-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 34
How To Get an Authentication Token for System Users IIB Sample
IBM Integration Bus (IIB) is a message bus platform that allows for enterprise level handling of messages. This page assumes that you are already familiar with IIB, but if you would like more information, you can find full product documentation in the IBM Knowledge Center.
This code sample is provided for reference and interfaces with the existing IBM Food Trust APIs. You may incorporate it into your existing IIB infrastructure, or use it as a starting point to get up to speed quickly.
- Download files
-
Code walkthrough
- (subflow) Submit IBM Food Trust XML -- submit an XML message to IBM Food Trust
- (subflow) IBM Food Trust Authenticate -- authenticate with IBM Food Trust
- IBM Food Trust Submit XML API Flow -- REST API interface that accepts JSON and submits XML to IBM Food Trust
- Try it out!
IIB_IFT_authentication_library.zip -- A shared library that handles the communication interchange with the IBM Food Trust authentication service.
IIB_IFT_submit_XML_API.zip -- A full end-to-end sample that includes the IBM Food Trust Authentication Library. It is an HTTP REST service that accepts an XML message and uploads it to the solution network. This can be dropped into your existing IIB environment and customized to fit your needs.
Download the files above and import them into your IIB Toolkit:
- File -> Import... -> Project Interchange
Because IIB handles messages in the SOAP format natively, some nodes were added to the flows to give the look and feel of a REST API. For example, instead of having subflows encapsulated in TryCatch nodes and throwing errors, local environment variables are set and checked via FilterNodes. A compute node at the end of the main IBM Food Trust Submit XML API Flow checks these variables and sets a 500 Response Header with a meaningful JSON response (to match the format of a successful 201 response).
