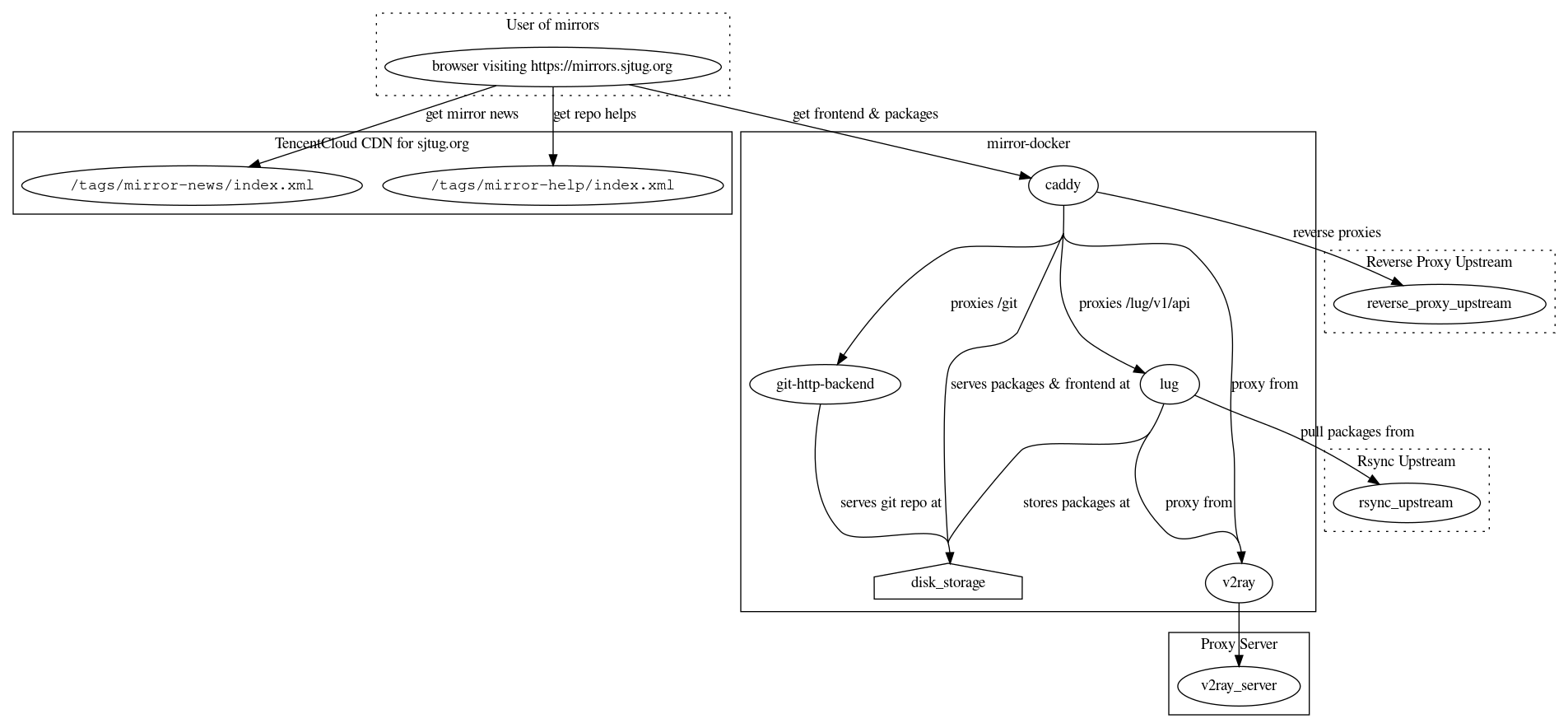
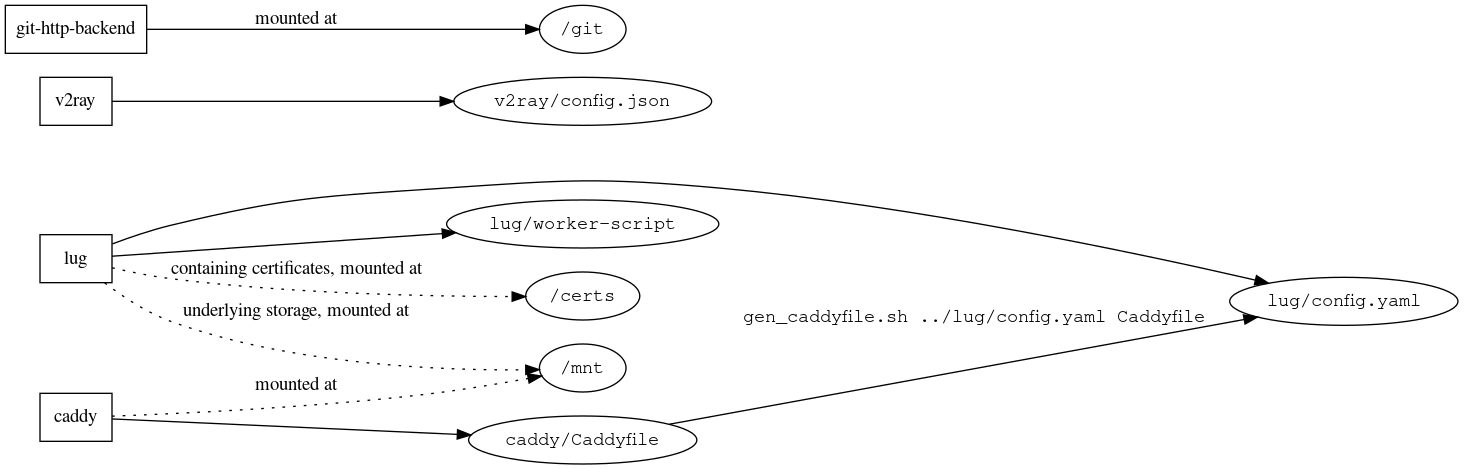
This repository contains essential configurations and steps to set up a mirror like https://mirrors.sjtug.sjtu.edu.cn
- lug is the component responsible for pulling packages from upstream by invoking various scripts under
lug/worker-script. It reads configuration fromlug/config.yamland stores data at/mnt. - caddy is the web server we used in mirror. It serves local packages from
/mnt, work as a reverse proxy for upstream, and provides basic authentication for lug API as its reverse proxy. It reads configuration fromcaddy/Caddyfile, which is generated by running./gen_caddyfile.sh ../lug/config.yaml Caddyfileincaddy/. The generator reads template fromcaddy/Caddyfile.template.p2. Additionally, the certificate for the website is currently externally provided: mounted at/certs. - v2ray is the proxy solution used in this stack. Both Lug and Caddy rely on it for reliable networks. It reads configuration from
v2ray/config.json. - git-http-backend is used to provide git repo mirroring service.
- Install Docker(>=17.06) following https://docs.docker.com/install
- Install docker-compose following https://docs.docker.com/compose/install/
- Update
/etc/docker/daemon.jsonto:
{
"storage-driver": "overlay2",
"registry-mirrors": ["https://docker.mirrors.ustc.edu.cn"],
"userland-proxy": false
}With Docker v.17.06 there is a new iptables chain called DOCKER-USER. Unlike the chain DOCKER it is not reset on building/starting containers. So you could add these lines to your iptables config/script for provisioning the server even before installing docker and starting the containers:
