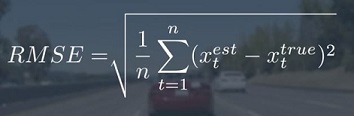This repository contains C++ code for implementation of Unscented Kalman Filter project. This task was implemented to partially fulfill Term-II goals of Udacity's self driving car nanodegree program.
Self driving cars make use of Laser sensor (LIDAR) and/or Radial distance and angle sensor (RADAR) for tracking moving objects such as vehicles, pedestrians, animals, etc. Data received from LIDAR and RADAR is fused to best estimate the trajectory of motion of the object. In this project, trajectory of a bicycle moving in the shape of numerical figure 8 is estimated using LIDAR and RADAR measurements. This is achieved with the help of vanilla Kalman filter and Unscented version of Kalman filter.
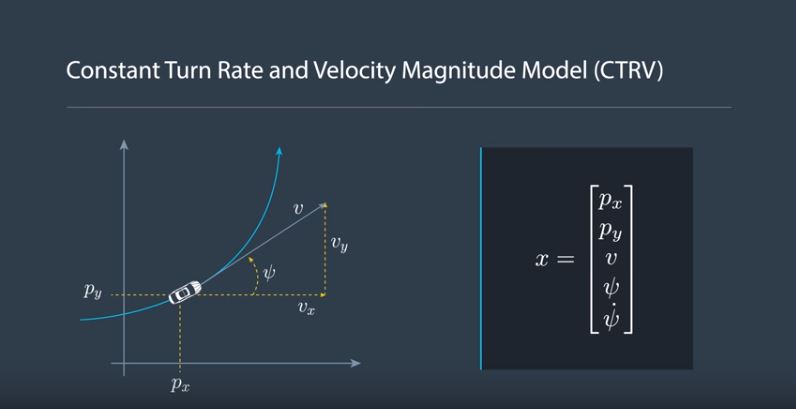
For this project, a Constant Turn Rate and Velocity (CTRV) model is assumed while building the state vector. The state vector contains following components:
- Position of the object in X axis (px)
- Position of the object in Y axis (py)
- Speed, or magnitude of velocity (v)
- Yaw angle (psi)
- Yaw rate, or rate of change of yaw angle (psidot)
where X and Y axis are relative to the direction in which the self driving car moves, shown below:
Following goals were achieved as a part of implementation:
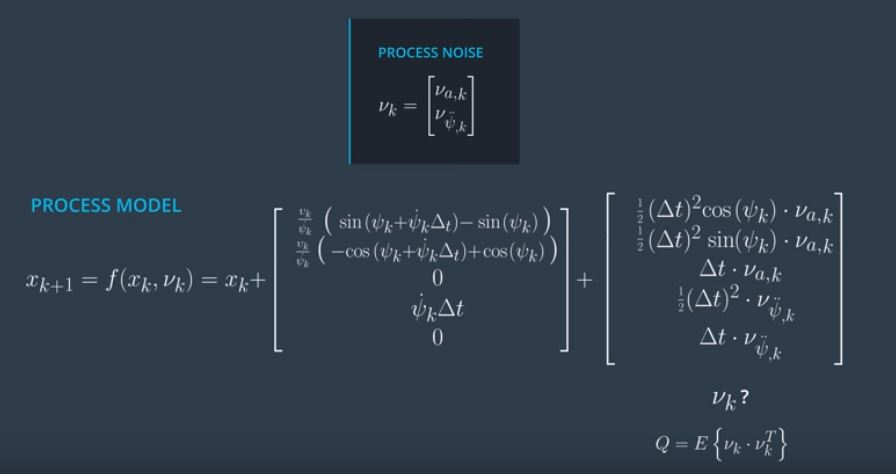
- Build the state vector and the state transition matrix. Derive state transition equation. This represents the deterministic part of motion model. Stochastic part of motion is represented by νak (For magnitude of acceleration) and νpsik (For yaw acceleration or the change in yaw rate). The state transition equation then derived is shown below:
where the noise is modelled by assuming Gaussian noise with zero mean and standard deviation. Hence, standard deviations are σa (For magnitude of acceleration) and σyaw (For yaw acceleration). This is shown below:
-
LIDAR measures the distance between self driving car and an object in X and Y axis. Hence, the measurement function for LASER updates, given by H_laser, is a linear transform.
-
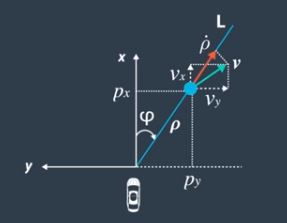
RADAR measures the radial distance, the bearing (or angle of orientation w.r.t car) and the radial velocity. This is represented below:
Hence, the measurement function for RADAR updates, given by H_radar, is a non-linear transform.