Local Environment Variables The flows utilize the following variable structure:
- LocalEnvironment
- Variables
- IBM Food Trust
- environment - name of the target IBM Food Trust environment (e.g. PRODUCTION)
- apikey
- orgId
- xml - The XMLNS object of the XML string passed into the flow
- error_message - message received from an API call
- error_location - name of the subflow where the error originated from
- error_message_detail - full context from the API error
- iam_token
- access_token
- token_type
- expires_in
- expiration
- scope
- service_token
- message_backup
- IBM Food Trust
- Variables

Flow highlights:
- Call Subflow Node: Call the IBM Food Trust_Authenticate subflow (see below)
- Filter Node: Check to see if the exchange token process was successful.
- HTTP Request Node: Submit the XML payload to IBM Food Trust with the API key acquired from the IBM Food Trust_Authenticate subflow
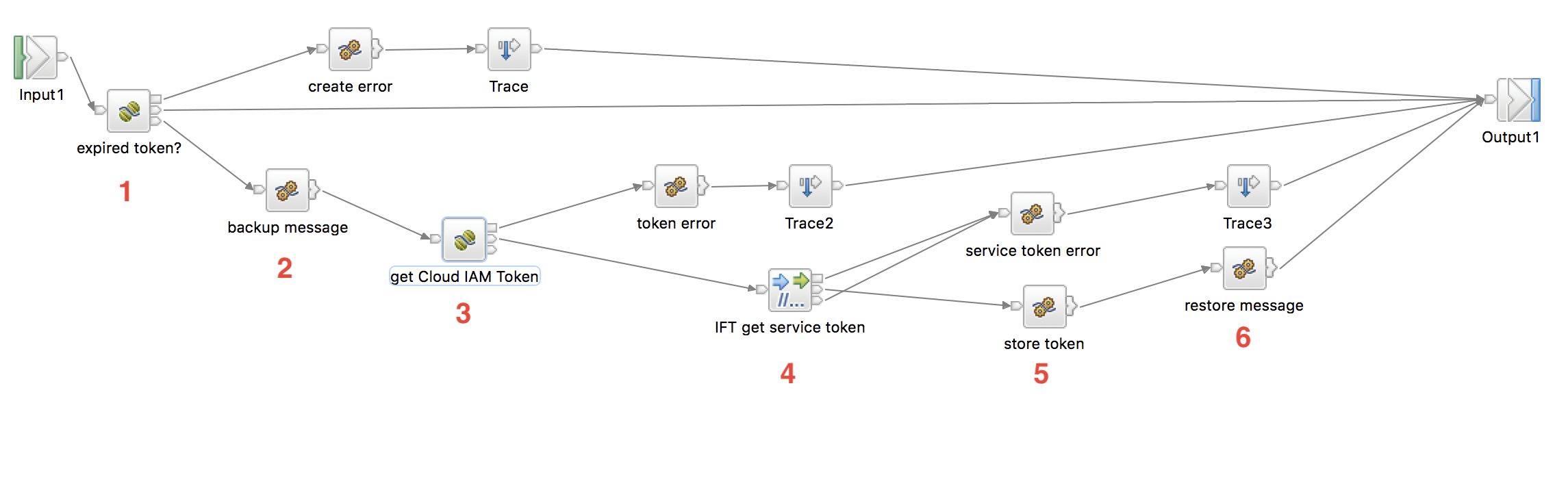
Flow highlights:
- Java Compute Node: Check the local environment variable for an existing token expiration value. If one exists, check it against the current time and if it has expired, obtain a new one; otherwise, skip the flow (too many calls to the obtain IBM Cloud IAM Service will be denied)
- Compute Node: Back up the existing message since the HTTP Request nodes will overwrite it.
- Java Compute Node: Call the IBM Cloud IAM service, request a token and store the token in LocalEnvironment Variables.
- HTTP Request Node: Call the IBM Food Trust Authentication API and exchange the token for a service token.
- Compute Node: Store the service token in a local environment variable.
- Compute Node: Restore the original inbound message into the message body.

The flow is configured for HTTP path: /ift_submit_xml/
Flow Highlights
