Thomas Huet, Niccolò Mazzucco, Miriam Cubas Morera, Juan Gibaja, F. Xavier Oms, António Faustino Carvalho, Ana Catarina Basilio, Elías López-Romero
NeoNet serves as a framework to study the transition from the Late Mesolithic to the Early Neolithic through spatio-temporal modeling of radiocarbon dates and by offering:
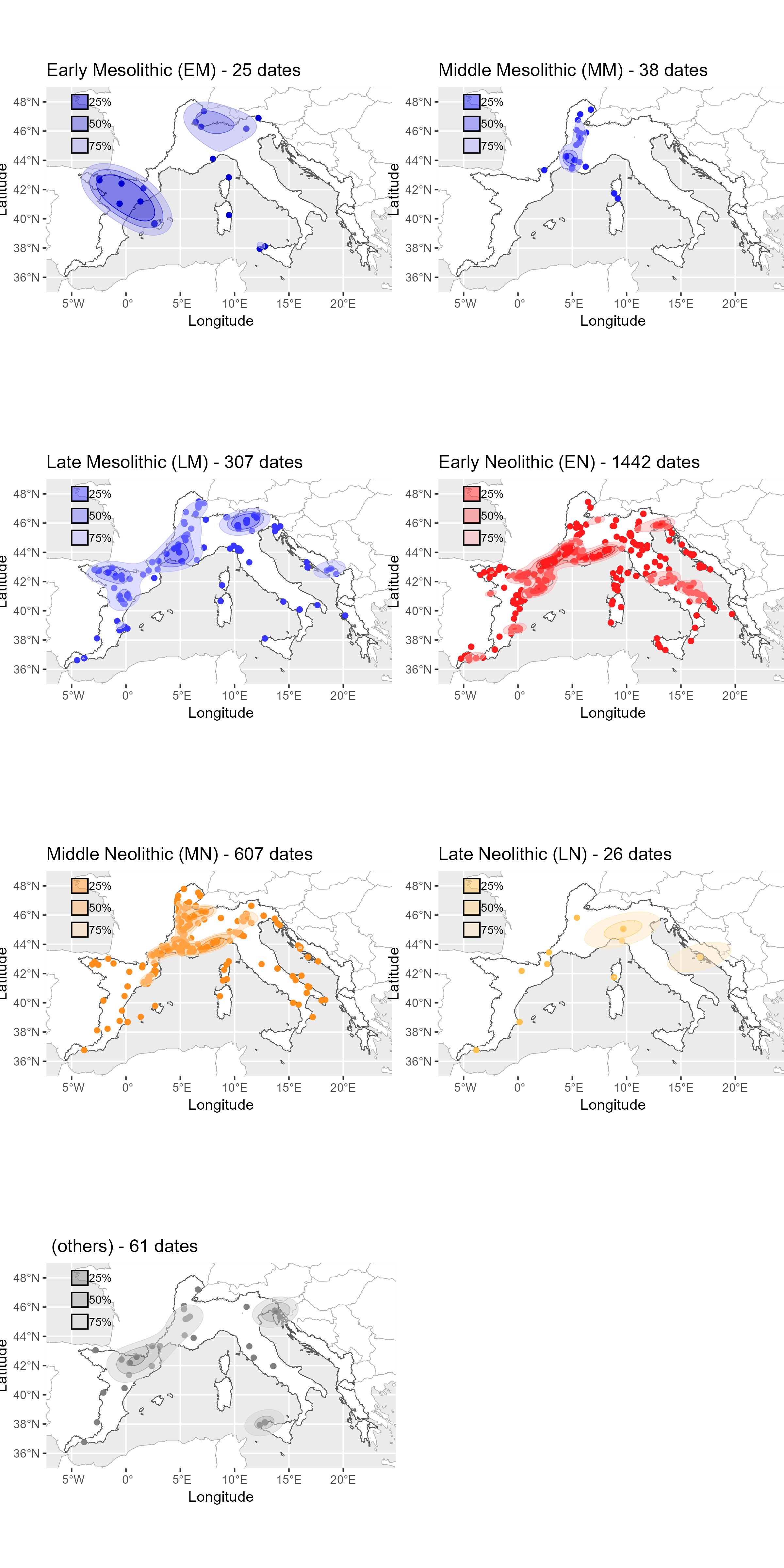
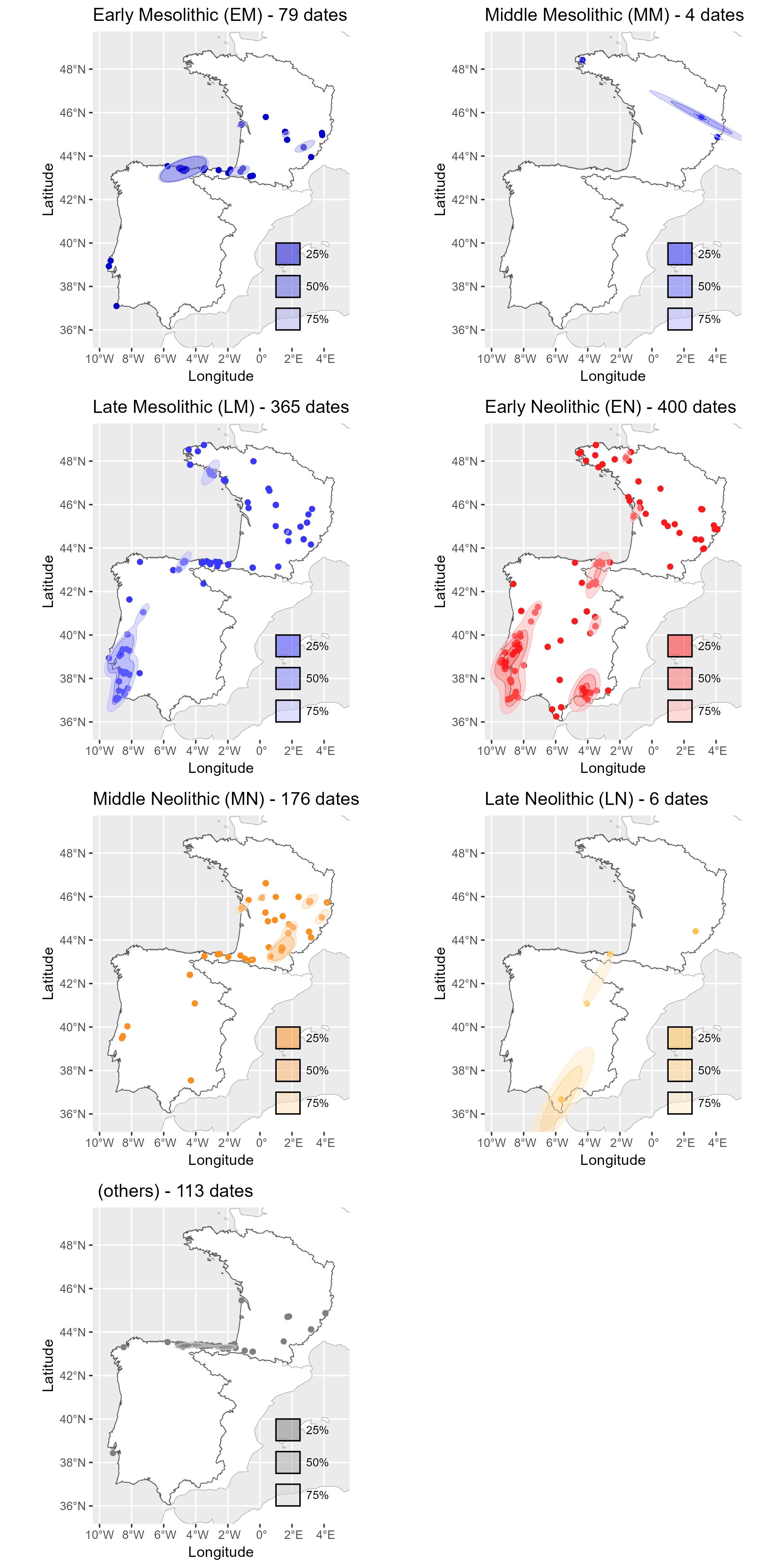
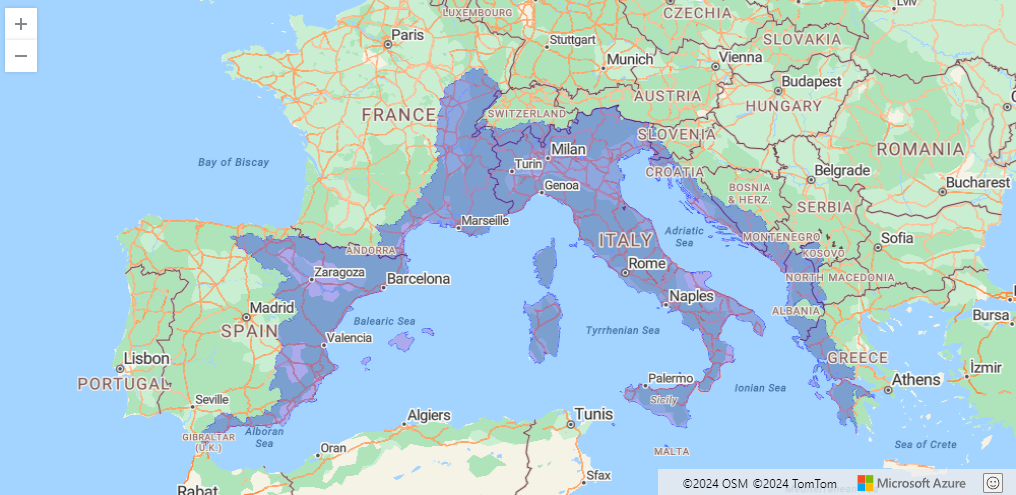
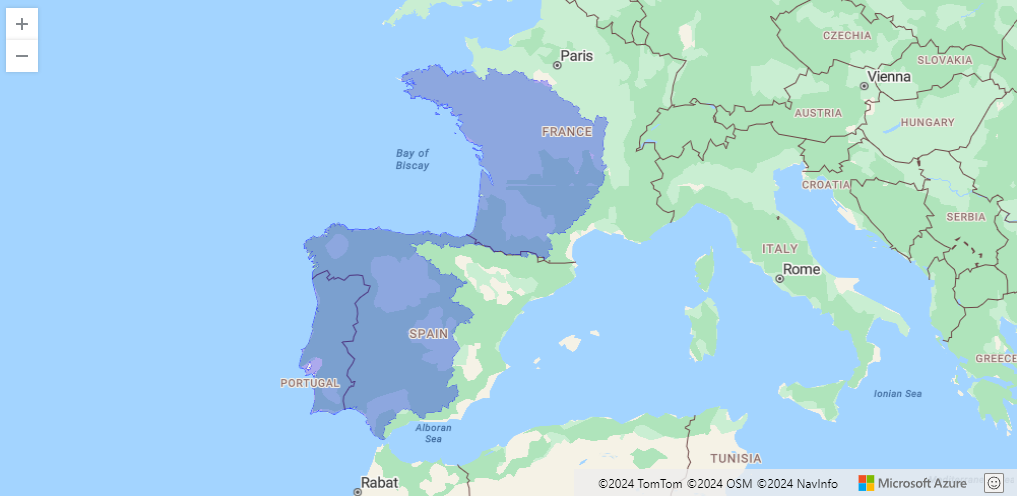
Neonet radiocarbon datasets: "NeoNet Med" (North-Central Mediterranean, location) and "NeoNet Atl" (European South Atlantic river basin, location), here filtered by periods.
- Studied periods
Studied periods are listed in the periods.tsv table:
These datasets are harvested by the c14bazAAR package, functions get_c14data("neonet") and get_c14data("neonetatl")
NeoNet app is an R Shiny application for mapping radiocarbon (C14). The application offers a mobile geographic window for date selection by location, various filters on chronology and date quality, a calibration window, and other tools to create a user-friendly interface supported by curated datasets of radiocarbon dates and archaeological contexts. NeoNet app is hosted on the server of the University of Pisa. This NeoNet app uses this radiocarbon dataset: https://doi.org/10.13131/archelogicadata-yb11-yb66 published as a data paper in the Journal of Open Archaeology Data and describe in this web document.
- On export action (download button), export this metadata:
- max SD
- selected periods
- dataset (Med, Atl) DOI
- timestamp
- bibliographical reference
NeoNet functions enable the handling of radiocarbon dates sourced from the dataset or exported from the interactive app. Current functions cover:
- data management
- SPD
- isochrones
- Koppen climate classes
- Harris matrices using the NeoNet-strati app.
