Combinatorial Optimization (CO) is a mathematical optimization area that involves finding the best solution from a large set of discrete possibilities, often under constraints. Widely applied in routing, logistics, hardware design, and biology, CO addresses NP-hard problems critical to computer science and industrial engineering.
ML4CO-Kit aims to provide foundational support for machine learning practices on CO problems, including the follow aspects.
algorithm: common post-processing algorithms.data: common test datasets and our generated traning dataset.draw: visualization of problems and solutions.evaluate: evaluator for problems and solvers.generator: data generation of various distributions.learning: implemented base classes that facilitate method development for ML4CO.solver: solvers' base classes and mainstream traditional solvers.utils: general or commonly used functions and classes.
⭐ Official Documentation: https://ml4co-kit.readthedocs.io/en/latest/
⭐ Source Code: https://github.com/Thinklab-SJTU/ML4CO-Kit
We are systematically building a foundational framework for ML4CO with a collection of resources that complement each other in a cohesive manner.
-
Awesome-ML4CO, a curated collection of literature in the ML4CO field, organized to support researchers in accessing both foundational and recent developments.
-
ML4CO-Kit, a general-purpose toolkit that provides implementations of common algorithms used in ML4CO, along with basic training frameworks, traditional solvers and data generation tools. It aims to simplify the implementation of key techniques and offer a solid base for developing machine learning models for COPs.
-
ML4TSPBench: a benchmark focusing on exploring the TSP for representativeness. It offers a deep dive into various methodology designs, enabling comparisons and the development of specialized algorithms.
-
ML4CO-Bench-101: a benchmark that categorizes neural combinatorial optimization (NCO) solvers by solving paradigms, model designs, and learning strategies. It evaluates applicability and generalization of different NCO approaches across a broad range of combinatorial optimization problems to uncover universal insights that can be transferred across various domains of ML4CO.
-
PredictiveCO-Benchmark: a benchmark for decision-focused learning (DFL) approaches on predictive combinatorial optimization problems.
| Problem | Generator | Basic Solver (IO) | Traditional Solver |
|---|---|---|---|
| ATSP | sat, hcp, uniform |
tsplib, txt, pkl |
LKH, OR-Tools |
| CVRP | uniform, gaussian |
vrplib, txt, pkl |
LKH, HGS, PyVRP |
| KP | uniform |
txt |
OR-Tools |
| LP | uniform |
txt |
Gurobi |
| MCl | er, ba, hk, ws, rb |
gpickle, txt, networkx |
Gurobi, OR-Tools |
| MCut | er, ba, hk, ws, rb |
gpickle, txt, networkx |
Gurobi, OR-Tools |
| MIS | er, ba, hk, ws, rb |
gpickle, txt, networkx |
Gurobi, KaMIS, OR-Tools |
| MVC | er, ba, hk, ws, rb |
gpickle, txt, networkx |
Gurobi, OR-Tools |
| OP | constant, uniform, dist |
txt, pkl |
Gurobi |
| PCTSP | uniform |
txt, pkl |
OR-Tools, ILS |
| SPCTSP | uniform |
txt, pkl |
REOPT |
| TSP | uniform, gaussian, cluster |
tsplib, txt, pkl |
LKH, Concorde, GA-EAX, OR-Tools, NeuroLKH |
| Problem | Visualization | Algorithm | Test Dataset | Train Dataset |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATSP | 📆 | 2 | 4 | 4 |
| CVRP | ✔ | 2 | 5 | 4 |
| KP | 📆 | 📆 | 📆 | 📆 |
| LP | 📆 | 📆 | 📆 | 📆 |
| MCl | ✔ | 6 | 5 | 2 |
| MCut | ✔ | 3 | 3 | 2 |
| MIS | ✔ | 10 | 6 | 4 |
| MVC | ✔ | 5 | 5 | 2 |
| OP | 📆 | 📆 | 📆 | 📆 |
| PCTSP | 📆 | 📆 | 📆 | 📆 |
| SPCTSP | 📆 | 📆 | 📆 | 📆 |
| TSP | ✔ | 5 | 7 | 6 |
1~99: Number of supports; ✔: Supported; 📆: Planned for future versions (contributions welcomed!).
