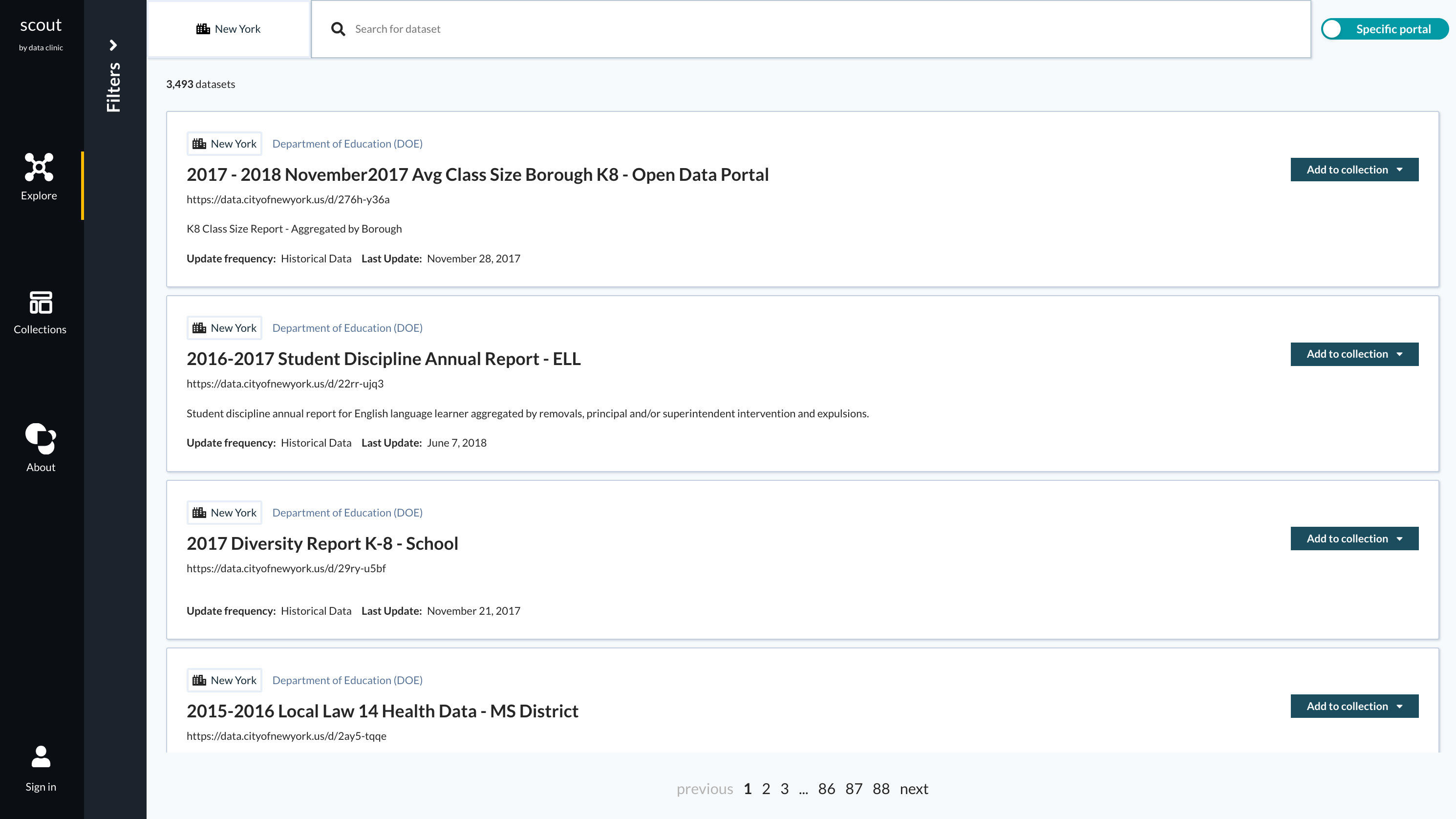
Scout is a data discovery tool for open data portals. It is an open source product that eases the search and curation of thematically related and joinable datasets to broaden the application of open data to uncover new insights. Scout is designed to help surface datasets in open data portals that might have escaped your attention before.
At the moment, Scout only provides access to open data portals made accessible via the Socrata API.
We love all contributions, be it a bug report, feature request, or change to the codebase. Check out our contributing guidelines for all the ways you can contribute to the project.
If you want to help with the development of Scout, you need to be able to run the code locally. The following steps will get you set up locally. If you run into problems, check out the troubleshooting section to see if the solution is already documented.
Make sure you have the following installed:
- Node
- Yarn
- Postgres (on MacOS we recommend installing with Homebrew rather than a manual download)
- Docker
To get started clone the repo and install requirements:
git clone https://github.com/tsdataclinic/scout.git
cd scout
yarn installYou need to set up your environment variables with the necessary API keys and configurations for the Scout app to run.
Add the following to your ~/.zshrc or ~/.bash_profile (depending on which shell you are running). If you are on Windows, you will need to add these as environment variables on your PowerShell, or whichever shell you use.
export SCOUT_GITHUB_CLIENT_ID='REPLACE_ME'
export SCOUT_GITHUB_CLIENT_SECRET='REPLACE_ME
export SCOUT_MAPBOX_API_KEY='REPLACE_ME'We use GitHub authentication for automated code searches to display helpful resources for datasets. You will need to replace these values with your GitHub Client ID and GitHub Client Secret which you can get by registering a GitHub application.
