-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 5
Home
Contact info: thomas.sauter@uni.lu or sebastien.delandtsheer@uni.lu
Please cite : De Landtsheer et al., FALCON: A Toolbox for the Fast Contextualisation of Logical Networks (2017), Bioinformatics Link
Copyright: This software is freely available for non-commercial users under the GPLv3 license
FALCON is a toolbox for the efficient contextualization of logical network models. Contextualized network models provide important qualitative and quantitative information about the system being modelled. Specifically, FALCON is well suited to assess the relative contributions of different signal transduction mechanisms to the behavior of the system at steady-state. The logical formulation of the interaction between different molecules is intuitive, and often is the only available information to systems biologists. A Bayesian interpretation of the logical ‘gates’ allows for an algebraic formulation of the system and an efficient calculation of the long-term steady-state of the system given the specified inputs. A gradient-descent optimizer (fmincon) is used to minimize the error function calculated as the sum of squared residuals between the simulated and experimentally measured nodes of interest. FALCON offers multiple types of analysis including identifiability analysis, systematic knock-out and differential regulation which can be applied to various biological applications.
The FALCON toolbox was developed based on Systems Biology applications. Some of the key features are displayed in the following figure:
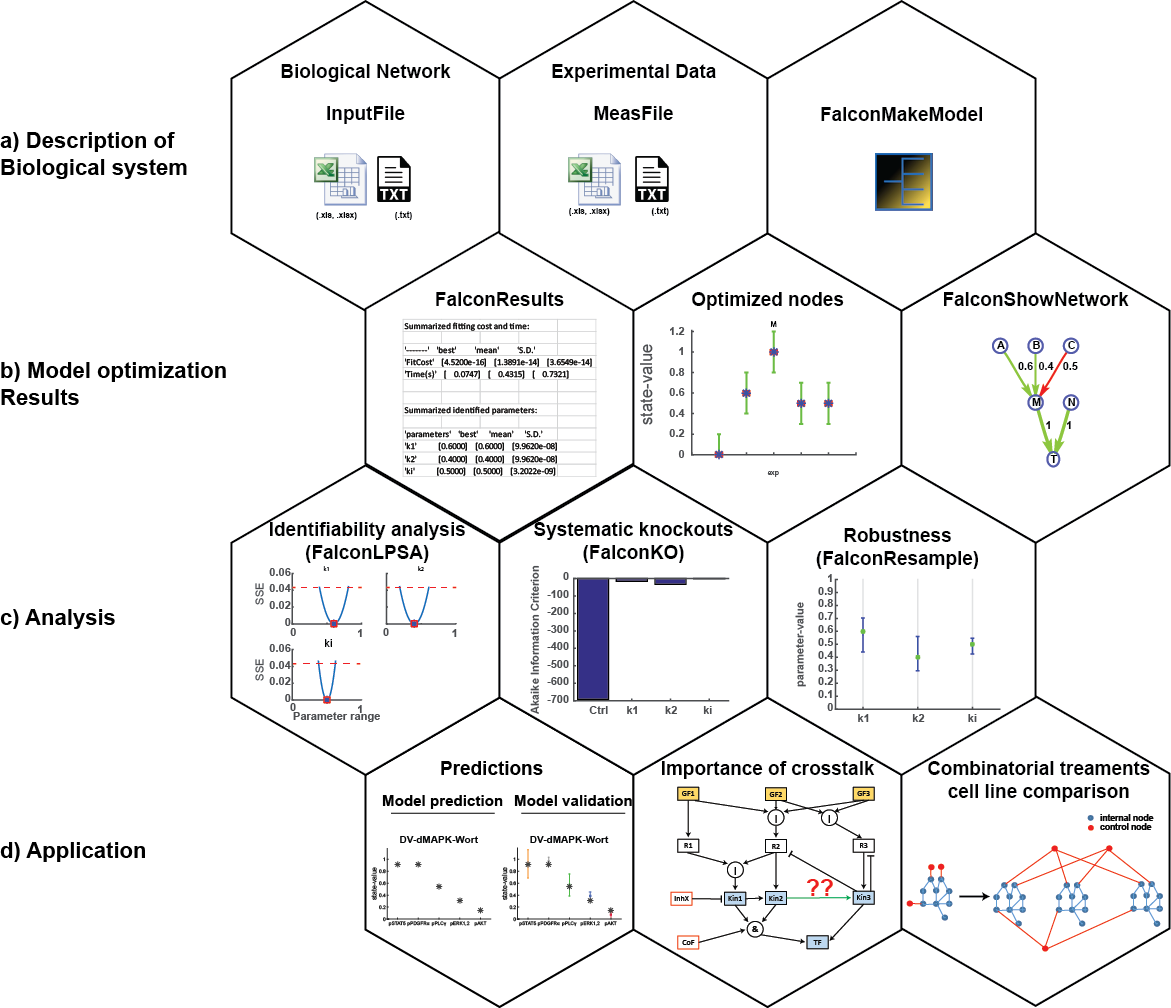
- Toy model
- PDGF (Trairatphisan,P. et al. (2016))
- MAPK (Saez-Rodriguez,J. et al. (2009))
- Apoptosis (Schlatter,R. et al. (2009))
In order to use the FALCON toolbox, the necessary scripts need to be included in the Matlab path. This can be done automatically by typing “FalconInstall” on the Matlab command window. The pipeline was developed under Matlab R2014b and has been successfully tested under Matlab R2015a and R2016b. It requires the build-in Matlab solver “fmincon”, which is a part of the Optimization Toolbox (http://nl.mathworks.com/products/optimization/), during the optimisation process. The parallel computing option in the FALCON pipeline which uses the “parfor” function requires the Parallel Computing Toolbox (http://nl.mathworks.com/help/distcomp/) and the (optional) plotting of network structure with optimised parameters requires the “biograph” function integrated in the Bioinformatics toolbox (http://nl.mathworks.com/help/bioinfo/) to be present.
In case you encounter any problems while running the FALCON pipeline on earlier of later versions of Matlab, please do not hesitate to contact the authors or post an issue under: https://github.com/sysbiolux/FALCON/issues.
The FALCON pipeline was rigorously tested before its release into the modelling community. Nevertheless, users might still encounter a few issues in the FALCON pipeline and we provide some potential solutions in this section.
- The FALCON scripts and examples are not added to the path
- The FALCON pipeline does not accept certain logical gate combinations
- The FALCON pipeline crashed during the analytical process
- Lommel,M.J. et al. (2016) L-plastin Ser5 phosphorylation in breast cancer cells and in vitro is mediated by RSK downstream of the ERK/MAPK pathway. FASEB J., 30, 1218–33. Link
- Saez-Rodriguez,J. et al. (2009) Discrete logic modelling as a means to link protein signalling networks with functional analysis of mammalian signal transduction. Mol. Syst. Biol., 5, 331. Link
- Schlatter,R. et al. (2009) ON/OFF and beyond--a boolean model of apoptosis. PLoS Comput. Biol., 5, e1000595. Link
- Trairatphisan,P. et al. (2016) A Probabilistic Boolean Network Approach for the Analysis of Cancer-Specific Signalling: A Case Study of Deregulated PDGF Signalling in GIST. PLoS One, 11, e0156223. Link
- Trairatphisan,P. et al. (2014) optPBN: an optimisation toolbox for probabilistic Boolean networks. PLoS One, 9, e98001. Link
- Del Mistro & Lucarelli et al. (2018) Systemic network analysis identifies XIAP and IκBα as potential drug targets in TRAIL resistant BRAF mutated melanoma. NPJ Systems Biology and Applications Link