- Now that the state transition and measurement functions are derived, Kalman filter is used to estimate the path of moving object. Upon receiving a measurement for timestamp k+1, following processes are triggered:
a. Kalman filter Predict: To use the state vector at timestamp k (Xk) and predict the state vector at timestamp k (Xk+1). This is the updated belief after motion. b. Use the measurement and update the belief using Kalman filter update once measurement is received.
- Kalman filter predict step is same for LASER and RADAR measurements. This step involves use of Unscented Kalman Filter algorithm to predict the mean and covariance for the next step. Given the belief of state and covariance matrix at state k, Unscented Kalman Filter algorithm consists of following steps:
a. Generate sigma points: In this step, 2n + 1 sigma points are generated, where n is the number of states in state vector. Here, one sigma point is the mean of state while rest all are chosen on the uncertainty ellipse of the Gaussian distribution. b. Predict sigma points: The sigma points generated in step a are then passed through the process model and to predict the sigma points for the state k+1. c. Predict the mean and covariance: Predicted sigma points from step b are then used to calculate the predicted mean and covariance for the state k+1.
-
When a LASER measurement at step k+1 is received, use vanilla Kalman filter (since the measurement function is linear) equations to update the predicted belief in step 5.
-
When a RADAR measurement at step k+1 is received, again use Unscented Kalman filter (since the measurement function is non-linear) equations to update the predicted belief in step 5.
-
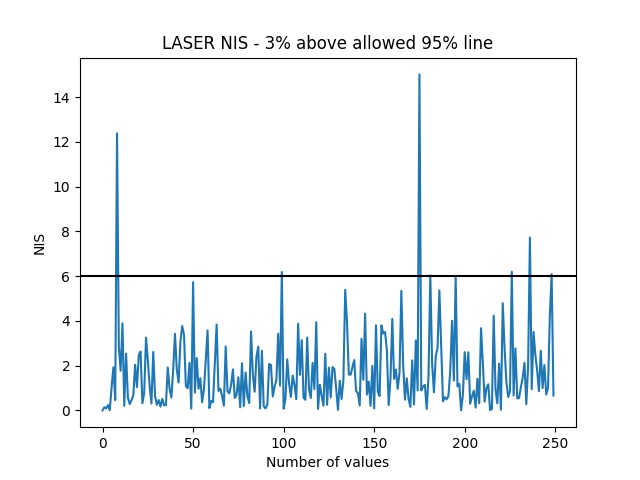
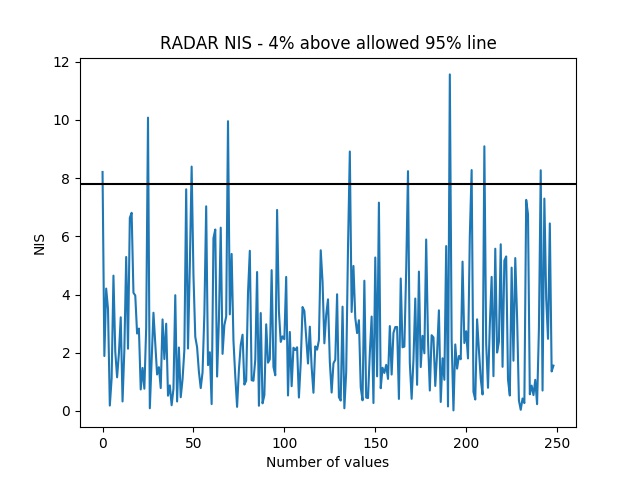
Take a note of Normalized Innovation Squared (NIS) at each step for both LASER and RADAR. Plot the NIS distribution and fine tune the process noise parameters (σa and σyaw) to attain consistency in the system. Equation for calculating NIS is given below:
- Calculate the root mean squared error (RMSE) after Kalman filter update at each time step. This is given by:
-
Implement Kalman filter algorithm in C++
-
Build the project and run the executable on dataset of LASER and RADAR measurements returned by Udacity simulator.
