https://www.zcyphygeodesy.com/en/h-nd-142.html
Using numerical integral of inverse Stokes, Hotine or Vening-Meinesz operation, compute the anomalous gravity field element from the ellipsoidal height grid of the equipotential boundary surface and height anomaly (m) or vertical deflection vector (″, SW) grid on the surface. Using the inverse Stokes, Hotine or Vening-Meinesz operation, compute the field element from height anomaly or vertical deflection, which can be employed for gravity field inversion in satellite altimetry.
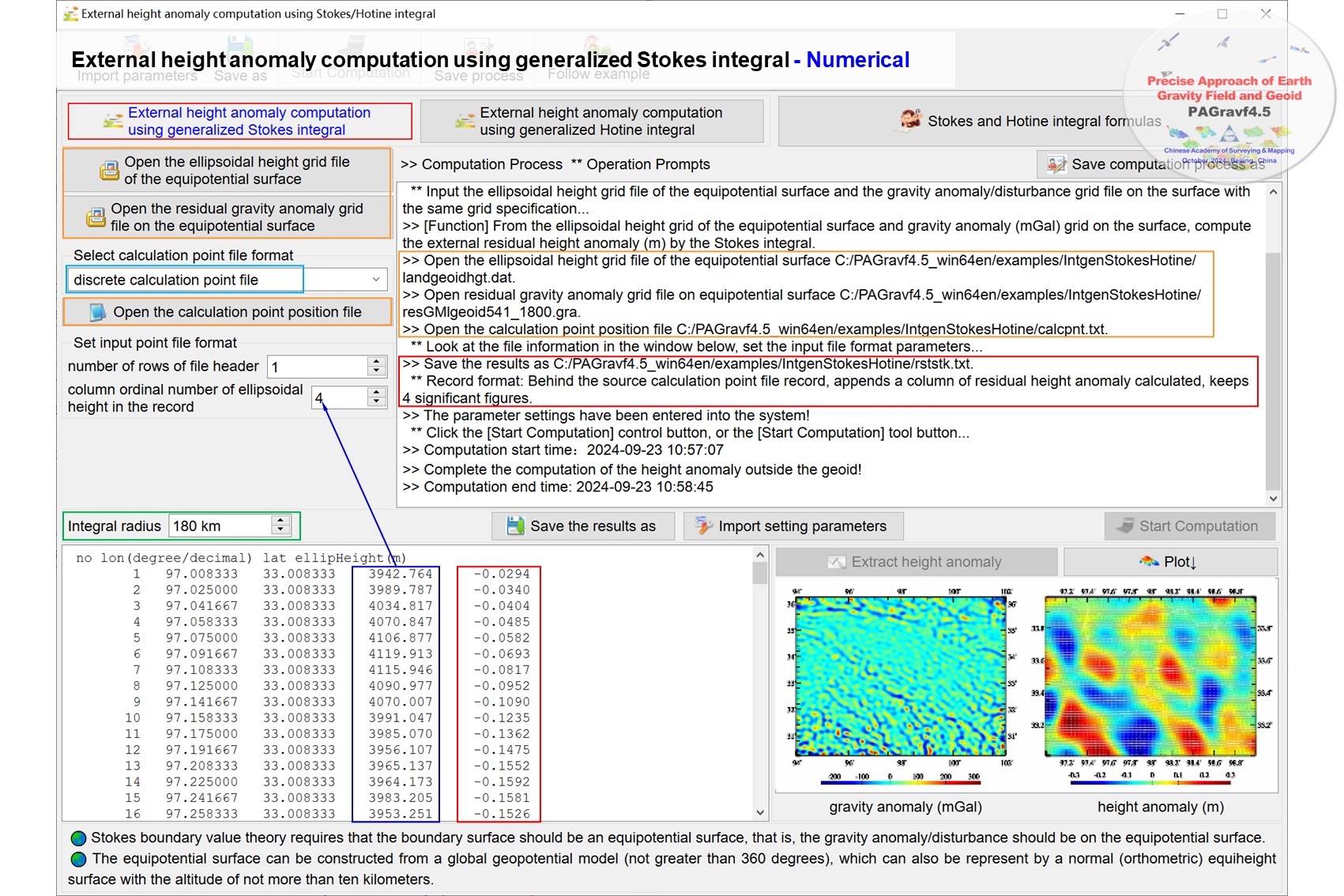
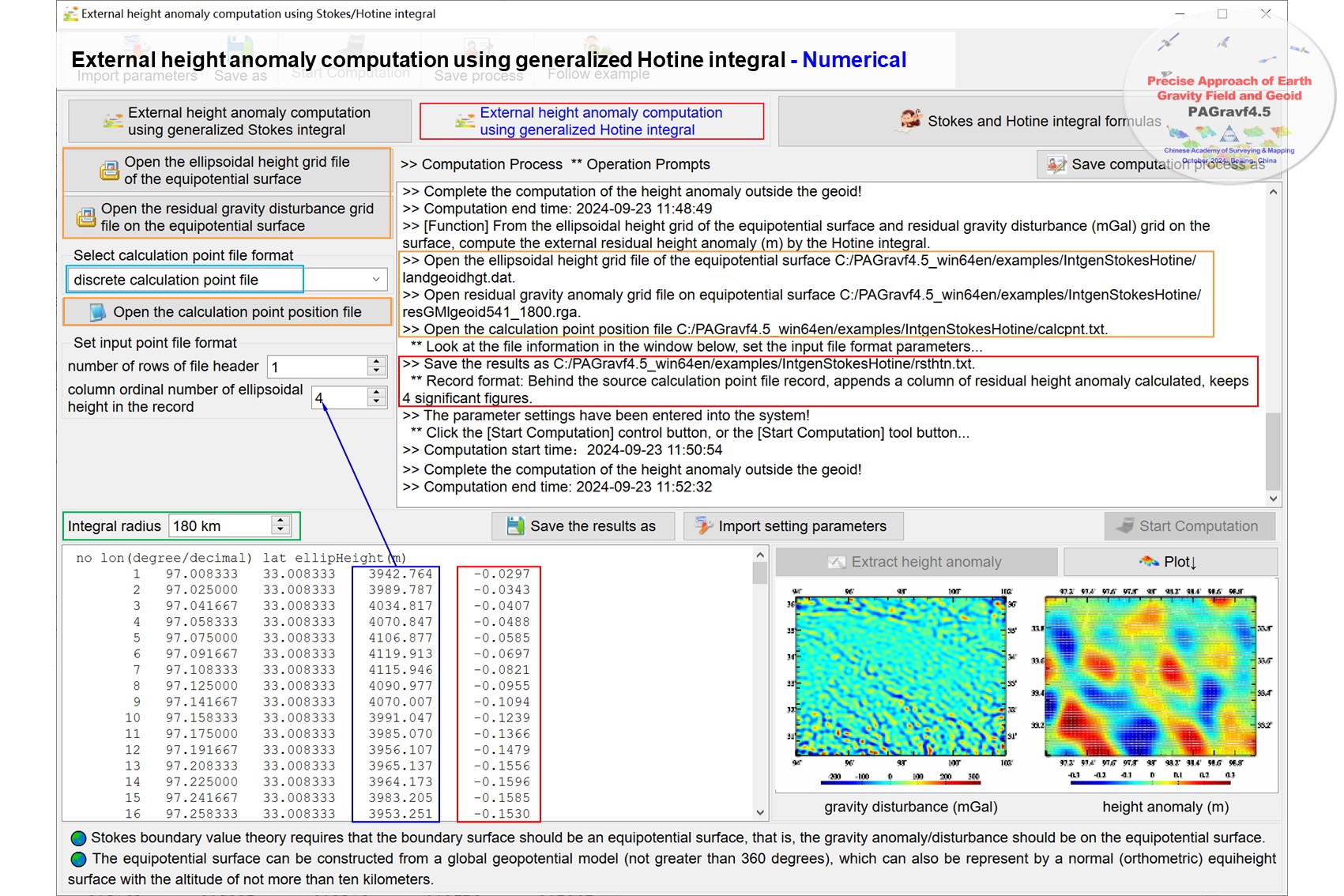
The integral of inverse operation formula belongs to the solution of the Stokes boundary value problem, which requires the integrand height anomaly or vertical deflection to be on the equipotential surface , and can be usually employed for marine gravity field inversion calculation in ocean satellite altimetry.
It is usually necessary to employ the remove-restore scheme with a reference geopotential model to use the finite radius for gravity field integral. Firstly, remove the model values of source field element on the equipotential boundary surface, then compute the residual values of target field element at the calculation point by integral of inverse operation, and finally restore the model values of target field element at the calculation point.
The equipotential surface can be constructed from a global geopotential model (not greater than 360 degrees), which can also be represent by a normal (orthometric) equiheight surface with the altitude of not more than ten kilometers.
