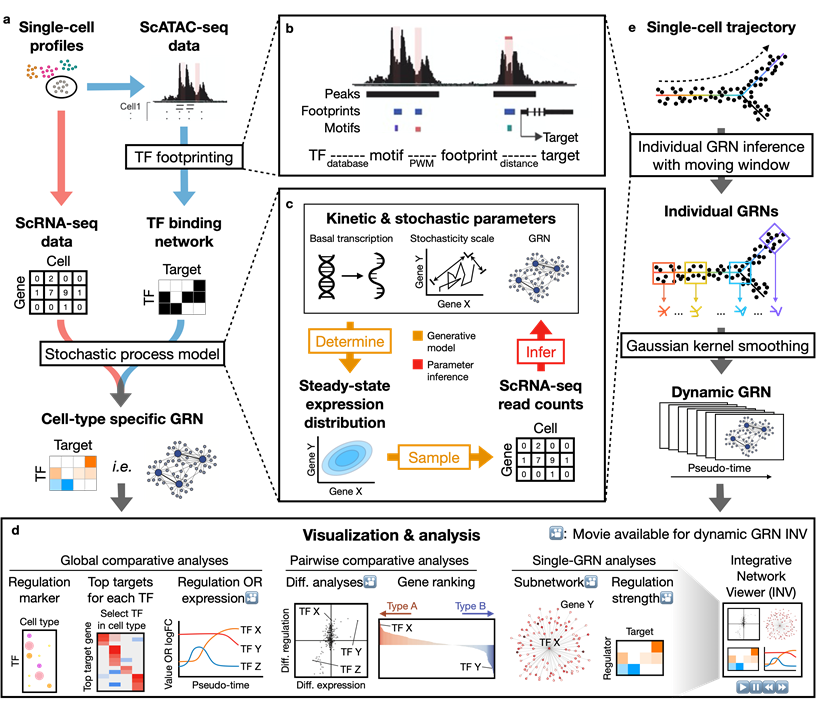
Dictys reconstructs cell-type specific and dynamic gene regulatory networks (GRN) from scRNA-seq and scATAC-seq datasets. Dictys first infers a Transcription Factor (TF) binding network with TF footprinting from single-cell chromatin accessibility. Then Dictys refines the edges with single-cell transcriptome. Dictys addresses traditional challenges in network inference by orienting causality with TF binding information, modeling transcriptional rate to reconstruct cycle-compatible networks, and using probabilistic programming to capture the scRNA-seq process.
Dictys provides network analysis and visualization at global (across all cell types), pairwise (between two cell types) and single GRN levels. Dictys directly quantifies TF regulatory activity from GRN and enables a series of analyses such as cell-type specific TF discovery as regulation markers, differential regulation analysis alongside differential expression, and TF regulatory program illustration through its subnetwork and top activation/repression targets. These GRN-based analyses can capture unique biological insights not available from mean expression.
Dictys infers and analyzes dynamic GRN from scRNA-seq and scATAC-seq datasets along (inferred) trajectories. This avoids artificial cell subsets and potential biases from population imbalance, and allows (pseudo-)time-resolved discovery and investigation of driver TFs and their individual regulations. Dictys provides an integrative network viewer for dynamic GRN visualization of synchronous panels in animation.
Dictys has dependencies not in python. The options below automatically install these dependencies. Installation should take ~<10 mins.
First install Anaconda/Miniconda. Then, install Dictys and PyTorch with CPU computation:
conda create -y -n dictys -c conda-forge python=3.9 mamba . activate dictys mamba install -y -c lingfeiwang -c bioconda -c conda-forge -c pytorch dictys pytorch torchvision torchaudio cpuonly
This will create a conda environment named dictys.
Alternatively, with GPU computation for PyTorch (here CUDA 11.7):
conda create -y -n dictys -c conda-forge python=3.9 mamba . activate dictys mamba install -y -c lingfeiwang -c bioconda -c conda-forge -c pytorch -c nvidia dictys pytorch torchvision torchaudio pytorch-cuda=11.7
Or, with earlier versions (here CUDA 11.3, only supported in PyTorch 1):
conda create -y -n dictys -c conda-forge python=3.9 mamba . activate dictys mamba install -y -c lingfeiwang -c bioconda -c conda-forge -c pytorch -c nvidia dictys pytorch==1.12.1 torchvision==0.13.1 torchaudio==0.12.1 cudatoolkit=11.3
Option 2: with bash script
First install Anaconda/Miniconda. Then, install Dictys and PyTorch with CPU computation:
wget https://tinyurl.com/dictys -O - | bash
This will create a conda environment named dictys.