- reference data
- standardised site names (raw | rendered)
- standardised radiocarbon labcodes
- outlier dates (raw | rendered)
Starting by running these neo_*() functions to manage a new XLSX dataset. Sourcing functions:
source("R/neo_subset.R")
source("R/neo_bib.R")
source("R/neo_matlife.R")
source("R/neo_calib.R")
source("R/neo_merge.R")
source("R/neo_html.R")
source("R/neo_datamiss.R")
source("R/neo_datasum.R")
source("R/neo_doi.R")Read the new dataset and bibliographic file
data.c14 <- paste0(getwd(), "/inst/extdata/", "NeoNet_atl_ELR (1).xlsx")
df.bib <- paste0(getwd(), "/inst/extdata/", "NeoNet_atl_ELR.bib")Cleaning the dataset and making it conform to the published NeoNet dataset
df.c14 <- openxlsx::read.xlsx(data.c14)
df.c14 <- neo_subset(df.c14,
rm.C14Age = TRUE,
rm.Spatial = FALSE,
rm.Period = FALSE)
df.c14 <- neo_calib(df.c14)
neo_doi(df.c14)Prepare the dataset for the Shiny application by merging it with NeoNet Med, calculating materil life duration, and HTML popup layouts
df.c14 <- neo_merge(df.c14 = df.c14,
data.bib = data.bib,
merge.bib = F)
df.c14 <- neo_matlife(df.c14)
df.c14 <- neo_html(df.c14)Export the merged dataset
write.table(df.c14, "C:/Rprojects/neonet/R/app-dev/c14_dataset_med_x_atl.tsv",
sep = "\t",
row.names = FALSE)source("R/neo_map.R")
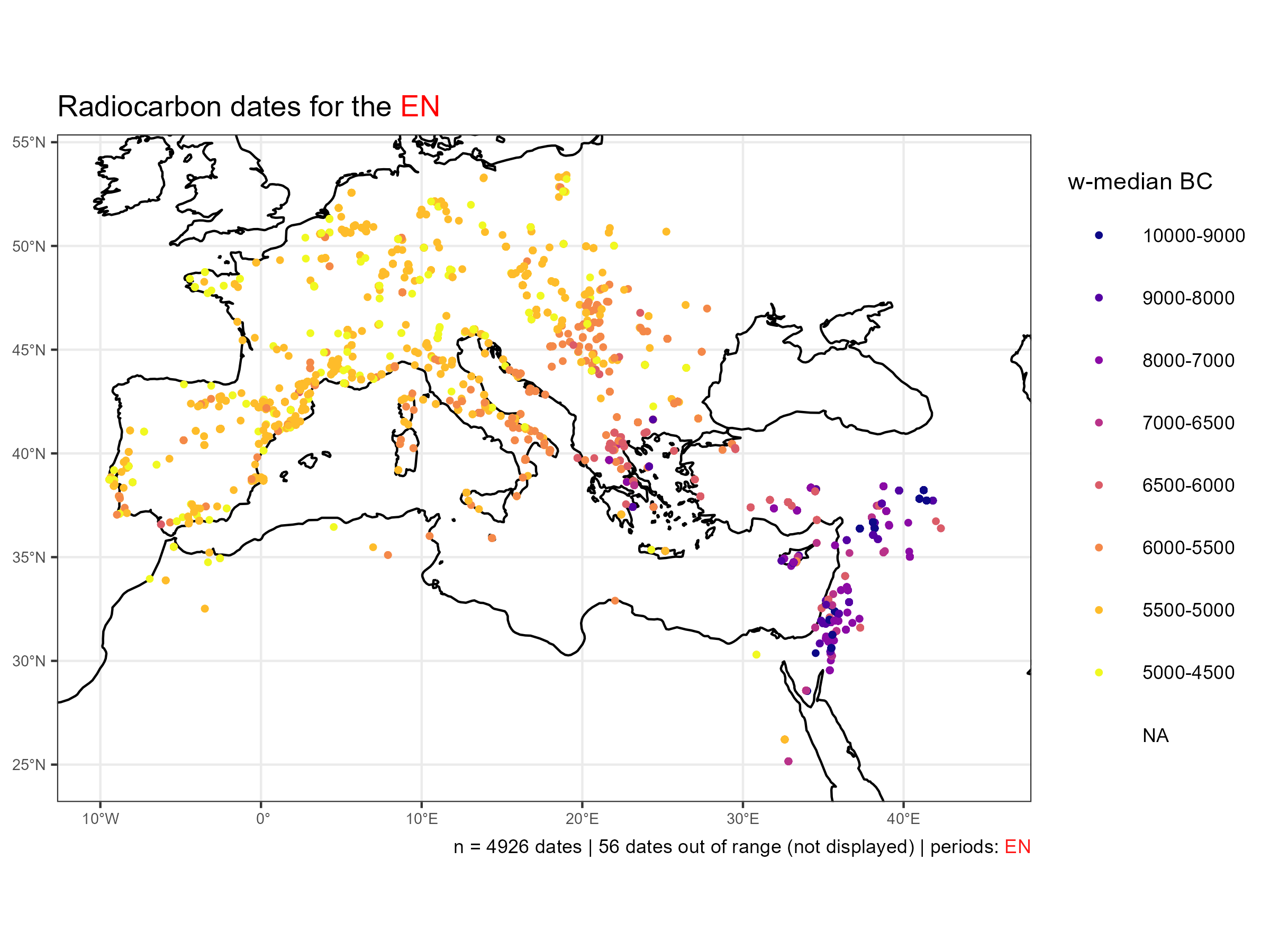
per <- 'EN'
tit <- paste0("Radiocarbon dates for the ", "<span style='color: ", "red", ";'>", per, "</span>")
gg.map <- neo_map(df.c14 = df_filtered,
selected.per = per,
breaks_values = c(-10000, -9000, -8000, -7000, -6500, -6000, -5500, -5000, -4500),
dates.size = 1,
title = tit,
roi = NA, dates.within.roi = FALSE)Gives:
Calculate basic statistics
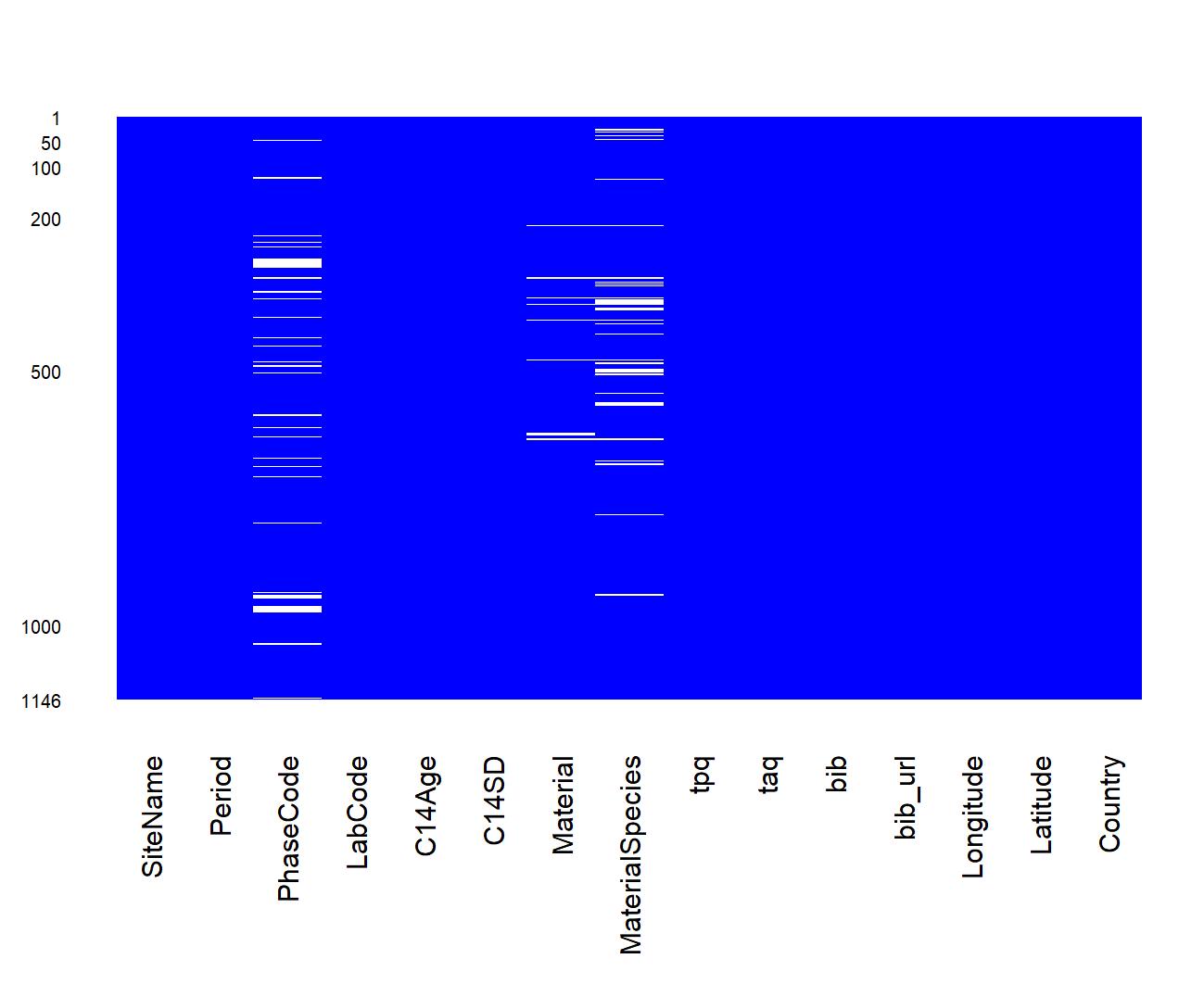
neo_datasum(df.c14)Calculate basic statistics: missing data
neo_datamiss(df.c14)Retrieve dates coming from other databases (with the c14bazAAR R package) and mapped to be compliant with the Neonet format (..., LM, EN, ...) and functions, using neo_dbs_parse(), a mapping table (XLSX) created with neo_dbs_create_ref(), and neo_dbs_align():
source("R/neo_dbs_parse.R")
source("R/neo_dbs_align.R")
# spatial and chronological limits
where <- sf::st_read("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/zoometh/neonet/main/doc/talks/2024-simep/roi.geojson", quiet = TRUE)
when <- c(-9000, -4000) # in cal BC
# parameters
l.dbs <- c("calpal", "medafricarbon", "agrichange", "bda", "calpal", "radon", "katsianis")
col.c14baz <- c("sourcedb", "site", "labnr", "c14age", "c14std", "period", "culture", "lon", "lat")
# collect the dates form different DBs, standardize the cultural period layout, filter on 'when' and 'where'
df <- neo_dbs_parse(l.dbs = l.dbs,
chr.interval.uncalBC = when,
roi = where,
col.c14baz = col.c14baz)
df.c14 <- neo_dbs_align(df,
mapping.file = "C:/Rprojects/neonet/doc/ref_table_per.xlsx")Alignments are done using the mapping file ref_table_per.xlsx, a default parameter in neo_dbs_align().
The XLSX file ref_table_per.xlsx has been created using:
df <- neo_dbs_parse(l.dbs = l.dbs,
chr.interval.uncalBC = when,
roi = where,
col.c14baz = col.c14baz)
# create the mapping file
neo_dbs_create_ref(df.all.res = df,
root.path = "C:/Rprojects/neonet/results",
outFile = "df_ref_per.xlsx")This mapping file ref_table_per.xlsx is a reference table to map cultural assessment coming from external DBs, collected throug c14bazAAR, to the Neonet one (..., LM, EN, ...) format. This XLSX file has to be updated manually by specialists.
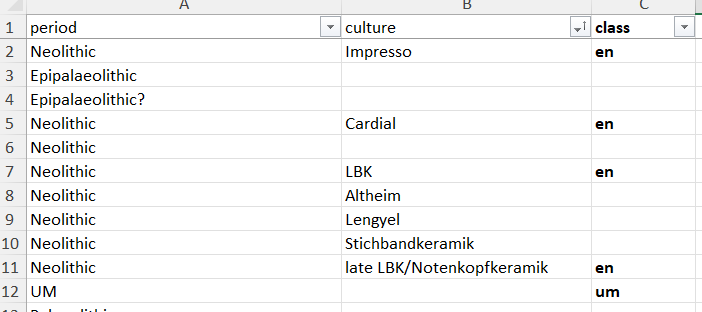
Equivalences between third part databases cultural assessment (columns 'period' and 'culture') and Neonet classes (column 'class')
For example:
df.c14 <- neo_dbs_align(df,
mapping.file = "C:/Rprojects/neonet/doc/ref_table_per.xlsx")
head(df.c14)Gives a dataframe where all fields have been renamed to be parsed with the Neonet functions. Among this mapping the column 'Period' with, for example, MM Middle Mesolithic) maps the bda period = Mésolithique 1 and culture = Capsien ancien or Capsien typique (columns 'db_period' and 'db_culture'):
| sourcedb | SiteName | LabCode | C14Age | C14SD | db_period | db_culture | Period | lon | lat |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| bda | Mechta el Arbi | Poz-92231 | 6600 | 80 | Mésolithique 1 | Capsien ancien | MM | 6.130900 | 36.09940 |
| bda | Mechta el Arbi | Poz-92232 | 6250 | 130 | Mésolithique 1 | Capsien ancien | MM | 6.130900 | 36.09940 |
| bda | Mechta el Arbi | Poz-92230 | 3500 | 120 | Mésolithique 1 | Capsien ancien | MM | 6.130900 | 36.09940 |
| bda | Kef Zoura D | UOC-2925 | 7787 | 48 | Mésolithique 1 | Capsien typique | MM | 7.682121 | 35.04205 |
| bda | Bortal Fakher | L-240A | 6930 | 200 | Mésolithique 1 | Capsien typique | MM | 8.176087 | 34.35480 |
| bda | Relilaï (B) | Gif-1714 | 7760 | 180 | Mésolithique 1 | Capsien typique | MM | 7.694694 | 35.04480 |
To filter aberrant dates, a combination of different function allow to retrieve the current information (once mapped to the Neonet layout) of these potential outliers and their original information (from their source database).