-
Calculate and capture the Normalized Innovation Squared (NIS) for LASER and RADAR. Plot the values and check for consistency. If not consistent, tune the process noise parameters σa and σyaw. The final tuned values for σa was 2 m/s2 and σyaw was 2 rad/s2. This resulted in NIS distributions shown below:
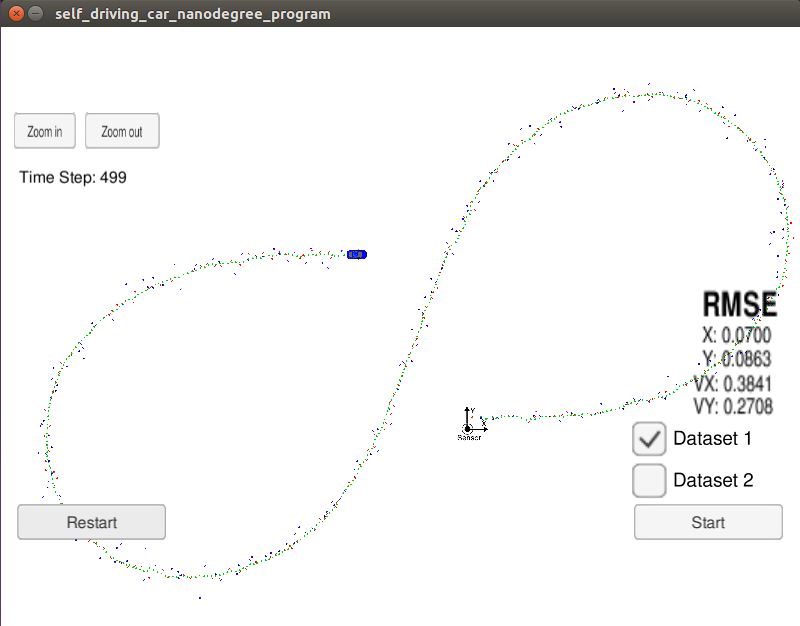
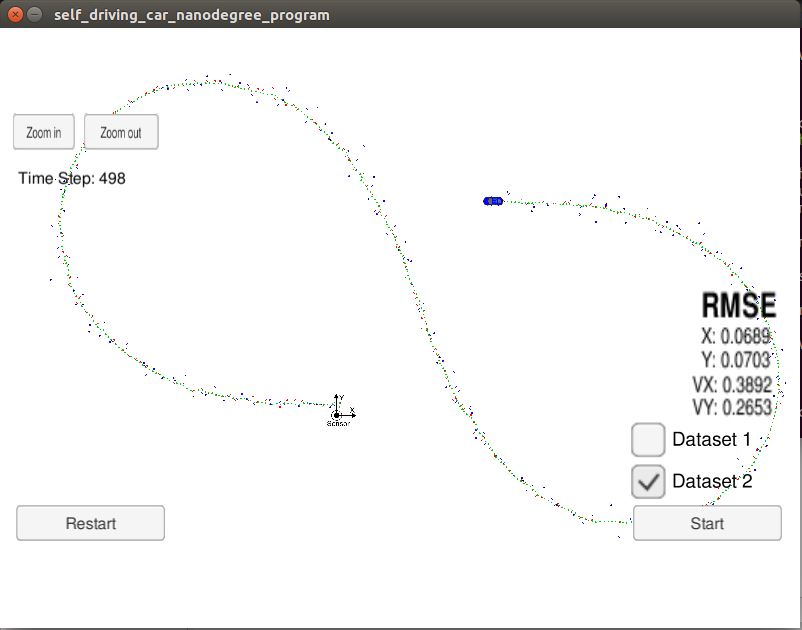
- Take a note of RMSE values at the last time step of dataset. Minimize the RMSE to bring it in the range of RMSE <= [.09, .10, 0.40, 0.30] for px, py, vx and vy respectively. RMSE values achieved after fine minimization are shown below:
Run on dataset 1
Run on dataset 2
-
cmake >= 3.5
-
All OSes: click here for installation instructions
-
Linux and Mac OS, you can also skip to installation of uWebSockets as it installs it as a dependency.
-
make >= 4.1(mac, linux), 3.81(Windows)
- Linux: make is installed by default on most Linux distros
- Mac: install Xcode command line tools to get make
- Windows: Click here for installation instructions
- Linux and Mac OS, you can also skip to installation of uWebSockets as it installs it as a dependency.
-
gcc/g++ >= 5.4
- Linux: gcc / g++ is installed by default on most Linux distros
- Mac: same deal as make - [install Xcode command line tools]((https://developer.apple.com/xcode/features/)
- Windows: recommend using MinGW
- Linux and Mac OS, you can also skip to installation of uWebSockets as it installs it as a dependency.
-
- Run either
install-mac.shorinstall-ubuntu.sh. This will install cmake, make gcc/g++ too. - If you install from source, checkout to commit
e94b6e1, i.e.Some function signatures have changed in v0.14.x.git clone https://github.com/uWebSockets/uWebSockets cd uWebSockets git checkout e94b6e1
- Run either
-
Simulator. You can download these from the Udacity simulator releases tab.
-
Execute every step from install-ubuntu.sh. This will install gcc, g++, cmake, make and uWebsocketIO API.
-
Build project a. mkdir build && cd build b. cmake .. c. make d. ./UnscentedKF
-
Run the Udacity simulator and test the implementation on dataset 1 and 2.