Alternatively, under a different conda environment name:
wget https://tinyurl.com/dictys -O - | CONDAENV_NAME=your_favorite_name bash
Alternatively, with GPU computation for PyTorch (here CUDA 11.7):
wget https://tinyurl.com/dictys -O - | CUDAVERSION_CONDA=11.7 bash
To pull and run the pre-built docker image for Dictys with CPU computation:
docker pull lfwa/dictys-cpu #Add public ports with '--expose' or '-p' to serve jupyter notebooks and bind mount with '-v' to transfer input/output data docker run -it lfwa/dictys-cpu
Inside the container, activate conda environment and serve jupyter notebooks:
. activate dictys jupyter notebook --allow-root
Then, you can access jupyter notebooks with the exposed or published ports.
For more advanced installation, see INSTALL.md and/or edit the install script.
Note: dynamic network inference is computationally intensive and GPU availability is highly recommended. Running time depends on the dataset, but it can take weeks or longer without a GPU.
If you need STREAM, ArchR, or other softwares upstream of Dictys, we recommend to install them in separate environments following their official instructions.
If your minor version is the latest (e.g. your installed version is 1.0.0 and the latest release is 1.0.9), you can update Dictys to the latest github version with pip3 install --no-deps --force-reinstall git+https://github.com/pinellolab/dictys inside your Dictys conda environment.
If your minor version is not the latest (e.g. your installed version is 1.0.0 but the latest release is 1.1.0), you should reinstall Dictys in a new conda environment with any option above.
We provide several tutorials for different data types. Please download each tutorial folder structure before running. Note that these tutorials are not intended to fully replicate the results