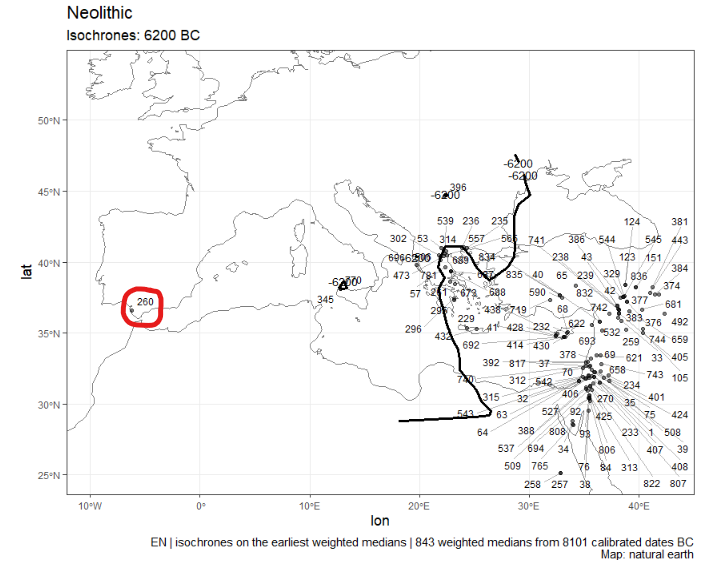
Here the dates 260 (circled in red), 396 and 345 seem aberrant
To check the info of the date numbered 260, do:
source("R/neo_find_date.R")
source("R/neo_dbs_info_date.R")
abber.date <- neo_find_date(df = isochr$data, print.it = FALSE, idf.dates = 260)
ad <- neo_dbs_info_date(df.c14 = df.c14, LabCode = abber.date$labcode)Gives:
[1] "Reads a 'sf' dataframe"
[1] "Layout for 'aberrant dates' format:"
neonetatl Sac-1676 El Retamar -6263 EN None None
Where neonetatl is the source DB, Sac-1676 is the labnum, El Retamar the site name, -6263 the weighted mean (cal BC), EN the period (Early Neolithic), None the culture (no data) and the second None a place holder for a description explaining why this date has been discarted.
If the archaeological documentation shows that date Sac-1676 (aka 260) is wrong (mixed assemblage, possibly coming from another layer, etc.). The last line neonetatl Sac-1676 El Retamar -6263 EN None None can be pasted as it into the c14_aberrant_dates.tsv file.
More info can be found for this date, reusing the ad dataframe. Running the following functions helps to contextualize the date.
source("R/neo_dbs_info_date_src.R")
neo_dbs_info_date_src(db = ad$sourcedb,
LabCode = ad$LabCode)Gives:
sourcedb sourcedb_version labnr c14age c14std site feature period material species country lat
1 neonetatl 2023-12-08 Sac-1676 7400 100 El Retamar Conchero 6 EN shell <NA> Spain 36.57873
lon shortref
1 -6.226273 Cantillo-Duarte et al. 2010
The list of aberrant dates, for example c14_aberrant_dates.tsv, is used to discard some dates with the neo_dbs_rm_date() function
source("R/neo_dbs_rm_date.R")
df_filtered <- neo_dbs_rm_date(df.c14)By default, dates having a dash prefix in their sourcedb column will be skipped (ex: -radon)
Screenshot of the 'c14_to_remove.tsv' table
A template script to run this operation: run_outliers.R
Site coordinates can be wrong, for example for the Jordian site of Sabha (Xronos | Google maps). Curated coordinates are listed in the c14_corrected_coordinates.tsv file and handle by the neo_dbs_coord_dates() function.
When aggregate different databases, using ce c14bazAAR package, two same sites can have different site names (ex: Pollera and Grotta della Pollera). To avoid these mismatches, the function neo_dbs_sitename_dates() uses the mapping table c14_corrected_sitenames.tsv
source("R/neo_dbs_sitename_dates.R")
df.c14 <- neo_dbs_sitename_dates(df.c14)AlternativeLabCode will be replaced by LabCode
source("R/neo_dbs_labcode_dates.R")
df.c14 <- neo_dbs_labcode_dates(df.c14)neo_calib_plot() reuse a rcarbon function.
source("R/neo_calib_plot.R")
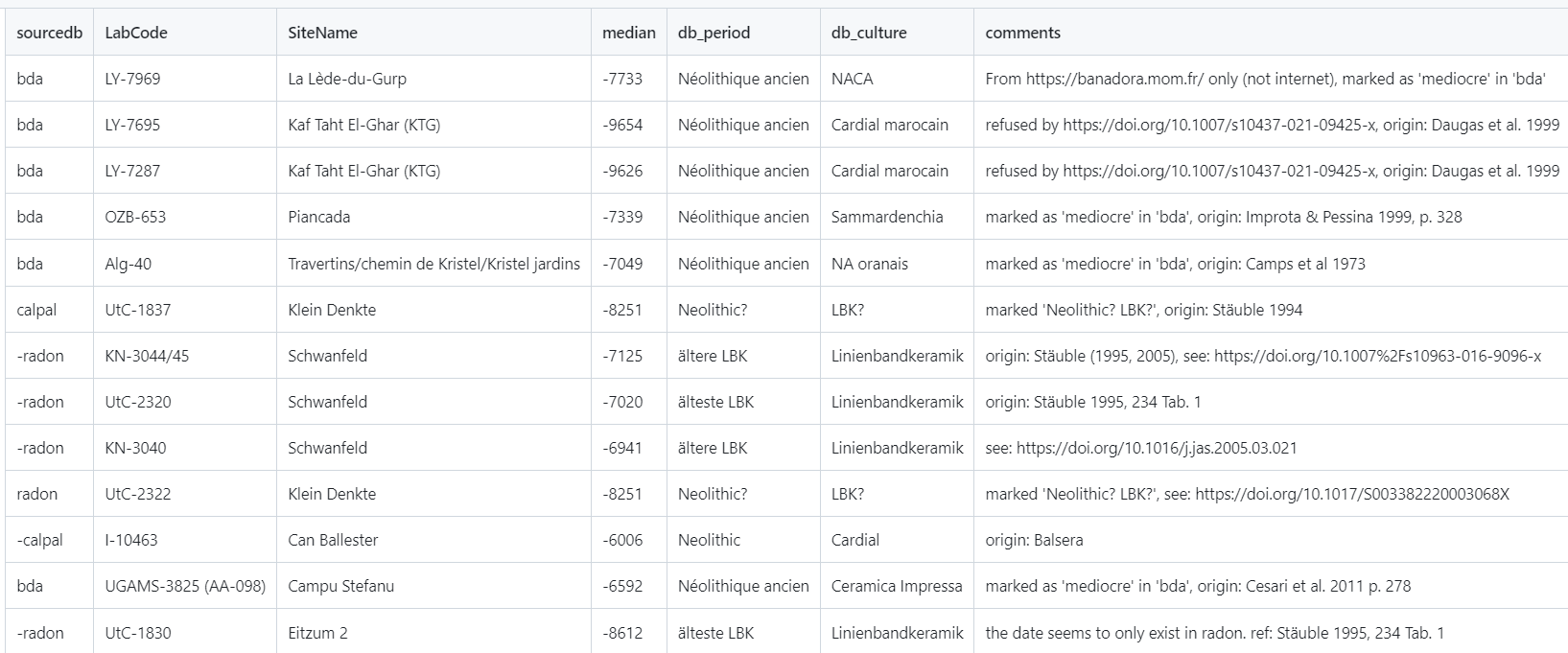
neo_calib_plot(df.c14 = c(6190, 100))Gives:
Calibrate one date showing its weighted median (w-median)
The function neo_calib_plot() can be used for one or many (a dataframe) dates. For the latter case, it will seriate the dates.
source("R/neo_calib_plot.R")
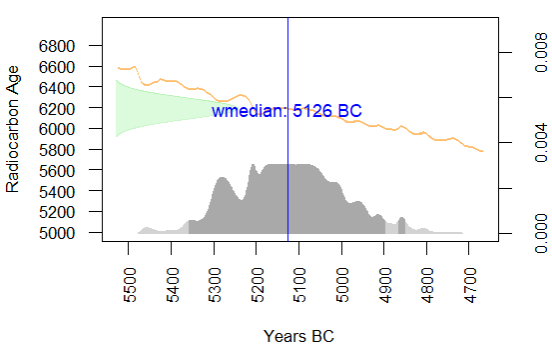
neo_calib_plot(df.c14 = isochr$data.raw)Gives:
Calibrate various dates seriated on their weighted median (w-median)
A subset on a site (Pendimoun)
source("R/neo_calib_plot.R")
source("R/neo_calib_plot.R")
df_filtered_ww_pendimoun <- df_filtered[df_filtered$SiteName == 'Pendimoun', ]
# rename columns
df_filtered_ww_pendimoun$site <- df_filtered_ww_pendimoun$SiteName
df_filtered_ww_pendimoun$labcode <- df_filtered_ww_pendimoun$LabCode
neo_calib_plot(df.c14 = df_filtered_ww_pendimoun)Plot the summed probabilty densities (SPD) of the two datasets, once df.c14 calculated. The function neo_spd() calls neo_spdplot(). The latter has been adapted from rcarbon::plot.stackCalSPD.R, to fetch NeoNet default period colors.
library(rcarbon)
source("R/neo_spd.R")
source("R/neo_spdplot.R")
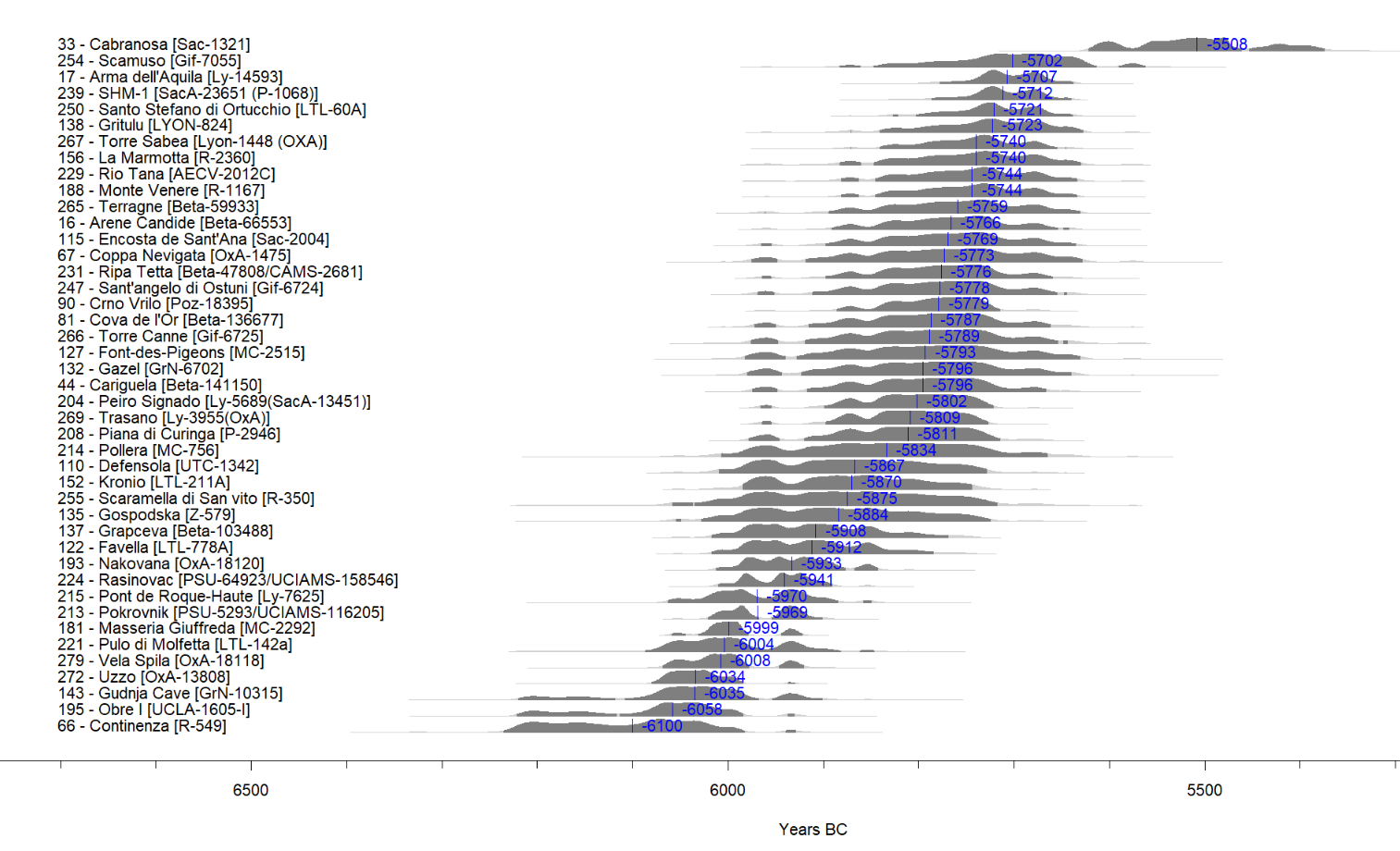
neo_spd(df.c14 = df.c14)Gives:
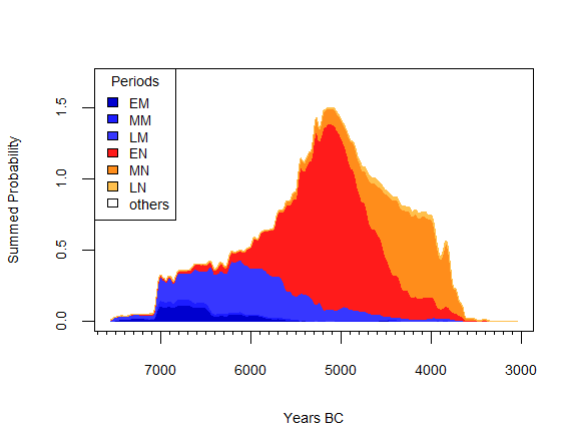
NeoNet dataset SPD with default period colors
neo_spd() can be run on a GeoJSON file exported from the NeoNet app (see "export dates" in the web document. For example neonet-data-2023-09-24.geojson, see also: isochrones
neo_spd(df.c14 = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/zoometh/neonet/main/results/neonet-data-2023-09-24.geojson",
export = T)In the same way, SPD can be done for KCC
source("R/neo_spd.R")
source("R/neo_spdplot.R")
source("R/neo_kcc_extract.R")
kcc.file <- c("koppen_6k.tif", "koppen_7k.tif", "koppen_8k.tif",
"koppen_9k.tif", "koppen_10k.tif", "koppen_11k.tif")
df_cc <- neo_kcc_extract(df.c14 = df_filtered,
kcc.file = kcc.file)
neo_spd(df.c14 = df_cc, color.on = "kcc")Create a map with isochrone contours to model the spread of Neolithic using the neo_isochr() function.