Dataset Link: https://huggingface.co/datasets/ML4CO/ML4CO-Bench-101-SL
ML4CO Organization:
We are still enriching the library and we welcome any contributions/ideas/suggestions from the community. A comprehensive modular framework built upon this library that integrates core ML4CO technologies is coming soon.
You can install the stable release on PyPI:
$ pip install ml4co-kitor get the latest version by running:
$ pip install -U https://github.com/Thinklab-SJTU/ML4CO-Kit/archive/master.zip # with --user for user install (no root)The following packages are required and shall be automatically installed by pip:
Python>=3.8
numpy>=1.24.4
networkx>=2.8.8
tqdm>=4.66.3
pulp>=2.8.0,
pandas>=2.0.0,
scipy>=1.10.1
aiohttp>=3.10.11
requests>=2.32.0
async_timeout>=4.0.3
pyvrp>=0.6.3
cython>=3.0.8
gurobipy>=11.0.3
scikit-learn>=1.3.0
To ensure you have access to all functions, such as visualization, you'll need to install the following packages using pip:
matplotlib
pytorch_lightning
We provide base classes with a user-friendly approach for implementing traditional and learning-based solvers. Taking TSPSolver as an example, it includes functionalities for data input and output, as well as an evaluation function. The solver supports different data inputs, such as Numpy arrays and .txt and .tsp files. The outputs can be saved to corresponding types of files as needed. Additionally, the solver offers an evaluation function, by which users can quickly obtain the average tour length, average gap, and standard deviation of the test dataset. Traditional solvers are directly incorporated in our library inheriting TSPSolver.
>>> from ml4co_kit.solver import TSPLKHSolver
# initialization
>>> tsp_lkh_solver = TSPLKHSolver(lkh_max_trials=500)
# input instances and reference solutions by a .txt file
>>> tsp_lkh_solver.from_txt("path/to/read/tsp500_concorde.txt", ref=True)
# lkh solving
>>> tsp_lkh_solver.solve(num_threads=10, show_time=True)
# evaluate
>>> tsp_lkh_solver.evaluate(calculate_gap=True)
(16.546304871926175, 16.545805334644392, 0.0030213676759083515, 0.009747905769875538)
# save solving results
>>> tsp_lkh_solver.to_txt("path/to/write/tsp500_lkh.txt")from ml4co_kit import TSPDataGenerator
# initialization
tsp_data_lkh = TSPDataGenerator(
num_threads=8,
nodes_num=50,