in the paper due to differences in software versions, computing platforms, various randomness e.g. in HOMER genome preparsing or Pytorch algorithms, etc.
- short-multiome: a single-notebook tutorial for the data preparation, inference, and analysis of context specific networks on 10x multiome data for human blood.
- full-multiome: an extended version of the above tutorial with detailed usage.
- full-skin: a short tutorial for the inference and analysis of dynamic networks on SHARE-seq data for mouse skin. Contains a simple demonstration to account for covariates.
The network analysis tutorials below use the same reconstructed networks as in the paper and are designed to fully replicate the results.
- analysis-blood: a simple tutorial for context specific and dynamic network analysis on separate scRNA-seq and scATAC-seq quantifications of human blood as in manuscript.
- analysis-skin: a simple tutorial for context specific network analysis on SHARE-seq of mouse skin as in manuscript.
The figures below are produced with the blood example dataset. You can reproduce them with the analysis-blood example. See Tutorials. Each figure is linked to the jupyter notebook that produces it.
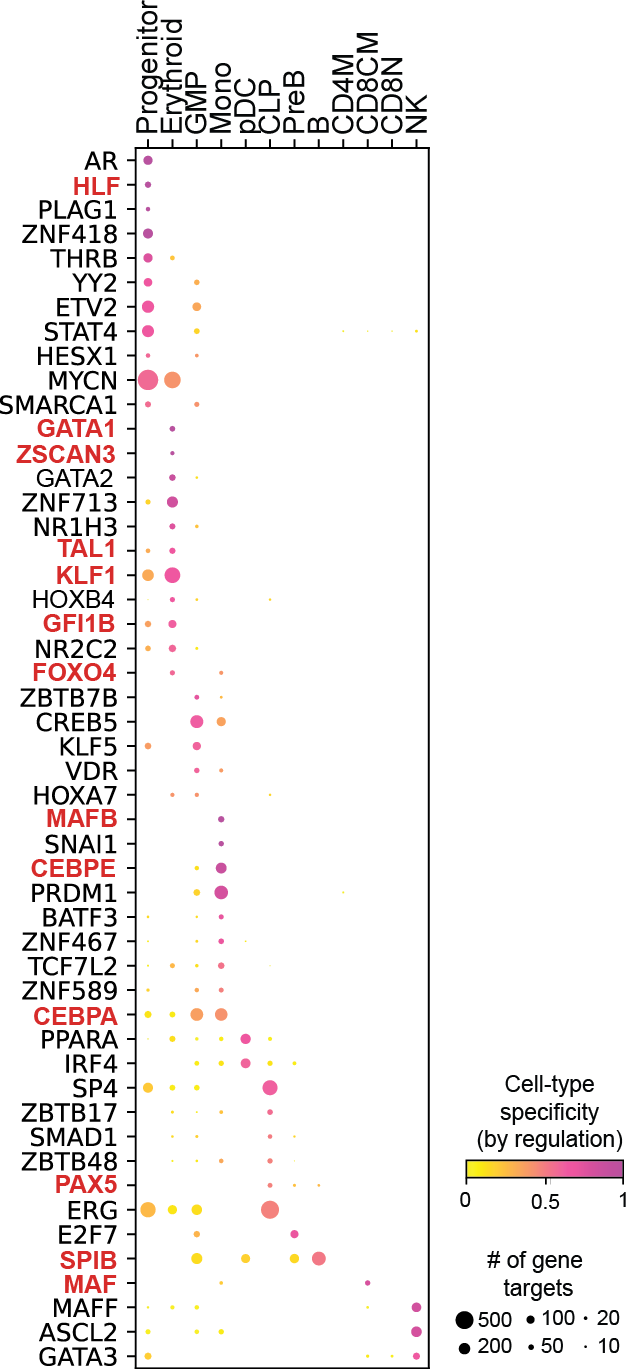
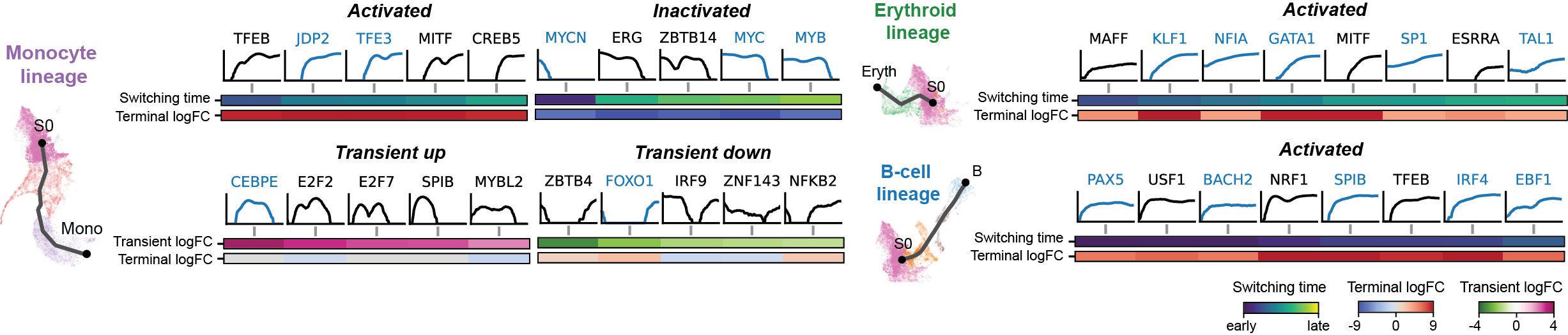
Regulation marker TF discovery
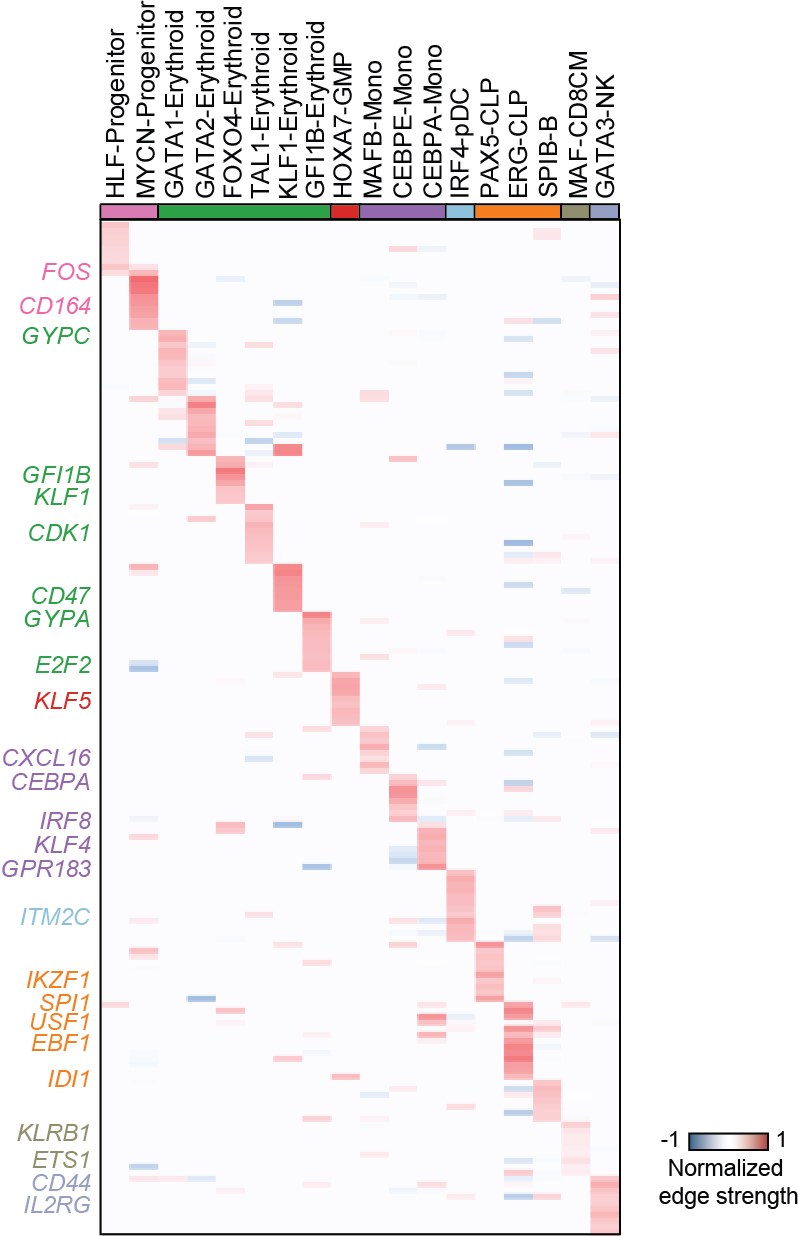
Top activation target heatmap for select TFs
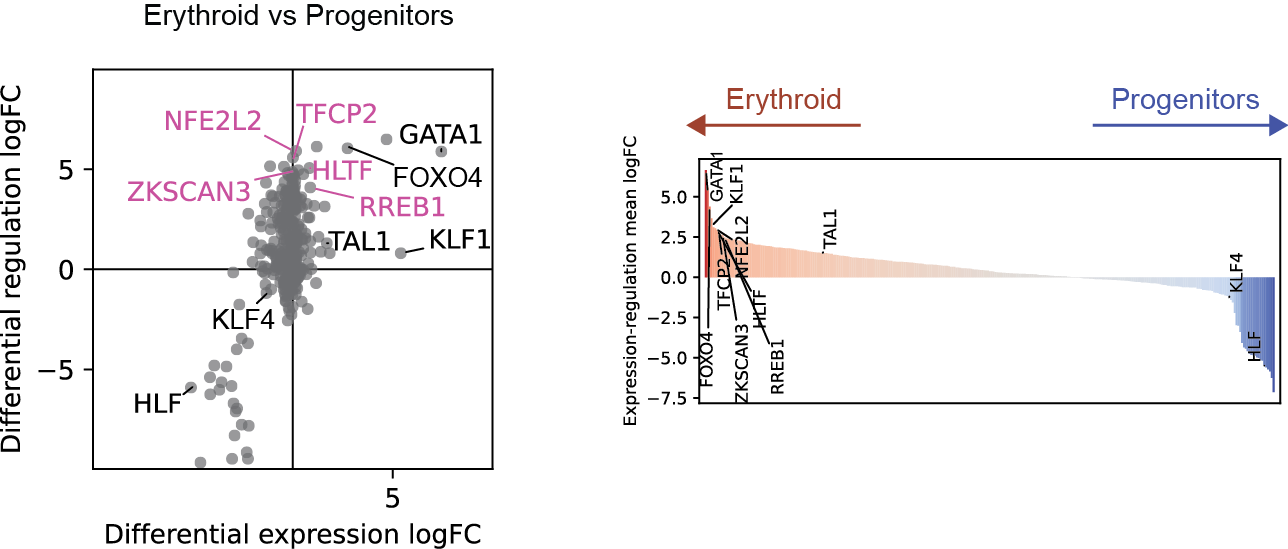
Differential regulation v.s. differential expression scatter plot; integrative TF rank plot
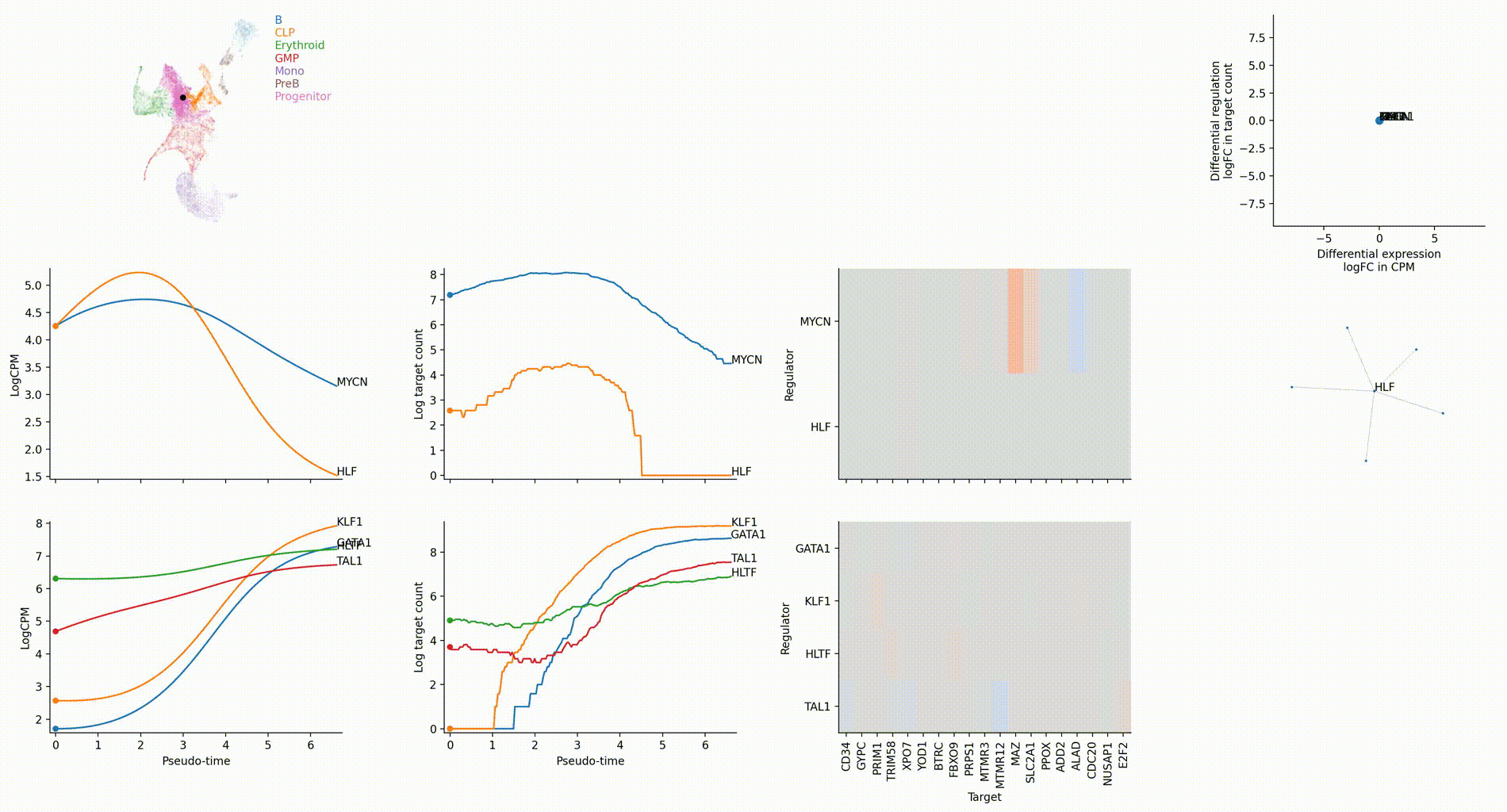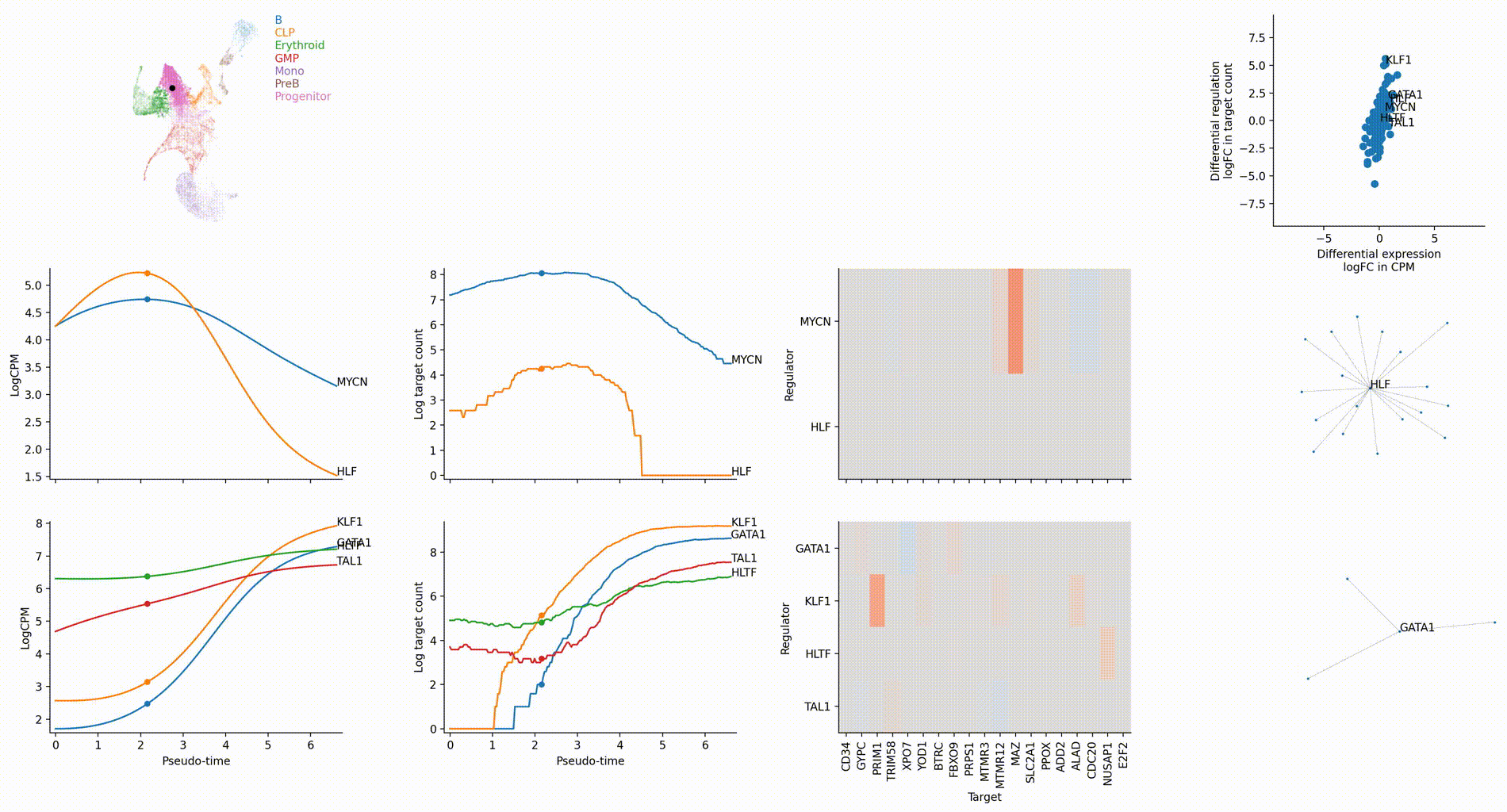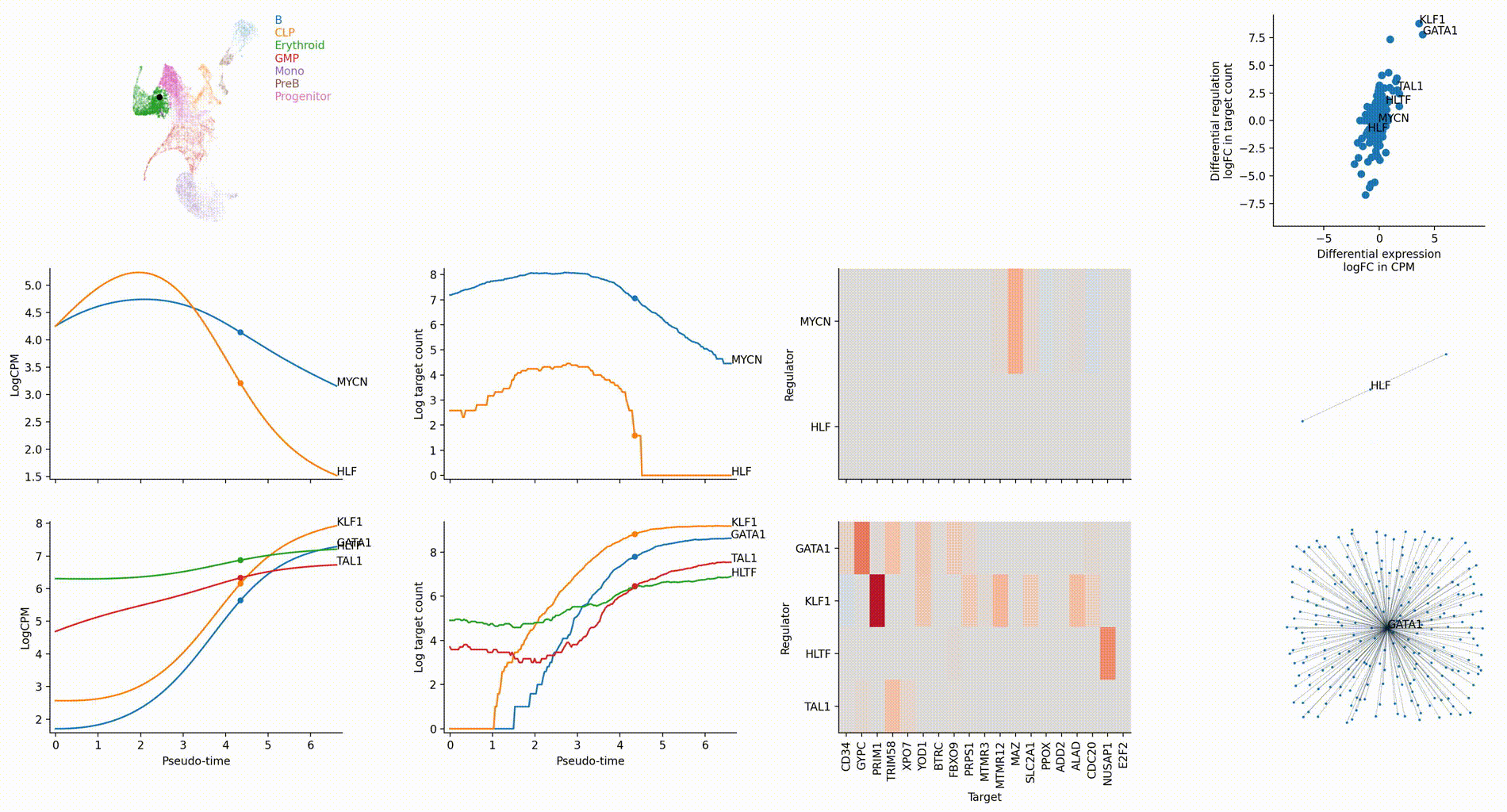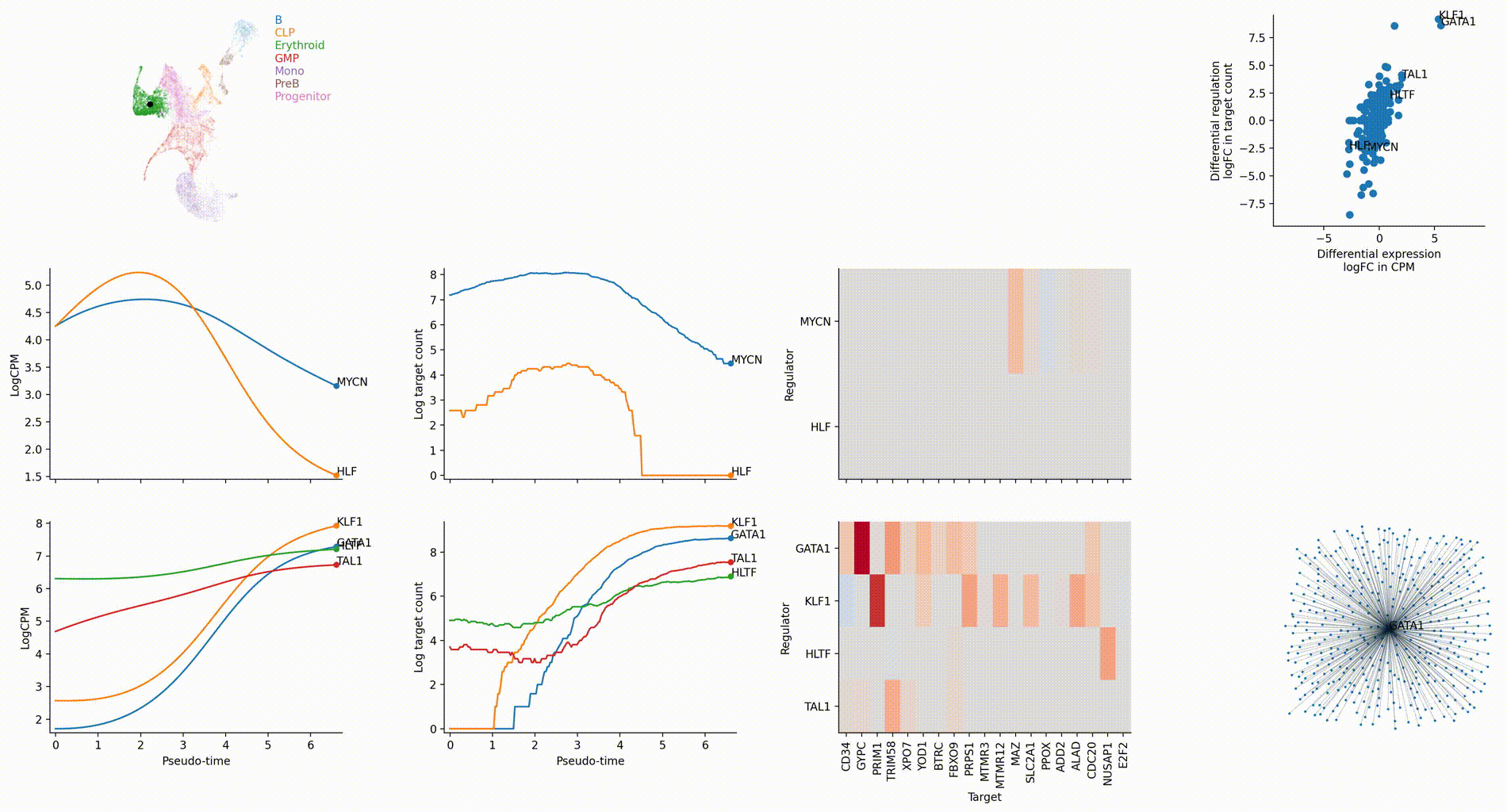
Driver TF discovery based on regulatory activity curve
Can I use fragments files instead of bam files for chromatin accessibility?