The file neonet-data-2023-09-24.geojson is an export from the NeoNet app (see "export dates" in the web document). This GeoJSON file can be curated in a GIS (ex: removing aberrant dates) before running the following functions (neo_isochr, neo_spd, etc.).
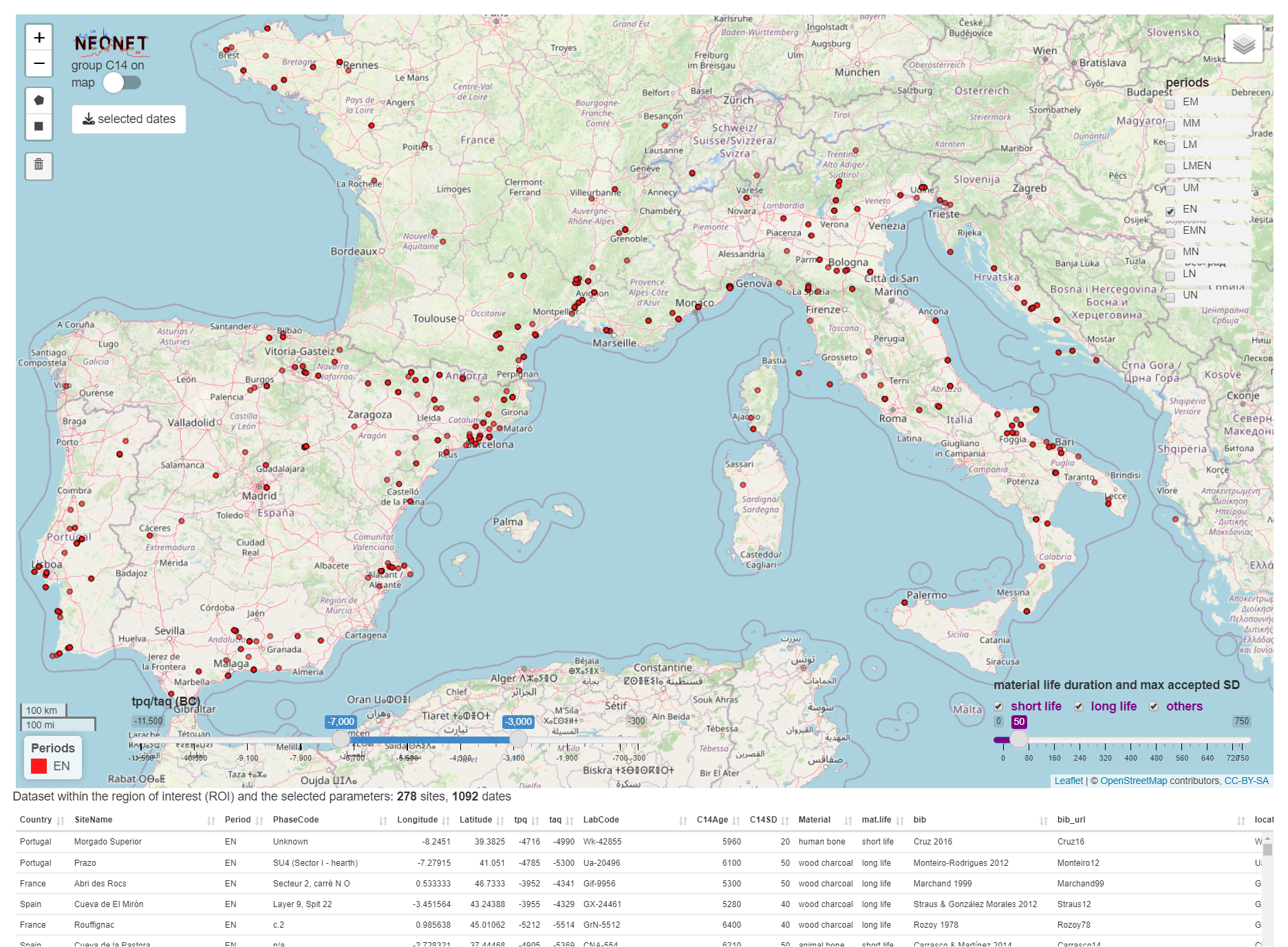
Screen capture of the NeoNet app before the export of the `neonet-data-2023-09-24.geojson` file: Early Neolithic (EN) dates only having a SD ≤ 50, and calBC interval between -7000 and -3000
The output is a map with isochrones calculated on the median of calibrated dates.
library(rcarbon)
source("R/neo_isochr.R")
source("R/neo_spd.R")
source("R/neo_calib.R")
neo_isochr(df.c14 = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/zoometh/neonet/main/results/neonet-data-2023-09-24.geojson",
show.lbl = FALSE)Where neo_calib() calculate the cal BC min and max (i.e, calibrates), and the medidan (with 'intcal20' and the Bchron R package)
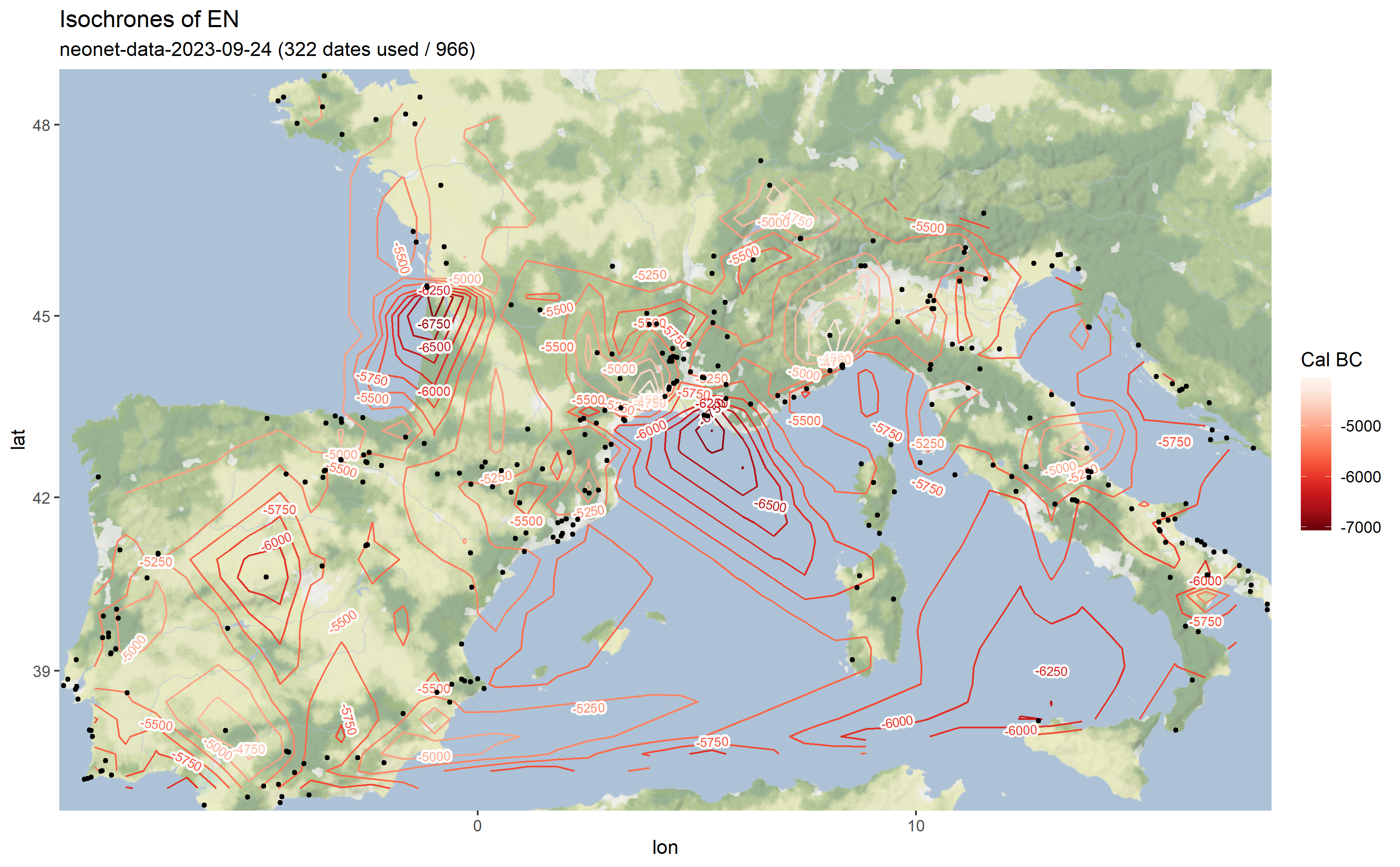
Output map from the `neonet-data-2023-09-24.geojson`
Isochrones are created from the interpolation map:
source("R/neo_isochr_inter_map.R")
inter.map <- neo_isochr_inter_map(isochr$inter)
inter.map
## Not Run
# ggplot2::ggsave(paste0(root.path, "img/", "isochrones-barriere-Italy-EN-inter-map.png"), inter.map, width = 7, height = 7)
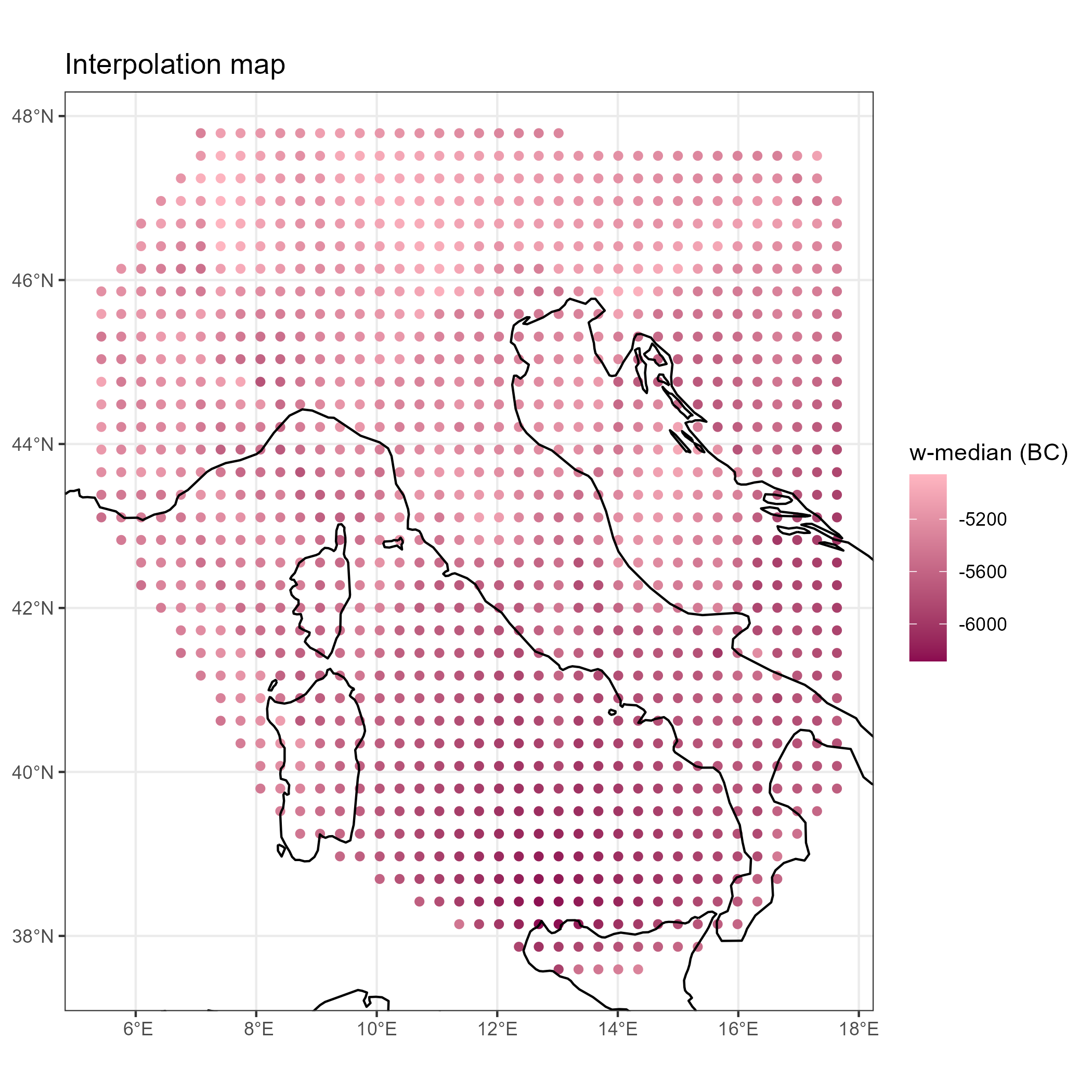
Weighted medians (w-median) interpolated
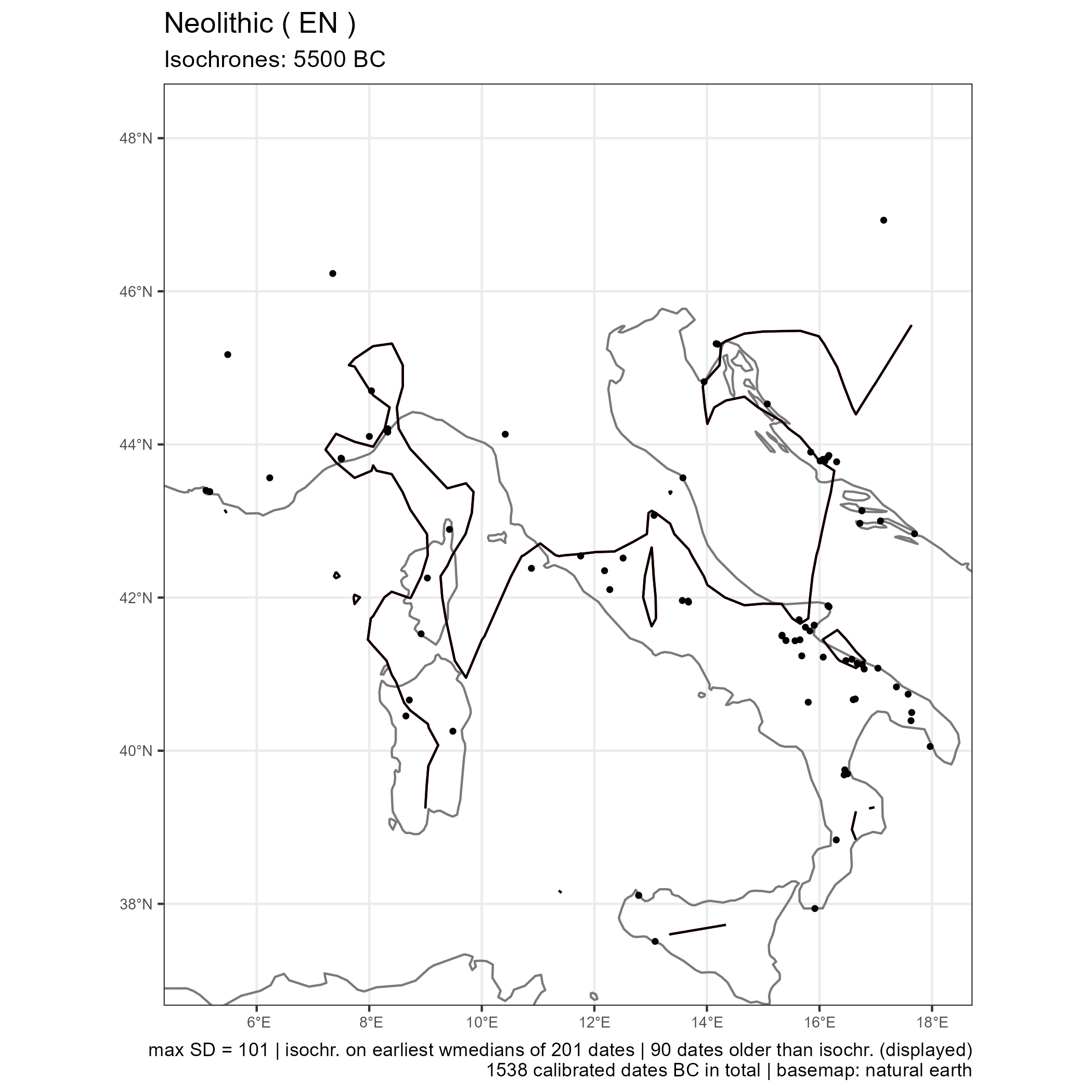
The same function can be used symetrically: instead of plotting the earliest dates of the Neolithic (EN), one can also plot the latest dates of the Paleolithic (or Late Mesolithic, LM)