Add these to iptables rules (/etc/sysconfig/iptables-config on Fedora):
-N DOCKER-USER
-A DOCKER-USER -p tcp -i enp+ -s 172.16.0.0/12 -j RETURN
-A DOCKER-USER -p tcp -i enp+ -s 192.168.0.0/16 -j RETURN
-A DOCKER-USER -p tcp -i enp+ --syn -m hashlimit --hashlimit 15/s --hashlimit-burst 30 --hashlimit-mode srcip --hashlimit-srcmask 32 --hashlimit-name forward-syn-reject -j RETURN
-A DOCKER-USER -p tcp -i enp+ --syn -j REJECT
Change enp+ to your names of physical interfaces.
Configure v2ray to connect to your v2ray-server. Follow docs at https://www.v2ray.com/.
Refer to Wiki for detailed explanation.
Refer to Caddy's docs.
cd into caddy. Run ./gen_caddyfile.sh ../lug/config.yaml Caddyfile
- Install
jqin your distribution cdintofrontend. Rundownload_latest.shto download the latest frontend release from https://github.com/sjtug/sjtug-mirror-frontend todist/.
- Change
/mnt/data12Tto your storage path - Change resource limits to your needs
Run at base: docker-compose -d
By default, the prometheus metrics of caddy and lug are exposed at :9180, :8081 respectively. You can set up Prometheus+Grafana stack on another server.
logz.io-based ELK stack
- Register a new account at logz.io
- Configure
config.yamlas follows:
logstash:
address: listener.logz.io:5050 # logstash sink. Lug will send all logs to this address
additional_fields:
token: "your_logz_token" - Also install logz docker logging collector on the host
- Enable "Log shipping - Data parsing" for
caddylog type - Done! Create your dashboard and alerts at app.logz.io