InvStokesHotineMeinesznumintg.f90
Input parameters: knd - type of inverse operation. knd=0 for inverse Stokes, knd=1 for inverse Hotine operation and knd=1 for inverse Vening-Meinesz operation.
Input parameters: dr - the integral radius (m).
Input parameters: calcpntfl - the calculation point file name on the equipotential boundary surface. The record format of the input calculation point file: ID (point no / point name), longitude (decimal degrees), latitude (decimal degrees),......
Input parameters: dwmhgrdfl - the ellipsoidal height grid file name of the equipotential boundary surface. The grid will be employed to calculate the integral distance.
Input parameters: gravgrdfl - the residual field element grid file name on the equipotential surface. When knd = 0 or 1, the field element is height anomaly (m), and when knd= 2 the field element is vertical deflection vector (″, SW).
InversenumIntegral(calcpntfl,dwmhgrdfl,gravgrdfl,knd,dr)
The output file reslt.txt, whose record format: Behind the input calculation point file record, appends a column of ellipsoidal height of the calculation point interpolated from the ellipsoidal height grid of the equipotential surface and a column of integral value of the residual gravity anomaly when knd=0, a column of integral value of the residual gravity disturbance when knd=1, or 3 columns of attributes including the residual height anomaly, gravity anomaly and gravity disturbance when knd=2.
real*8 function RaGradientBLH(BLH,gra,dwm,nlat,nlon,hd,dr,GRS)
Input parameters: BLH(3) - longitude (decimal degrees), latitude (decimal degrees), ellipsoidal height (m) of the calculation point.
Input parameters: dwm(nlat,nlon) - the ellipsoidal height grid of the equipotential boundary surface, which employed to calculate the integral distance.
Input parameters: gra(nlat,nlon) - the residual field element grid on the equipotential surface.
Input parameters: hd(6) - the grid specification parameters (minimum and maximum longitude, minimum and maximum latitude, longitude and latitude intervals of a cell grid).
Input parameters: GRS(6) - gm, ae, j2, omega, 1/f, default value
Return - the calculated residual radial gradient (in unit of /m).
AnVMdeflBLH(BLH,kai,nta,dwm,nlat,nlon,hd,dr,rst,GRS)
Input parameters: kai(nlat,nlon) - the residual vertical deflection (radian, S) grid on the equipotential surface.
Input parameters: nta(nlat,nlon) - the residual vertical deflection (radian, W) grid on the equipotential surface.
Return parameters: rst(3) - the residual height anomaly (m), gravity anomaly (m/s2) and gravity disturbance (m/s2) at the calculation point.
HGradientOne(BLH,rga,hgt,nlat,nlon,hd,tx,GRS)
Input parameters: rga(nlat,nlon) - the field element grid on the equipotential surface.
Input parameters: hgt(nlat,nlon) - the ellipsoidal height grid on the surface of field element.
Return parameters: tx(2) - the first-order horizontal gradient vector (NE, in unit of /m) at the calculation point.
GNormalfd(BLH,NFD,GRS)
Return parameters: NFD(5) - the normal geopotential (m2/s2), normal gravity (mGal), normal gravity gradient (E), normal gravity line direction (', expressed by its north declination relative to the center of the Earth center of mass) or normal gravity gradient direction (', expressed by its north declination relative to the Earth center of mass).
LegPn_dt2(pn,dp1,dp2,n,t) ! t=cos ψ
EqHestens(BPB,xx,nn,BPL); EqJordon(BPB,xx,nn,BPL)
EqCholesky(BPB,XX,nn,BPL); EqueSVD(BPB,XX,nn,BPL)
RidgeEstimate(BPB,xx,nn,BPL); ……
BLH_RLAT(GRS, BLH, RLAT); BLH_XYZ(GRS, BLH, XYZ)
RLAT_BLH(GRS, RLAT, BLH)
CGrdPntD2(lon,lat,dt,row,col,hd); PickRecord(line, kln, rec, nn)
Fortran90, 132 Columns fixed format. Fortran compiler. mkl_lapack95_ilp64.lib link library required..
[Algorithmic formula] PAGravf4.5 User Reference https://www.zcyphygeodesy.com/en/
1.4.1 Format convention for geodetic data file
7.9.3 Integral formula of inverse operation of anomalous gravity field element
7.1(4) Low-dgree Legendre function and its first and second derivative algorithms
The zip compression package in the attachment includes the test project in visual studio 2017 - intel fortran integrated environment, DOS executable test file and all input and output data.