myc14data <- "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/zoometh/neonet/main/results/1_AOI_France_E-W.geojson"
neo_isochr(df.c14 = myc14data, mapname = "France_EW")
neo_isochr(df.c14 = myc14data, mapname = "France_EW", selected.per = c("LM"))
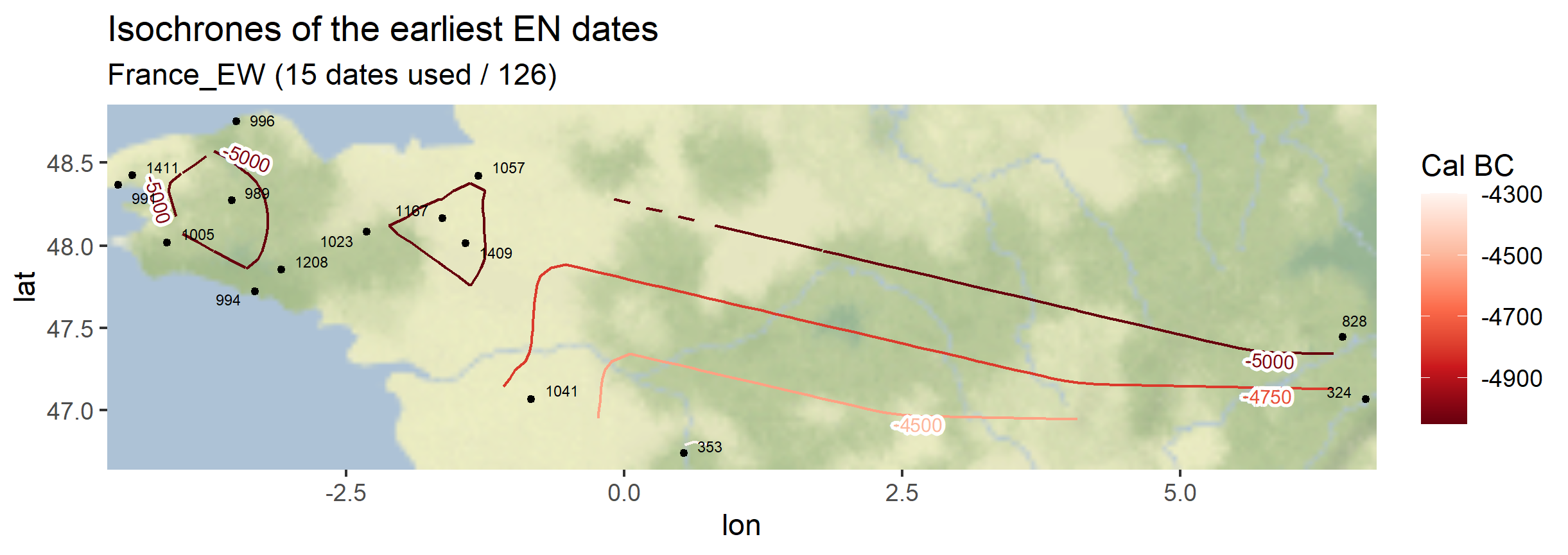
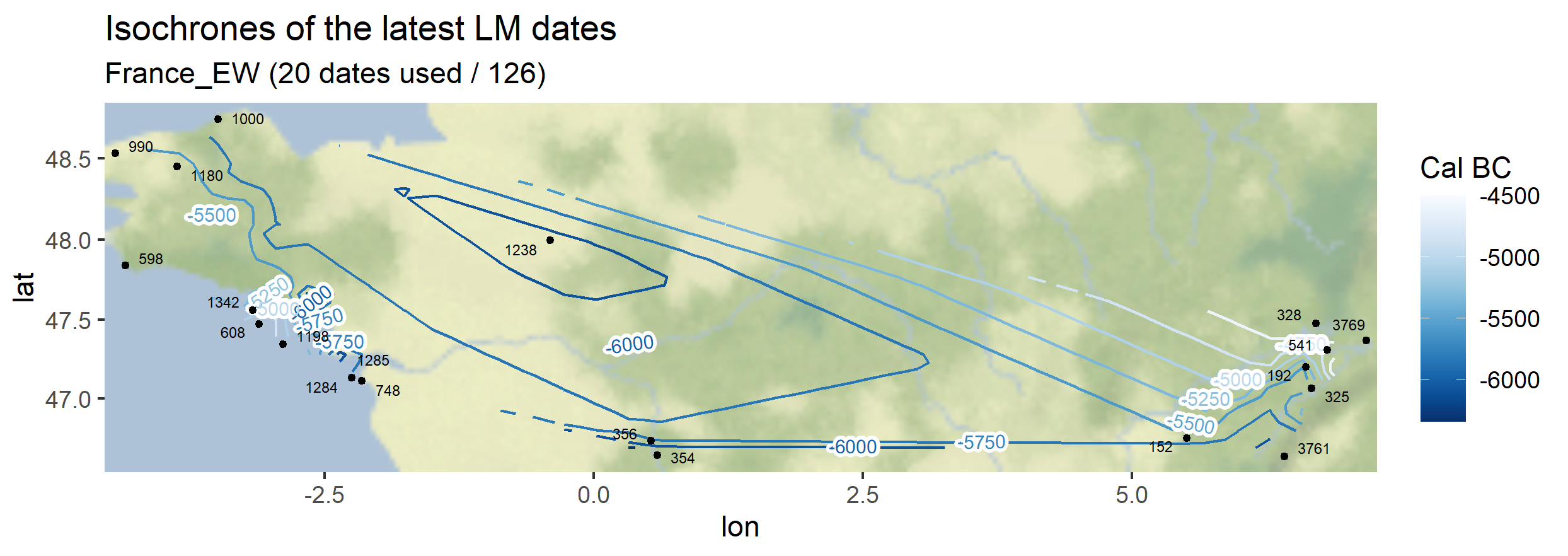
Output maps from the `1_AOI_France_E-W.geojson`: earliest Neolithic dates and latest Paleolithic dates
KCC, Koppen Climate Classification, Koeppen Climate Classification
The Neonet framework and online app integrate Koppen Climate Classification (KCC) for 6,000 BP to 10,000 BP.
Koppen classification uses five broad classes:
| code | climate | colors |
|---|---|---|
| A* | Tropical |    |
| B* | Arid |     |
| C* | Temperate |          |
| D* | Cold |             |
| E* | Polar |   |
And, there are 30 basic classes
The Koppen Climate Classes (KCC) are listed here
Koppen functions are designed not only for the Neonet dataset, but also for all radiocarbon dataset respecting the minimum data stracture (site, labcode, x, y, etc.).
The app integrates Koppen Climate Classification (KCC) for 6,000 BP to 10,000 BP created with the R pastclim package and the neo_kcc_create() function.
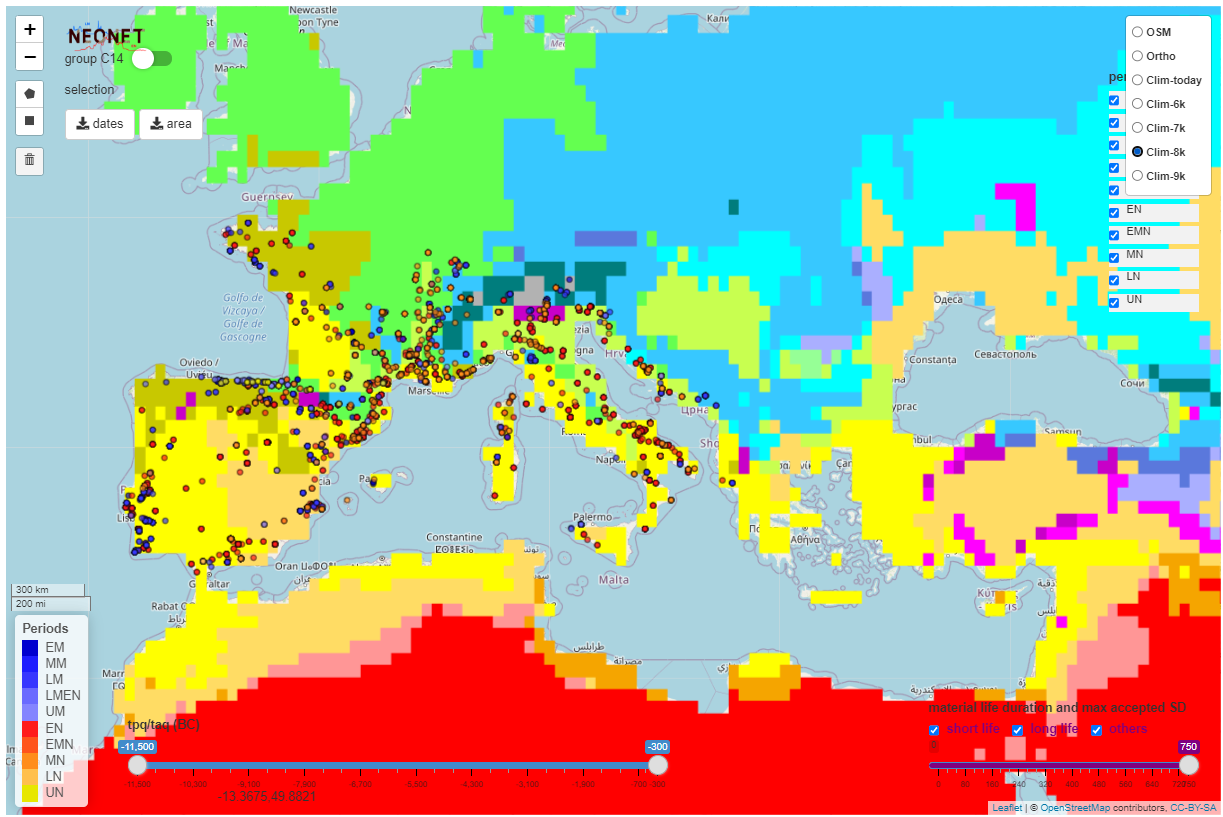
The Koppen Climate Classification calculated for 8,000 BP (8k) with the pastclim R package and hosted on a GeoServer
Neonet functions help to blend pastclim KCC and radiocarbon dates.
