React-Search is a UI widget for adding Vectara-powered semantic search to your React apps with a few lines of code.
Tip
Looking for something else? Try another open-source project:
- React-Chatbot: Add a compact Vectara-powered chatbot widget chat to your React apps.
- Create-UI: The fastest way to generate a working React codebase for a range of generative and semantic search UIs.
- Vectara Answer: Demo app for Summarized Semantic Search with advanced configuration options.
- Vectara Ingest: Sample templates and crawlers for pulling data from many popular data sources.
The search input looks like this:
When the user clicks the search input, they get a search prompt like this:
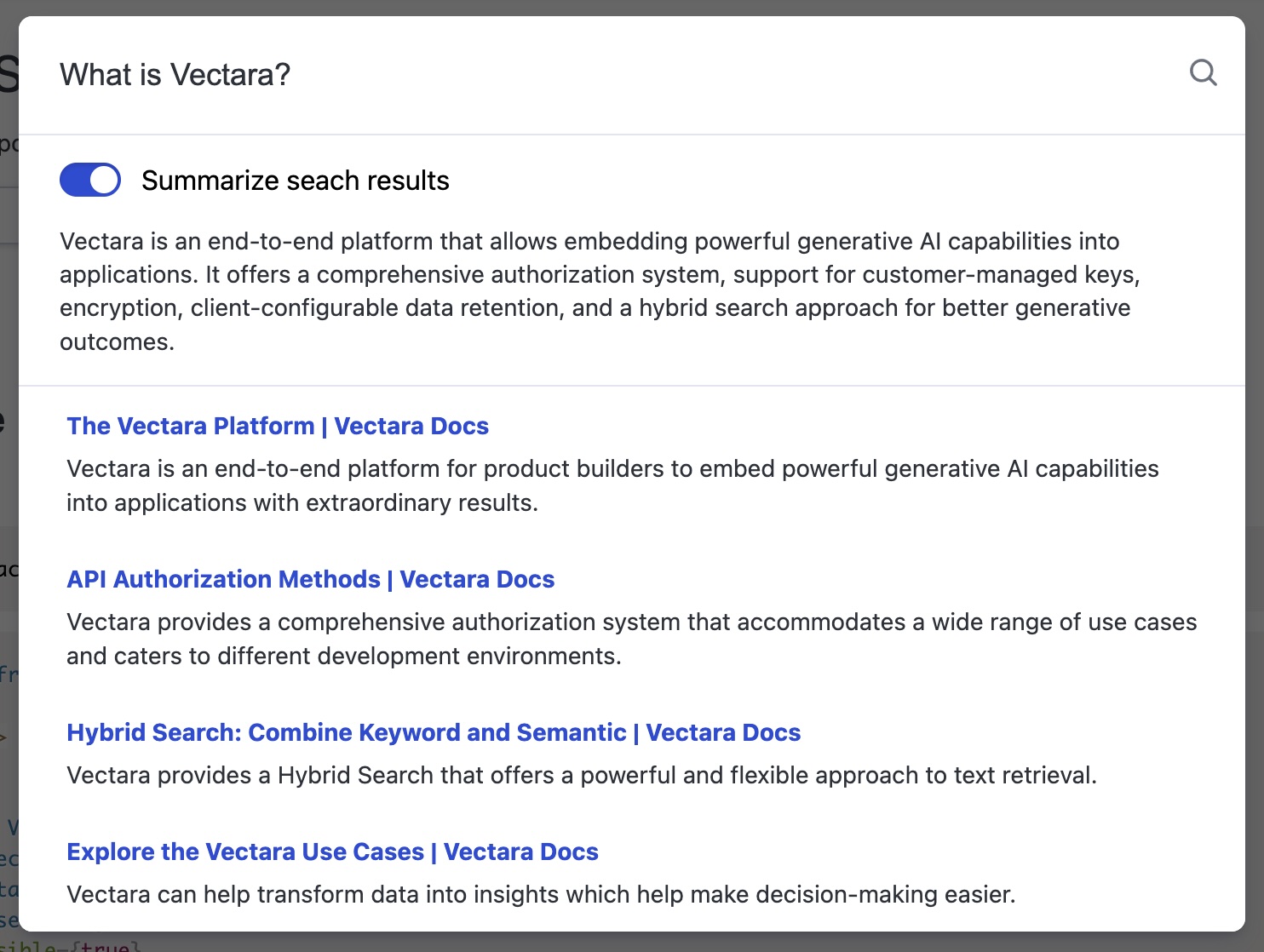
Search results look like this:
Install React-Search:
npm install --save @vectara/react-searchThen use it in your application like this:
import { ReactSearch } from "@vectara/react-search";
/* snip */
<ReactSearch
customerId="CUSTOMER_ID"
corpusId="CORPUS_ID"
apiKey="API_KEY"
placeholder="Search" // Optional search input placeholder
isDeepLinkable={true} // Optional boolean determining if search results will be deep-linked
openResultsInNewTab={true} // Optional boolean determining if links will open in a new tab
zIndex={1000} // Optional number assigned to the z-index of the search modal
isSummaryToggleVisible={true} // Optional boolean determining if users can summarize search results
rerankingConfiguration={{
rerankerId: 272725718
}}
/>;Every Vectara account is associated with a customer ID. You can find your customer ID by logging into the Vectara Console and opening your account dropdown in the top-right corner.