Dictys uses wellington (pyDNase) which does not accept fragments files. Most journals require raw data for publication so in theory you should be able to obtain the bam files or something equivalent. If you really cannot obtain bam files, there are ways that may circumvent this requirement: (i) fork and patch pyDNase to accept fragments files or (ii) convert fragments files to bams. Note that they are outside the scope of Dictys and we have not tried them. We do not support, endorse, or guarantee the validity of these approaches which are highly experimental in nature.
How do I perform network inference faster?
- Get a GPU, such as:
- Google Colaboratory offers free GPU access with zero/minimal setup. You can run Dictys on very small datasets for free, or larger datasets with paid membership.
- Major cloud computing service providers offer GPU access that is orders of magnitude cheaper than a scRNA-seq experiment.
- High-performance computing cluster with GPU access at institution or other levels. Dedicated computing server. Personal computer with high-end consumer level GPU.
- People or labs with the above access.
- Reduce the computational load, such as:
- For context specific networks, choose only cell clusters of your interest. For this, delete the uninterested cell clusters in data/subsets.txt.
- For dynamic networks, use fewer windows. This risks reducing time resolution. Details TBA.
- Reduce the number of training steps. This risks reducing network quality. Details TBA.
- Configure properly for a powerful CPU. Details TBA.
- Get a GPU, such as:
Why do I see this error:
AssertionError: Torch not compiled with CUDA enabled?This is because you installed a CPU-only pytorch but tried to run it on GPU. You have several options:
- To run pytorch on CPU, run
dictys_helper makefile_update.py path/to/config.mk '{"DEVICE": "cpu"}'to configure to CPU mode. See Tutorials to find the right place to run this command. - To run pytorch on GPU, reinstall Dictys with the correct options to enable GPU support at Installation.
- To run pytorch on CPU, run
How do I use a large motif database where each motif can map to multiple TFs, such as from SCENIC+?
You need to first convert the motif database into a
.motiffile in HOMER format. Each motif should be named asTFNAME_unique-suffixwhere TFNAME should match the gene name in your dataset including capitalization. For multi-TF motifs, merge them asTFNAME1,TFNAME2,TFNAME3_unique-suffixfor best speed, instead of duplicating them under each TF. Seemotifs.motifin tutorial inputs to understand file format. Important: the log odds detection threshold column needs to be filled properly.How do I use Dictys on multiple samples?
We used Dictys on multiple samples in the human blood dataset in our paper (Figs 2&5). However, we did not need to integrate multiple samples because the published dataset already did that. To check that on your own dataset, please see if samples display unintended separation in the low dimensions. If so, you may want to integrate them properly with any existing software before cell clustering or trajectory inference. These clusters or trajectories are inputs for GRN inference. In addition, you should try both including sample IDs as covariates in Dictys and not including them. We have not comprehensively tested covariate inclusion, so we suggest to choose the option that gives better biology for downstream analysis. See the Optional: Prepare covariates section in the full-skin tutorial on how to include covariates.
To prepare input files for Dictys, please make sure each cell has a unique name across samples in the read count matrix and in the bam file. For read count matrices, you can append sample names to cell names before merging these matrices. For bam files, you can split each of them by cells using the script provided by Dictys in a separate folder for each sample, append sample names to the file names, and then move all the bam files into a single folder.
How do I save figures from jupyter notebooks onto the disk?
You can use
plt.savefig('output.pdf')to save the current figure to disk. See matplotlib.pyplot.savefig.Some visualization functions in Dictys return two or more figures, such as
figs = net.draw_discover(...). You can save them separately withfigs[0].savefig('output1.pdf'); figs[1].savefig('output2.pdf'); .... See matplotlib.figure.savefig and issue 15.
Please raise an issue on github.
Dictys: dynamic gene regulatory network dissects developmental continuum with single-cell multiomics Nature Methods (2023)