# install the packages pastclim and terra
devtools::install_github("EvolEcolGroup/pastclim", ref="dev")
library(pastclim)
library(terra)
# set paths and create maps
outDir <- "C:/Rprojects/neonet/doc/data/clim/"
pastclim::set_data_path(path_to_nc = outDir)
source("R/neo_kcc_create.R")
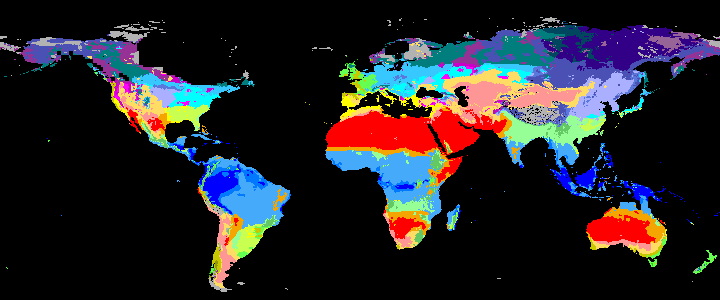
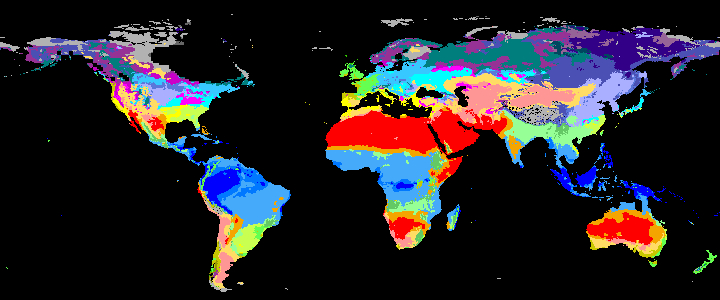
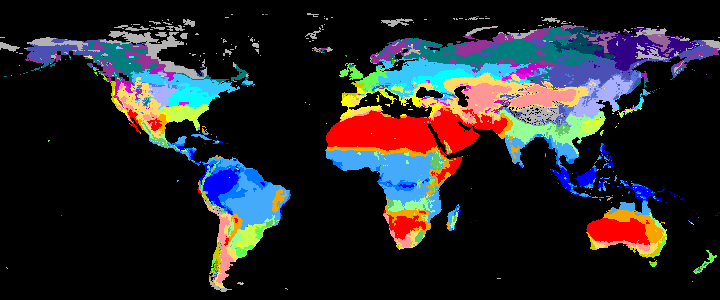
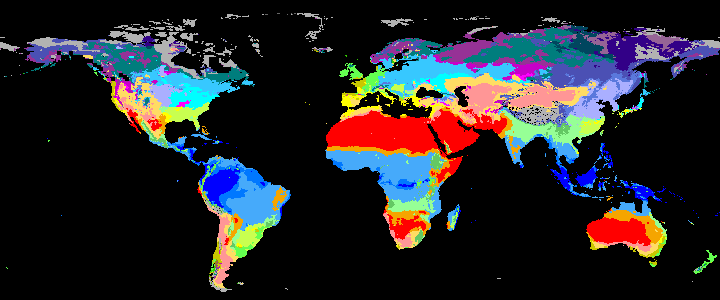
neo_kcc_create()Creates these KCC GeoTiffs:
KCC are created as GeoTiffs using the R pastclim package
| Geotiff image | description |
|---|---|
 |
koppen_11k download |
 |
koppen_10k download |
 |
koppen_9k download |
 |
koppen_8k download |
 |
koppen_7k download |
 |
koppen_6k download |
Past Koppen Climate Classification calculated in Kyears BP with the pastclim R package
To subset a specific area of a KCC map, select a KCC map (ex: 'koppen_7k') and a ROI (ex: 'roi-midi-france')
source("R/neo_kcc_crop.R")
kcc <- "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/zoometh/neonet/main/doc/data/clim/koppen_7k.tif"
roi <- "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/zoometh/neonet/main/doc/talks/2024-simep/roi-midi-france.geojson"
map.select <- neo_kcc_crop(kcc = kcc,
roi = roi)
terra::plot(map.select)Gives:
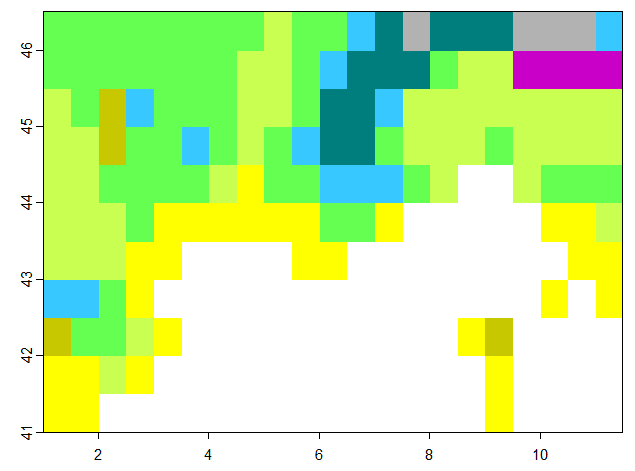
The 'koppen_7k' has been cropped with the ROI 'roi-midi-france'
This set of functions creates an interactive dataset of df.c14 dates and the climates to which they belong.
kcc.file <- c("koppen_6k.tif", "koppen_7k.tif", "koppen_8k.tif",
"koppen_9k.tif", "koppen_10k.tif", "koppen_11k.tif")
source("R/neo_kcc_extract.R")
df_kcc <- neo_kcc_extract(df.c14 = df.c14, kcc.file = kcc.file)
source("R/neo_kcc_extract_longformat.R")
df_kcc_long <- neo_kcc_extract_longformat(df_kcc)
source("R/neo_dbs_info_dates_datatable.R")
dt.out <- neo_dbs_info_dates_datatable(df.c14 = df_kcc_long,
fields = c("SiteName", "code", "Period", "median", "map", "LabCode", "db_period", "db_culture", "sourcedb", "X", "Y", "color"),
font.size = "16pt")
## Not Run
# htmlwidgets::saveWidget(dt.out, "C:/Rprojects/neonet/doc/talks/2024-simep/img/dates_kcc.html")The neo_kcc_map() creates a KCC map with a layer of dates above
source("R/config.R") # default variables: column names mapping, colors, etc.
df <- c14bazAAR::get_c14data("neonet")
df <- sf::st_as_sf(df, coords = c("lon", "lat"), crs = 4326)
neo_kcc_map(df.c14 = df,
kcc = "C:/Rprojects/neonet/doc/data/clim/koppen_7k.tif",
export = TRUE,
fileOut = "neonet_kcc.png" )Gives:
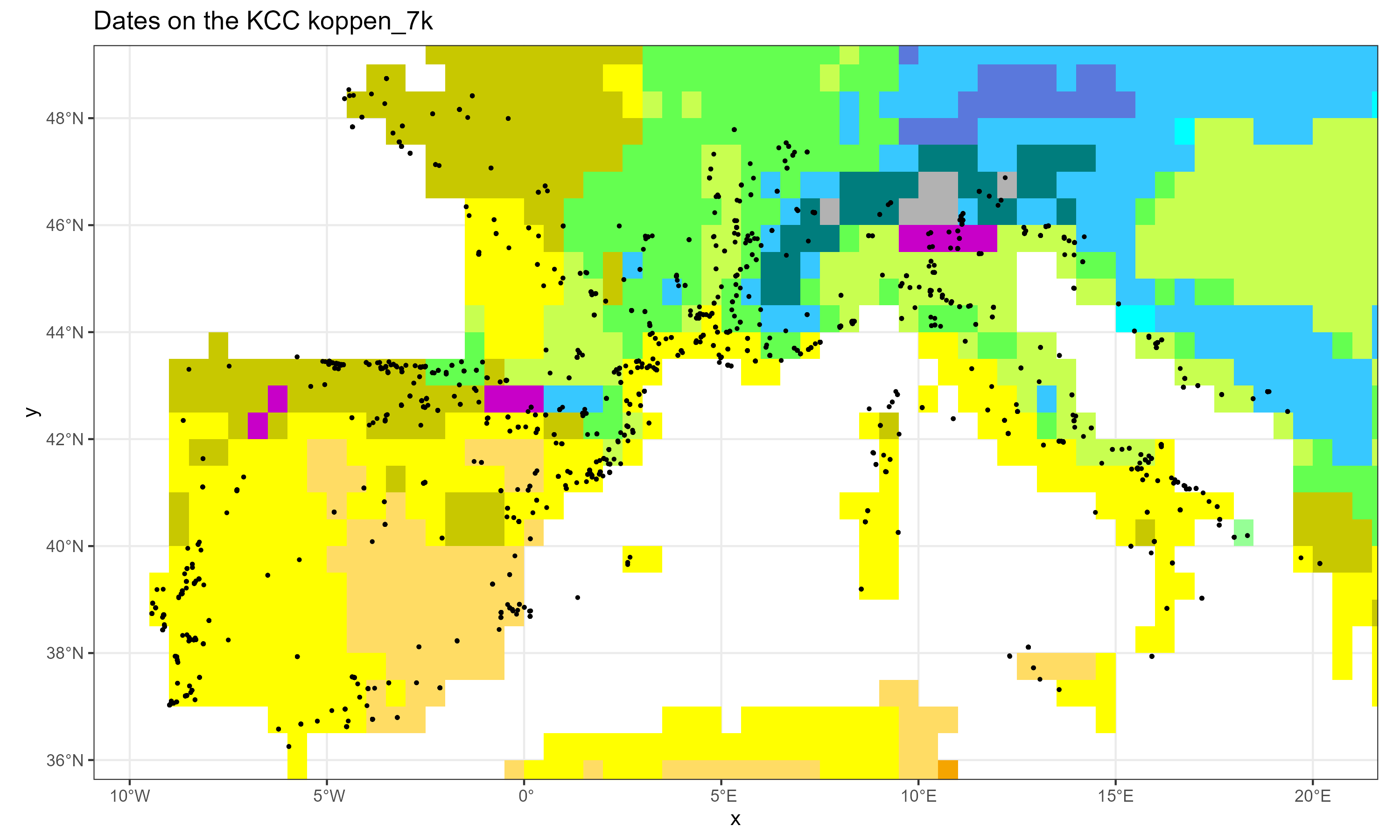
The neonet dataset over the KCC 7k
stacked plots
To assess what were the climates classes that where inhabited in the past, during the Late Mesolithic (LM) and Middle Mesolithic (MM) based on previous dates
df.c14 <- neo_calib(df.c14)
df.c14 <- sf::st_as_sf(df.c14, coords = c("lon", "lat"), crs = 4326)
kcc.file <- c("koppen_6k.tif", "koppen_7k.tif", "koppen_8k.tif",
"koppen_9k.tif", "koppen_10k.tif", "koppen_11k.tif")
df_cc <- neo_kcc_extract(df.c14 = df.c14, kcc.file = kcc.file)
col.req <- gsub(pattern = ".tif", "", kcc.file)
neo_kcc_plotbar(df_cc = df_cc,
kcc.file = c("koppen_8k.tif", "koppen_9k.tif"),
col.req = col.req,
selected.per = c("EN"),
title = "Neolithic: transition btw 7,000 and 6,000 BC",
legend.show = FALSE)Gives:
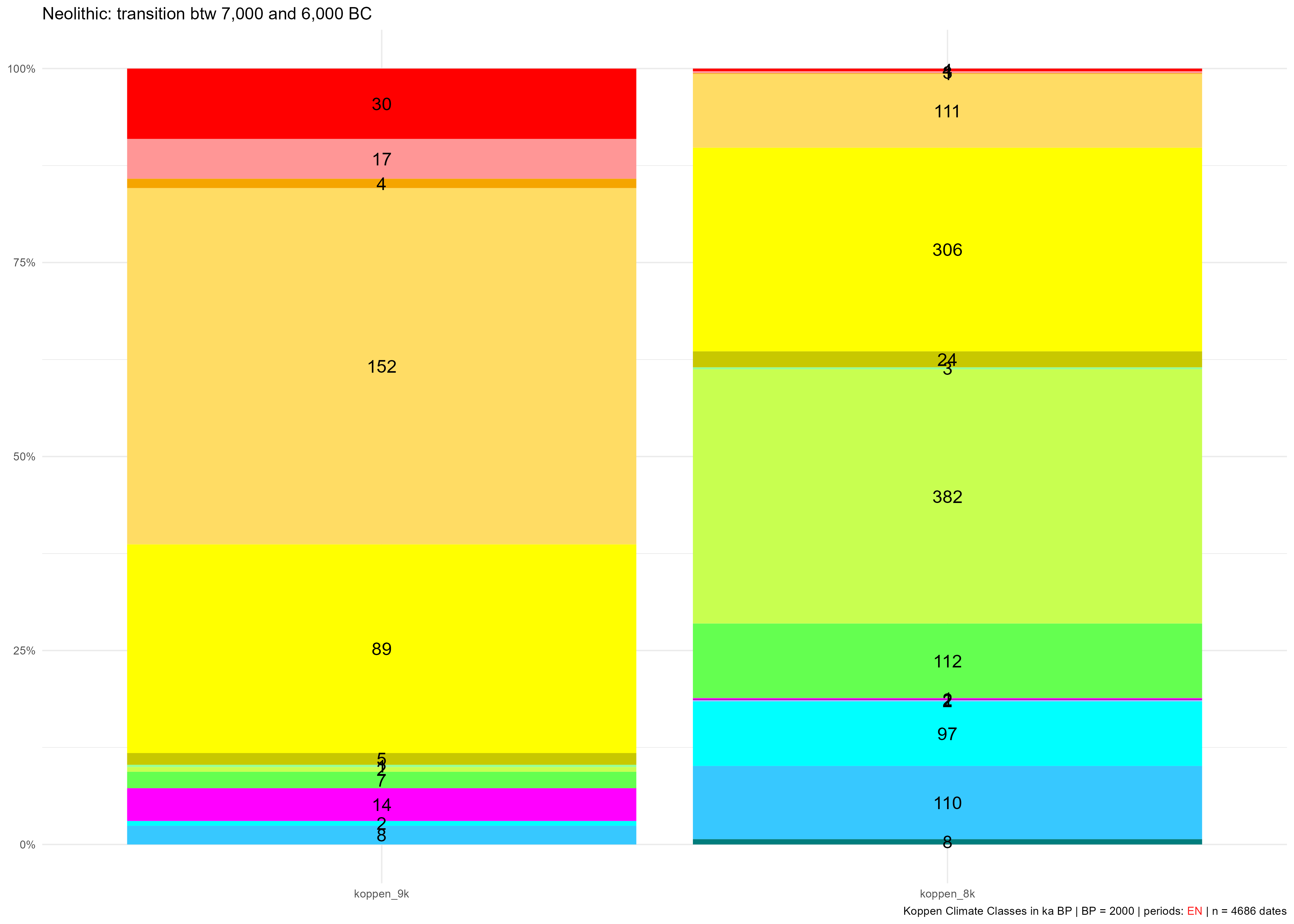
KCC occupied during the EN between 7,000 and 6,000 BC (9 ka and 8 ka BP) with counts of dates belonging to these time slices
To do the same, not sliced on KCC (koppen_8k, koppen_9k, ...) but time span, use the neo_kcc_plotbar_time_intervals() function. For example on the time span 6100-5000 BC (koppen_8k, koppen_7k maps), using the function neo_subset_when(), each 100 years, and on a selected area using the function neo_subset_roi().