- Compute Node: Read the inbound JSON payload and store the values in local environment variables. Note -- the XML payload was stored as a string, so this node converts the node into a proper XMLNS format and stores it as a local environment variable.
- Call Subflow Node: Call the Submit_IBM Food Trust_XML subflow from the shared library (see above for details).
- Filter Node: Check a local environment variable to see if an error message exists and route as needed.
- Compute Node: Format the error response.
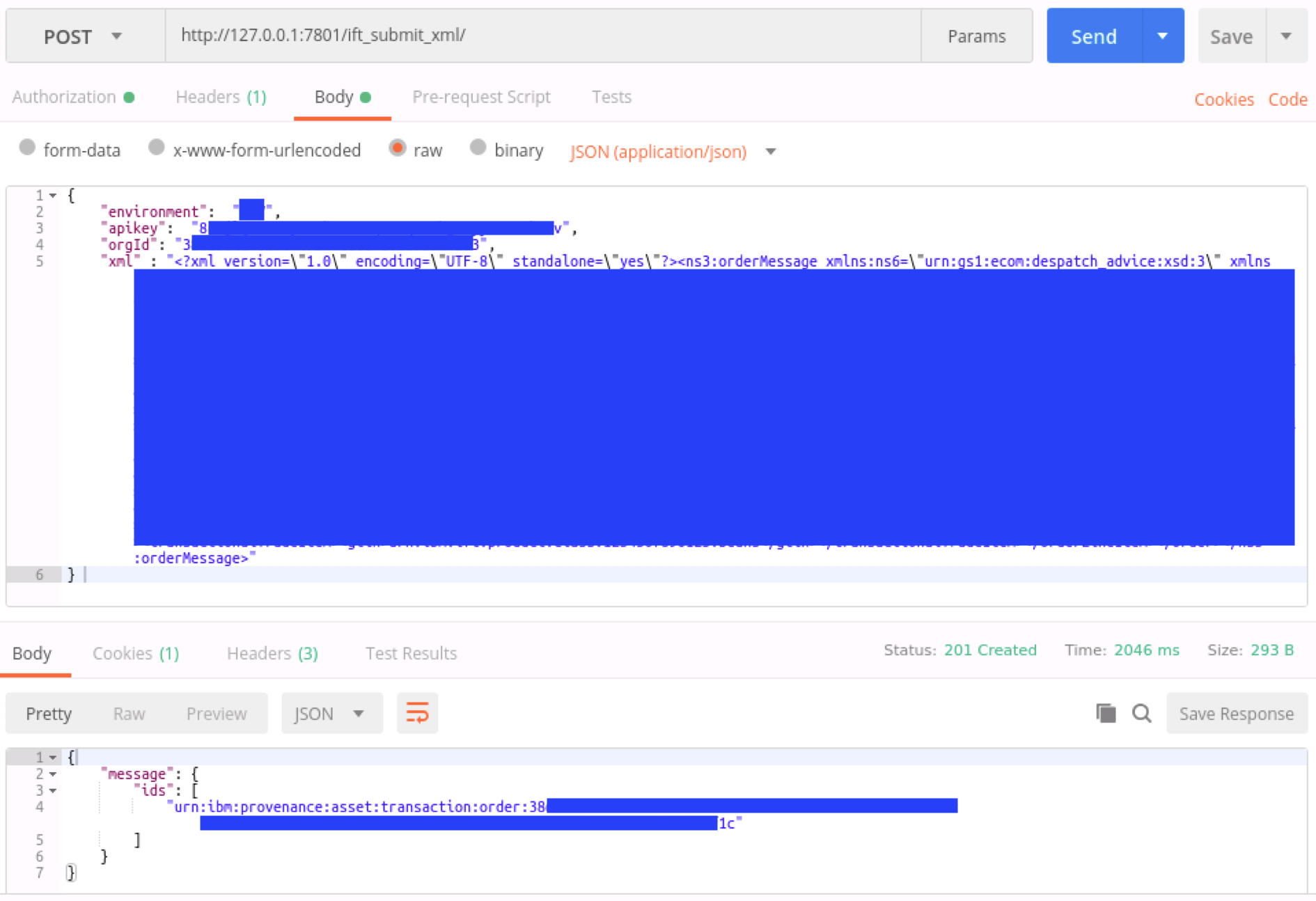
Once deployed to your IIB Integration Node, you can send a JSON payload through the flow. The flow expects the following format:
URL format: http://<integration node>:<debug port>/ift_submit_xml/
Payload format:
Note: If your organization is registered in the IBM Food Trust Integration environment, you can specify
"environment": "INTEGRATION",
{
"environment": "PRODUCTION",
"apikey": "...",
"orgId": "...",
"xml" : "<?xml version=\"1.0\" ...."
} Sample Postman:
WELCOME!
Modules
Membership
Languages
Browsers
ONBOARDING
Onboarding Steps
Data Requirements
Data Types
Supplier Data
Payload Data
Insights Data
HOW-TO
Join by Invitation
Log in as New User
Authenticate Human Users
Authenticate System Users
Java Sample
Typescript Sample
IIB Sample
Assign User Roles
Upload Data
Automate Data Upload
Convert Spreadsheets
Convert Data
Whitelist Custom URLs
APIs-Swagger
Connector API
Documents API
Converter API
Trace API
Insights API
APIs-Usage
APIs
Insights API
Insights API Usage
Trace API
Connector API Errors
API Error Codes
REFERENCE
GS1
GS1 Identifier Reuse
Authentication
Identifiers
Message Codes
Cryptographic
Signatures
Signature Header
Access Control
Firewall Settings
XML to JSON
EPCIS Aggregation Add
EPCIS Aggregation Delete
EPCIS Object Add
EPCIS Object Delete
EPCIS Object Observed
EPCIS Transformation
Purchase Order
Despatch Advice
Receiving Advice
Master Data Item
Master Data Facility
Standard Business
Document Header