data_type="uniform",
solver="LKH",
train_samples_num=16,
val_samples_num=16,
test_samples_num=16,
save_path="path/to/save/"
)
# generate
tsp_data_lkh.generate()>>> from ml4co_kit.evaluate import TSPLIBOriEvaluator
>>> from ml4co_kit.solver import TSPLKHSolver
>>> lkh_solver = TSPLKHSolver(scale=1)
>>> evaluator = TSPLIBOriEvaluator()
>>> evaluator.evaluate(lkh_solver, norm="EUC_2D")
solved_costs ref_costs gaps
eil51 429.983312 429.983312 0.000000e+00
berlin52 7544.365902 7544.365902 3.616585e-14
st70 677.881928 678.597452 -1.054416e-01
eil76 544.837795 545.387552 -1.008012e-01
pr76 108159.438274 108159.438274 -1.345413e-14
kroA100 21285.443182 21285.443182 0.000000e+00
kroC100 20750.762504 20750.762504 0.000000e+00
kroD100 21294.290821 21294.290821 3.416858e-14
rd100 7910.396210 7910.396210 0.000000e+00
eil101 642.244814 642.309536 -1.007642e-02
lin105 14382.995933 14382.995933 0.000000e+00
ch130 6110.739012 6110.860950 -1.995428e-03
ch150 6532.280933 6532.280933 -2.784616e-14
tsp225 3859.000000 3859.000000 0.000000e+00
a280 2587.930486 2586.769648 4.487600e-02
pr1002 259066.663053 259066.663053 0.000000e+00
pr2392 378062.826191 378062.826191 0.000000e+00
AVG 50578.945903 50578.963027 -1.020227e-02
>>> evaluator.evaluate(lkh_solver, norm="GEO")
solved_costs ref_costs gaps
ulysses16 74.108736 74.108736 1.917568e-14
ulysses22 75.665149 75.665149 3.756248e-14
gr96 512.309380 512.309380 0.000000e+00
gr202 549.998070 549.998070 -8.268163e-14
gr666 3843.137961 3952.535702 -2.767786e+00
AVG 1011.043859 1032.923407 -5.535573e-01>>> from ml4co_kit import TSPSolver, tsp_insertion_decoder
# create solver and load data
>>> solver = TSPSolver()
>>> solver.from_txt("your/txt/data/path", ref=True)
# use insertion algorithm to solve the problems
>>> tours = tsp_insertion_decoder(points=solver.points)
>>> solver.from_data(tours=tours, ref=False)
# evaluate (average length, ground truth, gap, std)
>>> solver.evaluate(calculate_gap=True)
(6.299320133465173, 5.790133693543183, 8.816004478345556, 3.605743337834312)Below, we use TSP, MIS, and CVRP as representative examples for illustration.
>>> from ml4co_kit.solver import TSPConcordeSolver
>>> from ml4co_kit.draw.tsp import draw_tsp_solution, draw_tsp_problem
# use TSPConcordeSolver to solve the problem
>>> solver = TSPConcordeSolver(scale=1)