source("R/neo_subset_roi.R")
source("R/neo_subset_when.R")
source("R/neo_kcc_extract.R")
source("R/neo_kcc_plotbar_time_intervals.R")
when <- c(6100, 5000)
where <- c(-10, 35, 19, 45) # Central Western Mediterranean (xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax)
df_filtered_space <- neo_subset_roi(df_filtered, where = where)
df_filtered_space_time <- neo_subset_when(df.c14 = df_filtered_space,
when = when,
period = "EN",
top.date = TRUE)
df_cc <- neo_kcc_extract(df.c14 = df_filtered_space_time, kcc.file = c("koppen_7k.tif", "koppen_8k.tif"))
neo_kcc_plotbar_time_intervals(df_cc,
time.interval = when,
time.bin = 100)Gives
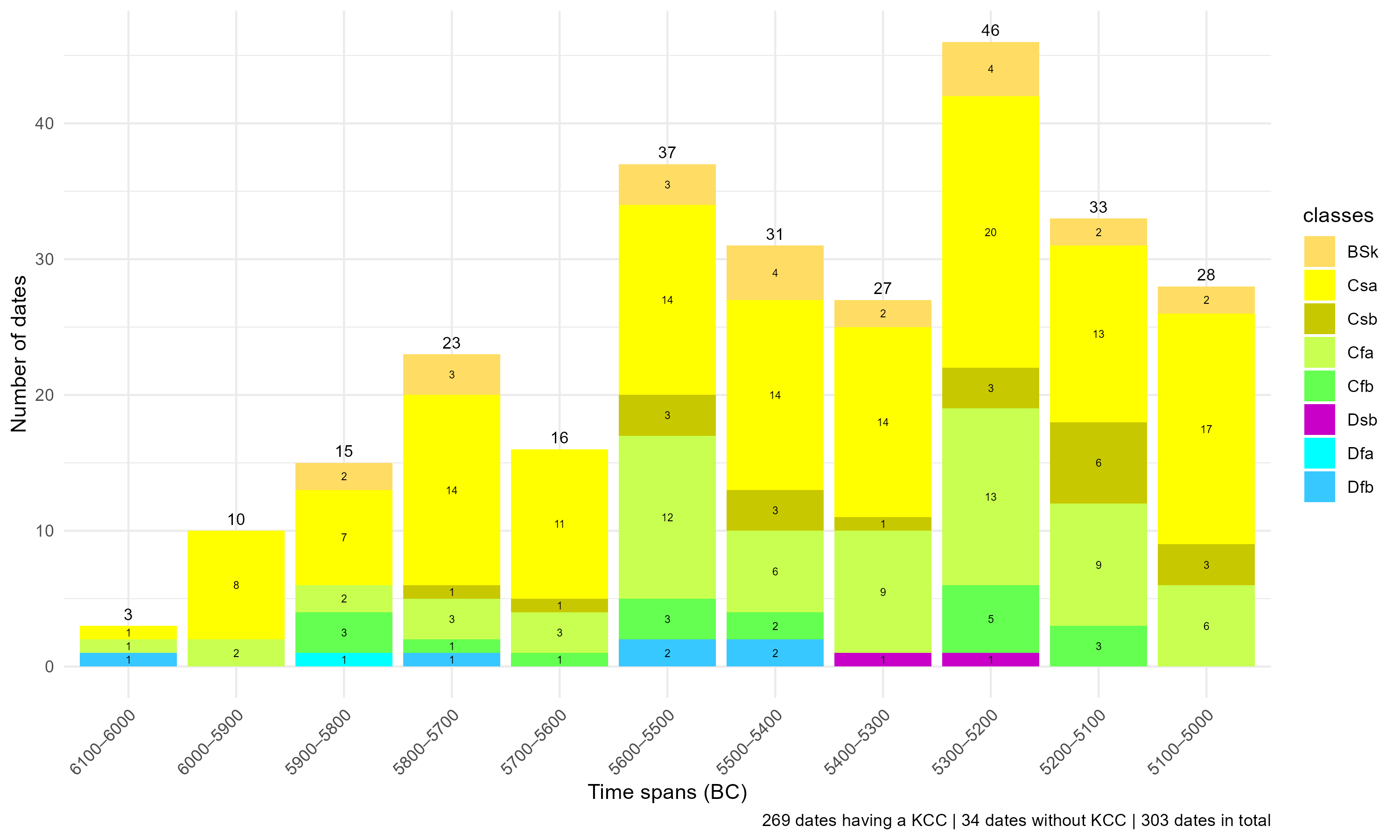
KCC occupied during the EN between 6,100 and 5,000 BC with counts of dates belonging to these time slices
Sankey plots
To run this before-after diagram on 'koppen_8k' and 'koppen_7k', for a specified area 'roi-midi-france':
source("R/neo_kcc_sankey.R")
gout <- neo_kcc_sankey(kcc_data = c("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/zoometh/neonet/main/doc/data/clim/koppen_8k.tif", "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/zoometh/neonet/main/doc/data/clim/koppen_7k.tif"),
roi = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/zoometh/neonet/main/doc/talks/2024-simep/roi-midi-france.geojson")
goutGives:
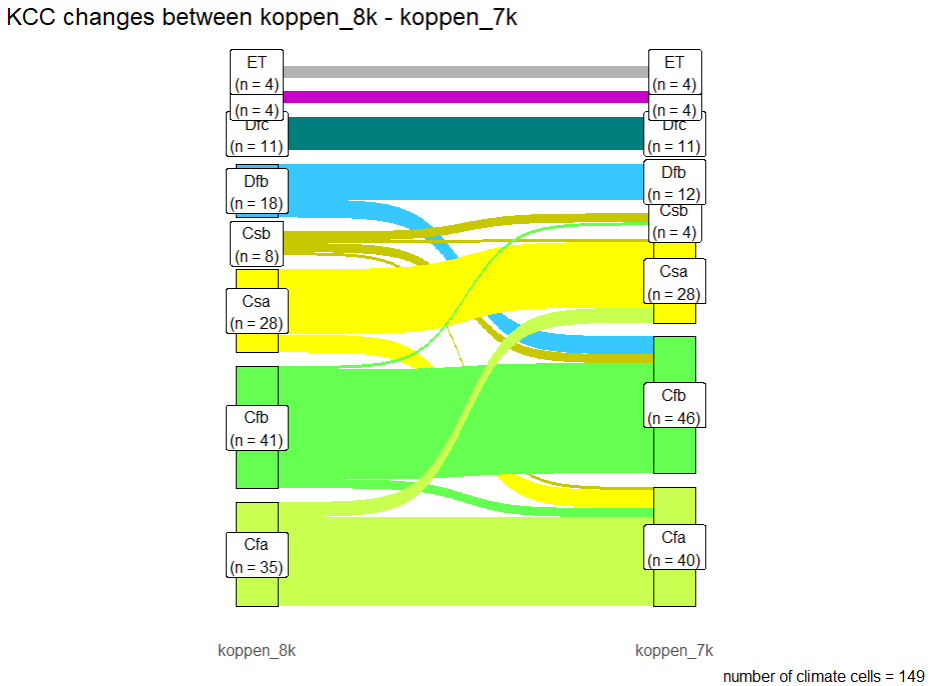
Sankey diagram for the whole 'roi-midi-france' between 'koppen_8k' and 'koppen_7k'. Here the changes are assessed for the whole area, that is to say all KCC map cells (n = 149)
The neo_kcc_extract() function collects the KCC values (climates) of each date.
NeoNet-strati is an online R Shiny interactive app to record the stratigraphy of NeoNet's archaeological sites in an editable dataframe based on LabCode identifiers.
flowchart TD
A[NeoNet dataset] --is read by--> B{{<a href='https://trainingidn.shinyapps.io/neonet-strati'>neonet-strati</a>}}:::neonetshiny;
B --edit<br>site stratigraphy--> B;
B --export<br>site stratigraphy<br>file--> C[<a href='https://github.com/historical-time/data-samples/blob/main/neonet/Roc%20du%20Dourgne_2023-07-30.csv'>Roc du Dourgne_2023-07-30.csv</a>];
C --is read by--> D{{<a href='https://github.com/historical-time/caa23/blob/main/neonet/functions/neo_strat.R'>neonet_strat</a>}}:::neonetfunct;
D --export --> E[maps<br>charts<br>listings<br>...];
classDef neonetfunct fill:#e3c071;
classDef neonetshiny fill:#71e37c;
Strati app and strati analysis overall Workflow
The app is composed by different panels: a site to be recorded (Site Stratigraphy panel), and the complete dataset (All sites panel). A site name is copied from All sites panel to Site Stratigraphy panel.
Plot a selected site in an editable table to record its stratigraphical relationships.
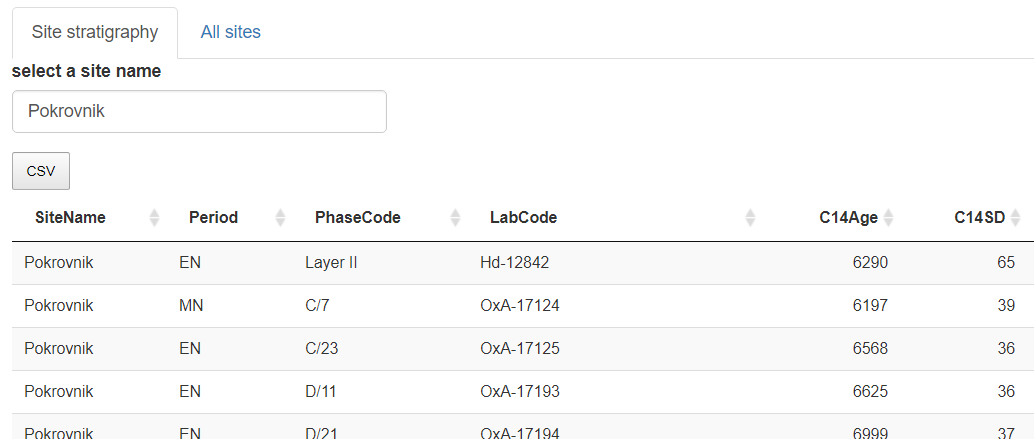
Panel "Site Stratigraphy" editable dataframe. By default the app opens on "Pokrovnik"
Show the complete NeoNet dataset. A site can be selected by searching it in the selection search bar (top-right) and copying its name (Site Name column). Here Roc du Dourgne, highlighted in blue.