Remember to run source ~/.zshrc or source ~/.bash_profile to reload your environment variables after you've changed them.
NOTE: these instructions are just for local development which is all you need if you want to contribute. To deploy in production, you need to configure Azure AD B2C authentication as well. You can find the instructions on how to do that in the repo wiki.
The search backend uses OpenSearch. To run it locally, the easiest way to do it is with docker-compose:
docker-compose -f docker-compose.yml up
Note if you see an error about max_map_count then you need to increase that number with the following command:
sudo sysctl -w vm.max_map_count=262144
The TYPEORM variables in packages/server/.env are configured to point to a local postgres scout database. So we will need to create this database locally. First, start your postgres client:
psql postgres
Then, run the following commands inside it:
CREATE DATABASE scout;
CREATE USER postgres;
\c scout;
CREATE EXTENSION IF NOT EXISTS "uuid-ossp";
That's all you need to do in postgres. You can quit postgres by entering \q.
Make sure you are in the packages/server directory for all of the next commands. These will not work correctly from the root directory.
Change directory:
cd packages/server
Now create the necessary postgres tables:
yarn build
yarn sync-schemaIf you see a message that says Schema syncronization finished successfully. then it means you're good to go. Now that the tables are created, you need to populate them with data.
yarn seed-database-dev
This might take a while. It will populate postgres and OpenSearch with data from three open data portals. We intentionally do not add all 120+ portals to avoid waiting hours for this command to complete. If you wanted to populate your database with all portals, then run yarn seed-database-full-new. This is not recommended during development.
When you see the following message:
Done updating all data
Then it means the data refresh is done.
The API server uses NestJS and runs on https://localhost:5000. To start the API server:
cd packages/server
yarn start
The frontend is built in React and is bundled together using Create React App. It runs on https://localhost:3000 by default. To start the frontend server:
cd packages/frontend
yarn start
Then go to https://localhost:3000 to view the application. You're all set up now!
This is a collection of common problems that might come up during setup. If you run into a problem not listed here, please submit an issue about it so we can update this guide if necessary.
The TYPEORM_PASSWORD environment variable in packages/server/.env expects an empty password locally. If you installed Postgres through Homebrew then the Postgres user is configured by default to not require a password. If you installed Postgres through a different method, the password should be whichever you used when installing the database. You can resolve this problem with any of these three approaches:
- Open
pg_hba.confwherever Postgres is installed (usually in/usr/local/var/postgres/pg_hba.conf) and modify allMETHODvalues totrust. This should remove any password requirements. - Uninstall Postgres and re-install it using homebrew:
brew install postgresql - Change the
TYPEORM_PASSWORDin.envto be equal to the password you use to access your Postgres (which should be your system password or whatever you used when installing the database). If you add your password to.env, remember to NOT commit this password back.
Make sure you've set up your environment variables correctly.
Remember to reload your environment variables after you've changed them. You can do this by just opening a new terminal window. Alternatively, run source ~/.zshrc or source ~/.bash_profile (depending on your shell) to reload your environment variables after you've changed them.
Make sure your postgres server is running. If you just installed Postgres or just rebooted your computer, then it's likely your Postgres server is not running yet.
pg_ctl -D /usr/local/var/postgres start
If this command doesn't work then you should replace /usr/local/var/postgres with the path to your Postgres data directory. If you installed Postgres through homebrew then it might be in /opt/homebrew/var/postgres (you can run brew info postgres to find out where the data directory is).
If you see an error like this:
/home/runner/work/scout/scout/node_modules/react-scripts/node_modules/dotenv-expand/lib/main.js:11
var parts = /(.?)\${?([a-zA-Z0-9_]+)?}?/g.exec(match)
^
RangeError: Maximum call stack size exceeded
at RegExp.exec (<anonymous>)
at /home/runner/work/scout/scout/node_modules/react-scripts/node_modules/dotenv-expand/lib/main.js:11:49
at Array.reduce (<anonymous>)
at interpolate (/home/runner/work/scout/scout/node_modules/react-scripts/node_modules/dotenv-expand/lib/main.js:10:20)
at /home/runner/work/scout/scout/node_modules/react-scripts/node_modules/dotenv-expand/lib/main.js:26:17
at Array.reduce (<anonymous>)
at interpolate (/home/runner/work/scout/scout/node_modules/react-scripts/node_modules/dotenv-expand/lib/main.js:10:20)
at /home/runner/work/scout/scout/node_modules/react-scripts/node_modules/dotenv-expand/lib/main.js:26:17
at Array.reduce (<anonymous>)
at interpolate (/home/runner/work/scout/scout/node_modules/react-scripts/node_modules/dotenv-expand/lib/main.js:10:20)
Then it is likely because you have not set up your local environment variables which is causing an error when the servers try parsing the .env files.
If you're on MacOS running yarn seed-database-dev and you're getting an error that says that port 5000 is already in use, something that looks like this:
[Nest] 2416 - 06/10/2022, 10:17:30 AM ERROR [NestApplication] Error: listen EADDRINUSE: address already in use :::5000 +2ms
Error: listen EADDRINUSE: address already in use :::5000
at Server.setupListenHandle [as _listen2] (node:net:1372:16)
at listenInCluster (node:net:1420:12)
at Server.listen (node:net:1508:7)
at ExpressAdapter.listen
Then this could be because of AirPlay Receiver listening on that port by default. You can turn this off by following the instructions in this Apple support thread.
User guide coming soon.