>>> solver.from_tsplib(tsp_file_path="examples/tsp/tsplib/kroA150.tsp")
>>> solver.solve(norm="EUC_2D")
# draw images of problem and solution
>>> draw_tsp_problem(
save_path="docs/assets/tsp_problem.png",
points=solver.ori_points,
)
>>> draw_tsp_solution(
save_path="docs/assets/tsp_solution.png",
points=solver.ori_points,
tours=solver.tours
)Visualization Results:
>>> from ml4co_kit.solver import KaMISSolver
>>> from ml4co_kit import draw_mis_problem, draw_mis_solution
# use KaMISSolver to solve the problem
>>> mis_solver = KaMISSolver(time_limit=10)
>>> mis_solver.solve(
src="examples/mis/instance",
out="examples/mis/solution"
)
# draw images of problem and solution
>>> draw_mis_problem(
save_path="docs/assets/mis_problem.png",
graph_data=mis_solver.graph_data[0],
self_loop=False
)
>>> draw_mis_solution(
save_path="docs/mis_solution.png",
graph_data=mis_solver.graph_data[0],
self_loop=False
)Visualization Results:
>>> from ml4co_kit import CVRPHGSSolver
>>> from ml4co_kit import draw_cvrp_problem, draw_cvrp_solution
# use CVRPHGSSolver to solve the problem
>>> solver = CVRPHGSSolver(
depots_scale=1,
points_scale=1,
time_limit=1.0
)
>>> solver.from_vrplib("examples/cvrp/vrplib_1/problem/A-n32-k5.vrp")
>>> solver.solve()
# draw images of problem and solution
>>> draw_cvrp_problem(
save_path="docs/assets/cvrp_problem.png",
depots=solver.depots[0],
points=solver.points[0]
)
>>> draw_cvrp_solution(
save_path="docs/assets/cvrp_solution.png",
depots=solver.depots[0],
points=solver.points[0],
tour=solver.tours
)Visualization Results:
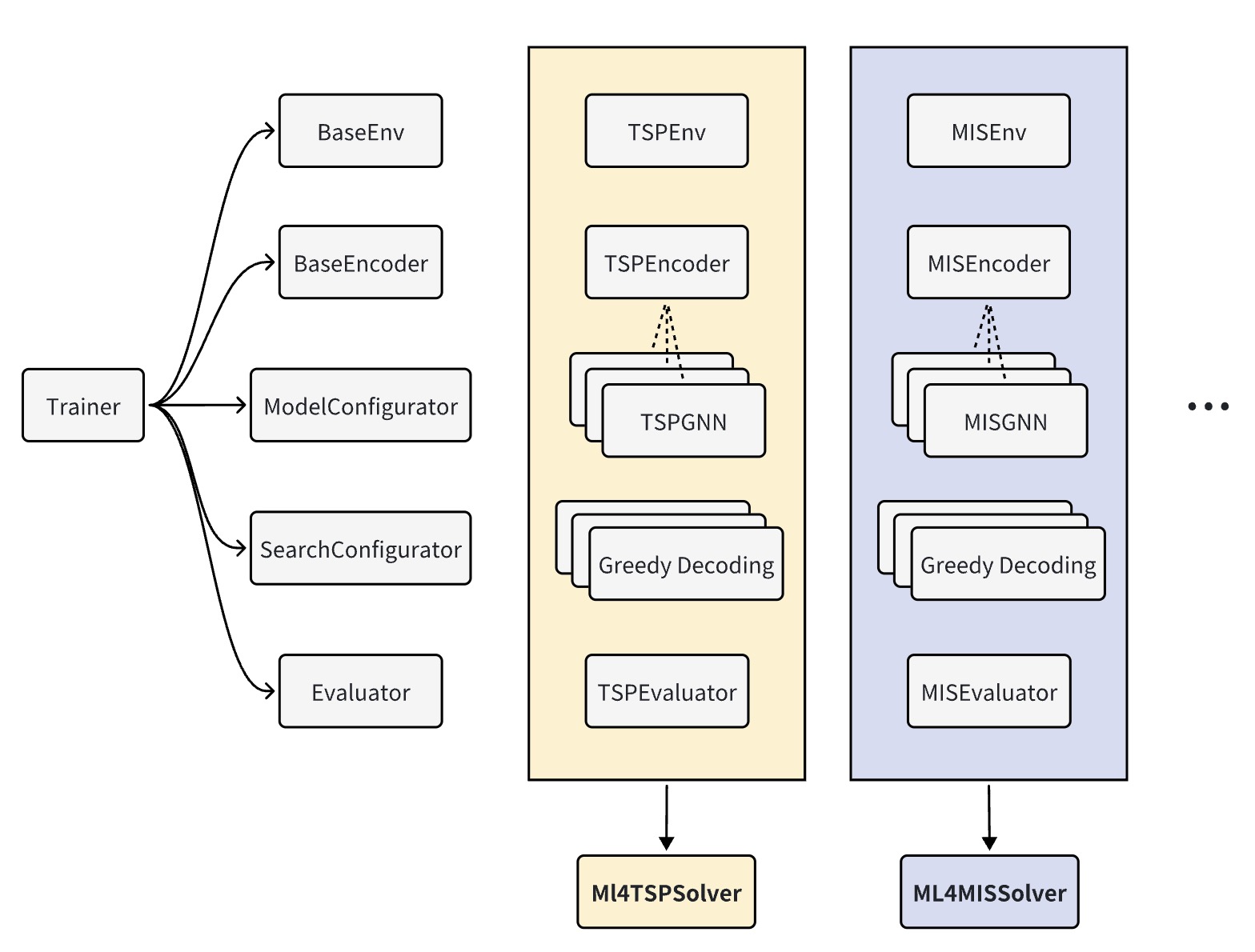
Please refer to ml4co_kit/learning for the base classes that facilitate a quick establishment of a ML4CO project. You can easily build a project by inheriting the base classes and additionally implement task-specific and methodology-specific functions according to [ML4CO Organization](#ML4CO Organization:).
If you find our code helpful in your research, please cite
@inproceedings{li2025streamlining,
title={Streamlining the Design Space of ML4TSP Suggests Principles for Learning and Search},
author={Yang Li and Jiale Ma and Wenzheng Pan and Runzhong Wang and Haoyu Geng and Nianzu Yang and Junchi Yan},
year={2025},
booktitle={International Conference on Learning Representations}
}