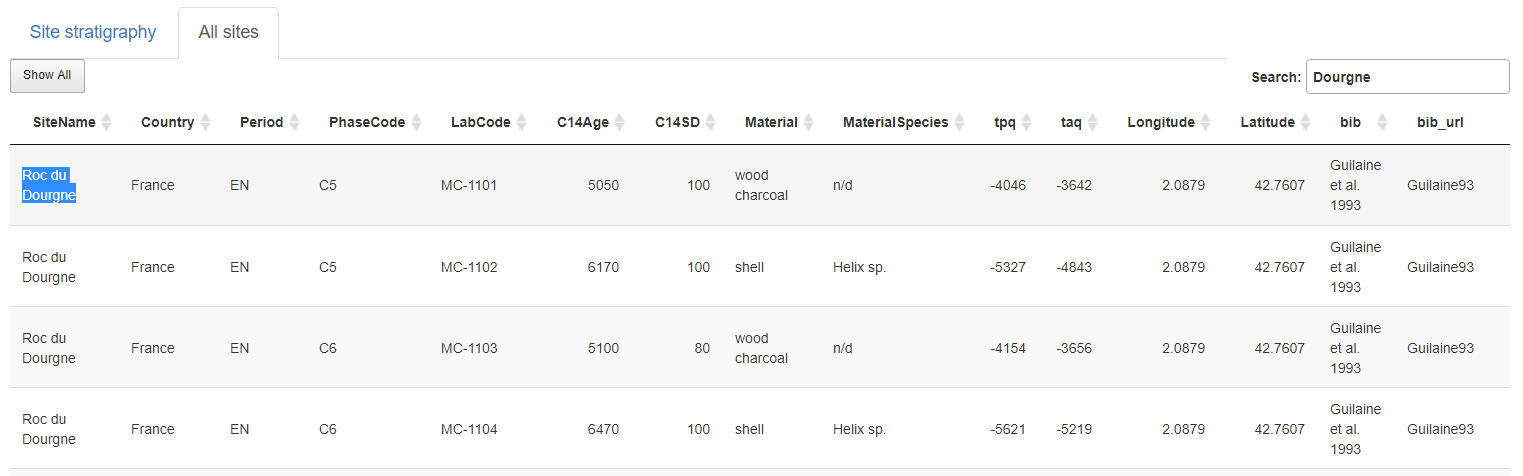
Panel "All sites". Selection of the "Roc du Dourgne" site
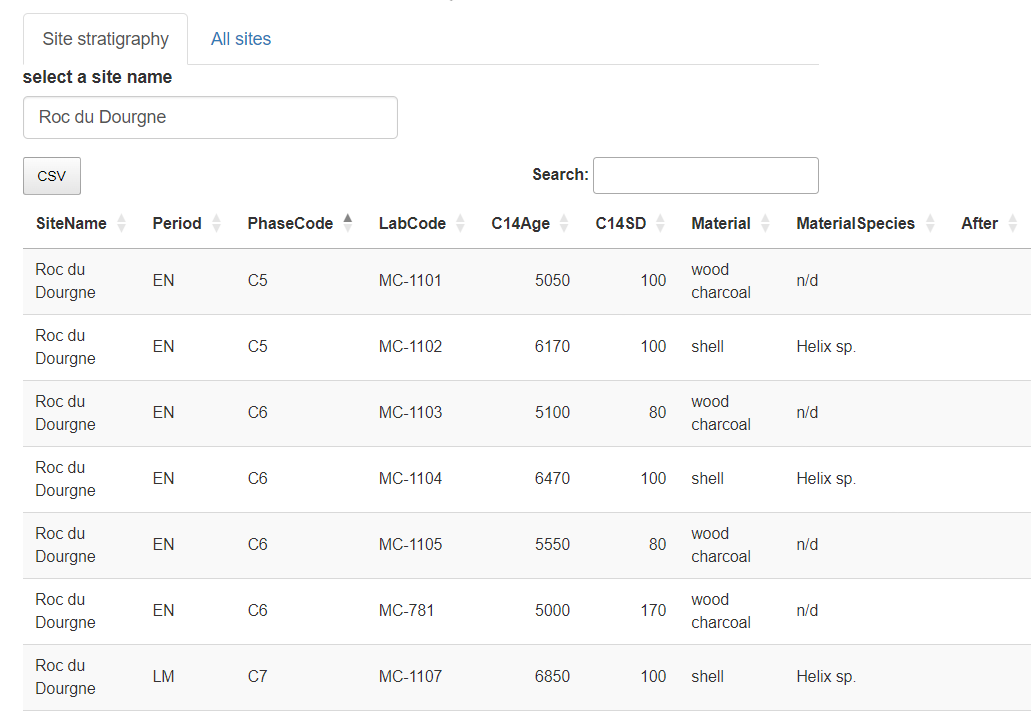
"Roc du Dourgne" site sorted on its "PhaseCode"
The stratigraphical relations can be added into the "After" column, and thereafter exported in CSV
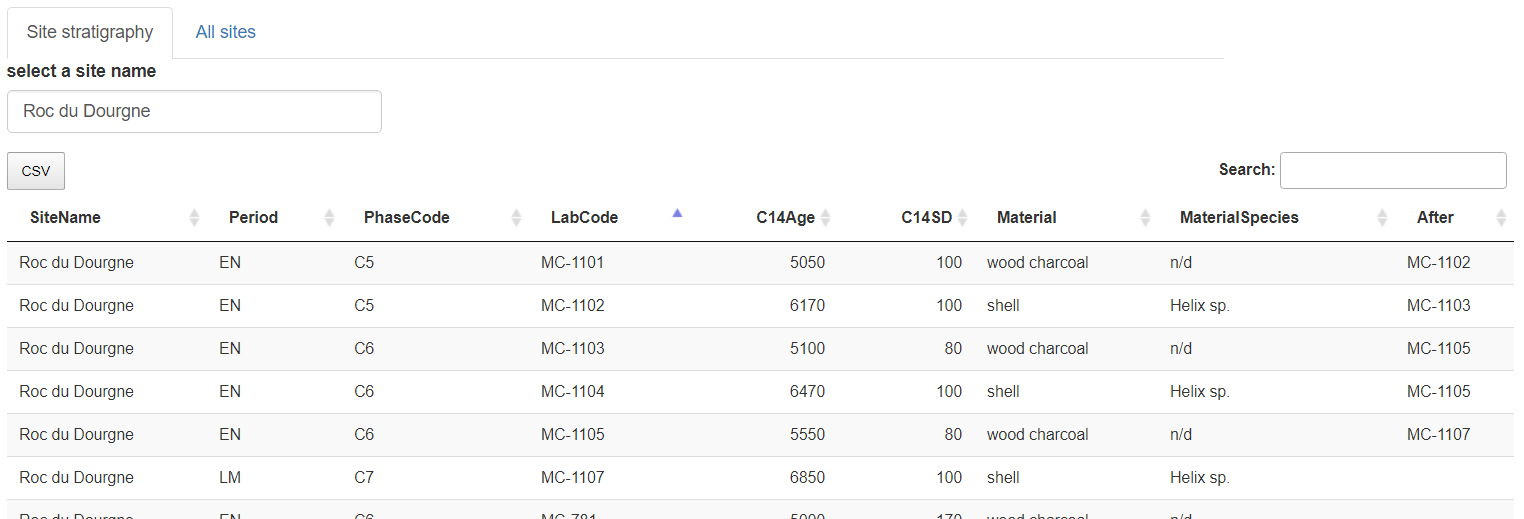
"Roc du Dourgne" stratgraphical relationships (column "After") after edition
For example, "Roc du Dourgne" relationships are:
| LabCode | After | Period | PhaseCode | C14Age | C14SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MC-1101 | MC-1102 | EN | C5 | 5050 | 100 |
| MC-1102 | MC-1103 | EN | C5 | 6170 | 100 |
| MC-1103 | MC-1105 | EN | C6 | 5100 | 80 |
| MC-1104 | MC-1105 | EN | C6 | 6470 | 100 |
| MC-1105 | MC-1107 | EN | C6 | 5550 | 80 |
| MC-1107 | LM | C7 | 6850 | 100 | |
| MC-781 | EN | C6 | 5000 | 170 | |
| MC-782 | LM | Layer 7 | 5770 | 170 |
The first row can be read as: "the layer containing radiocarbon date MC-1101 comes after the layer containing radiocarbon date MC-1102".
Once the site stratigraphy recorded, save the changes by downloading the dataset pressing the button (top-left) as a CSV file. The output file name is the site name and the current date (ex: Roc du Dourgne_2024-04-12.csv).
The file exported from the NeoNet strati app can be read by the neo_strati() function (see Harris Matrix)
The output CSV file exported by NeoNet-strati can be read by the neo_strat() function. For example, ploting the C14Age and the PhaseCode.
neo_strat(inData = 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/historical-time/data-samples/main/neonet/Roc du Dourgne_2023-07-30.csv',
outLabel = c("C14Age"))
neo_strat(inData = 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/historical-time/data-samples/main/neonet/Roc du Dourgne_2023-07-30.csv',
outLabel = c("PhaseCode"))Gives:
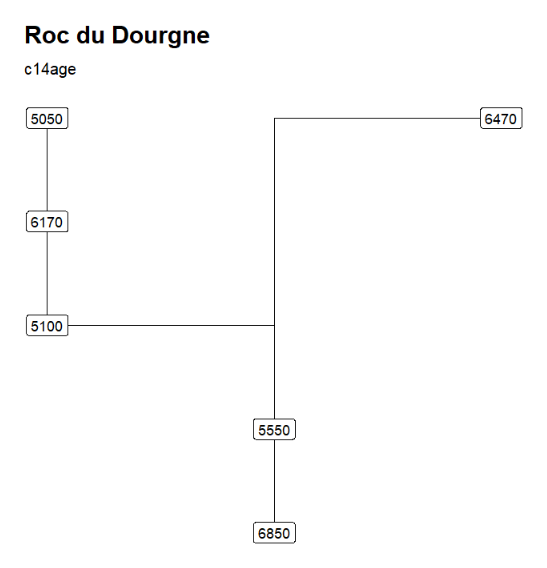
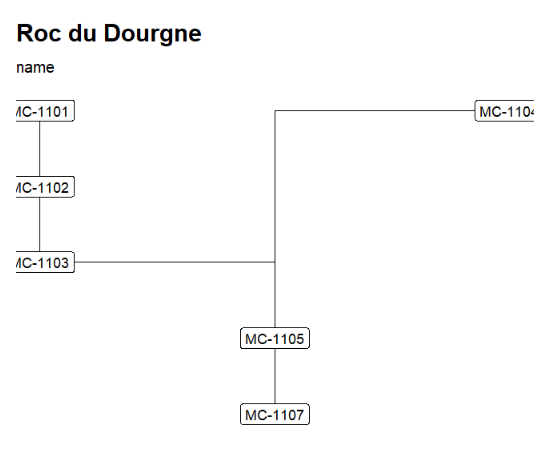
"Roc du Dourgne" stratgraphical relationships using LabCode identifiers, ordered on the "LabCode" column, displaying the C14Age (left) and the LabCode (right)
Changing the outLabel to Period allows to color on periods using the default period colors (see the web document)
neo_strat(inData = 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/historical-time/data-samples/main/neonet/Roc du Dourgne_2023-07-30.csv',
outLabel = c("Period"))Gives:
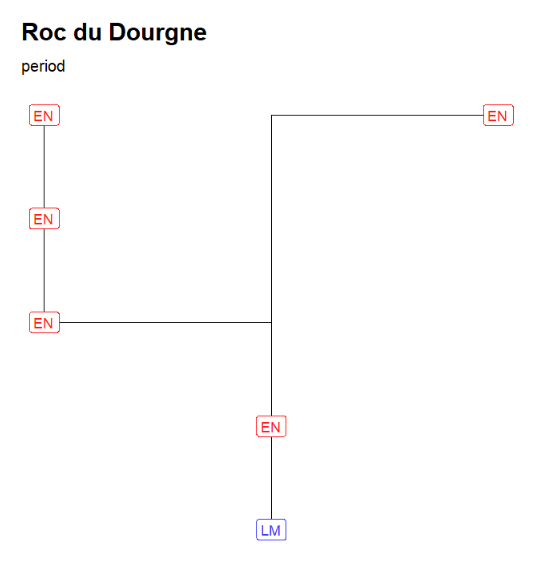
"Roc du Dourgne" stratgraphical relationships using LabCode identifiers, ordered on the "LabCode" column
Using neo_leapfrog(DT = T) to merge dataframe from NeoNet and Leapfrog on common C14 LabCode values: https://historical-time.github.io/caa23/neonet/results/NN_and_LF.html

Screen capture of [NN_and_LF.html](https://historical-time.github.io/caa23/neonet/results/NN_and_LF.html)
There are mainy IT-based projects dealing with radiocarbon dates, such as the comprehensive platform Xronos, the radiocarbon aggregator C14bazAAR, and many others, see the open-archaeo site
- NeoNet app web document
- Contribution rules
- NeoNet package license
- 2024, Big Historical Data Conference
- Shiny server (with the app embeded): http://shinyserver.cfs.unipi.it:3838/neonet/bhdc
- GitHub (without the app embeded): https://zoometh.github.io/neonet/doc/talks/2023-bhdc
- Neonet workshop
- 2024, Oxford Seminar Series
- 2024, SIMEP
- 2024, ASD-CSIC
- 2025, ENE2025
- 2025, Paléorient