After you create a corpus, you can find its ID by navigating to the corpus and looking in the top-left corner, next to the corpus name.
API keys enable applications to access data inside of corpora. Learn how to create a QueryService API key.
By default, React-Search sends query requests to the Vectara servers. If you want to use a proxy server, you can configure this option with the URL of your proxy.
Configure the placeholder text in the search modal's input.
Defaults to false. Set this option if you want to persist a search query to a URL parameter. This will enable users to share or bookmark the URL. Loading the URL will automatically open the search modal and search for the query that's stored in the URL.
Defaults to false. Set this option if you want a search result to open in a new tab.
Define the z-index of the search modal.
Accepts a callback that will receive a boolean argument indicating whether the "Summarize search results" toggle is enabled.
Whether users will be able to summarize search results or not.
If users can toggle summarization, whether the toggle should be enabled by default.
Specifies a search result reranker to use, along with its configuration. For more information, see our docs on reranking.
Install React-Search:
npm install --save @vectara/react-searchThen use the useSearch hook in your application like this:
import { useSearch } from "@vectara/react-search/lib/useSearch";
/* snip */
const { fetchSearchResults, isLoading } = useSearch(
"CUSTOMER_ID",
"CORPUS_ID",
"API_KEY",
"API_URL", // optional
{ rerankerId: 12345 } // optional
);The values returned by the hook can be passed on to your custom components as props or used in any way you wish.
fetchSearchResults: async (query: string, summarize: boolean) => Promise<{ searchResults: DeserializedSearchResult[]; summary?: string }>
This is used to send a message to the search API. When the search succeeds, an object consisting of an array of search results and an optional summary is returned. Each search result is a DeserializedSearchResult object. More information on types can be found here.
A boolean value indicating whether or not a search request is still pending
Using React-Search with SSR frameworks may require additional infrastructure. Here are some common gotchas:
React-Search offers a ReactSearchNext variant that is compatible with Next.js. It accepts the same props that ReactSearch does.
It can be imported as:
import { ReactSearchNext } from "@vectara/react-search/lib/ReactSearchNext";In addition to using this Next.js-compatible component, you will also need to use the "use client" directive in the file that imports ReactSearchNext.
React-Search pulls data from your Vectara corpus. To set this up:
Pro-tip: After you create an API key, navigate to your corpus and click on the "Access control" tab. Find your API key on the bottom and select the "Copy all" option to copy your customer ID, corpus ID, and API key. This gives you all the data you need to configure your <ReactSearch /> instance.
Vectara enables you to define metadata on your documents. React-Search behaves differently based on the presence of specific metadata fields:
title: If this field is defined it will be rendered as the title of a search result. Typically this is something like the title of the document or webpage.url: If this field is defined, React-Search will render the search result as a link to the defined URL.
This codebase comes with a development environment to facilitate enhancements and bug fixes. It allows maintainers to quickly iterate on the code and verify changes instantly.
From the root directory, run:
npm install
This will install all dependencies necessary for building the component and running the dev environment. Once this completes, run:
npm run docs
This spins up an application running at http://localhost:8080/. Your latest changes will be reflected here.
Once the development environment is running, any changes made to .ts and .tsx files in the /src directory will trigger a rebuild of the component and a reload of the webpage.
Additionally, any changes to the development app source code at /docs/index.tsx will also trigger a rebuild + reload.
Vectara React-Search is an open-sourced software licensed under the Apache 2.0 license.
This repository contains sample code that can help you build UIs powered by Vectara, and is licensed under the Apache 2.0 License. Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.